4G LTE Market Size (2024 – 2030)
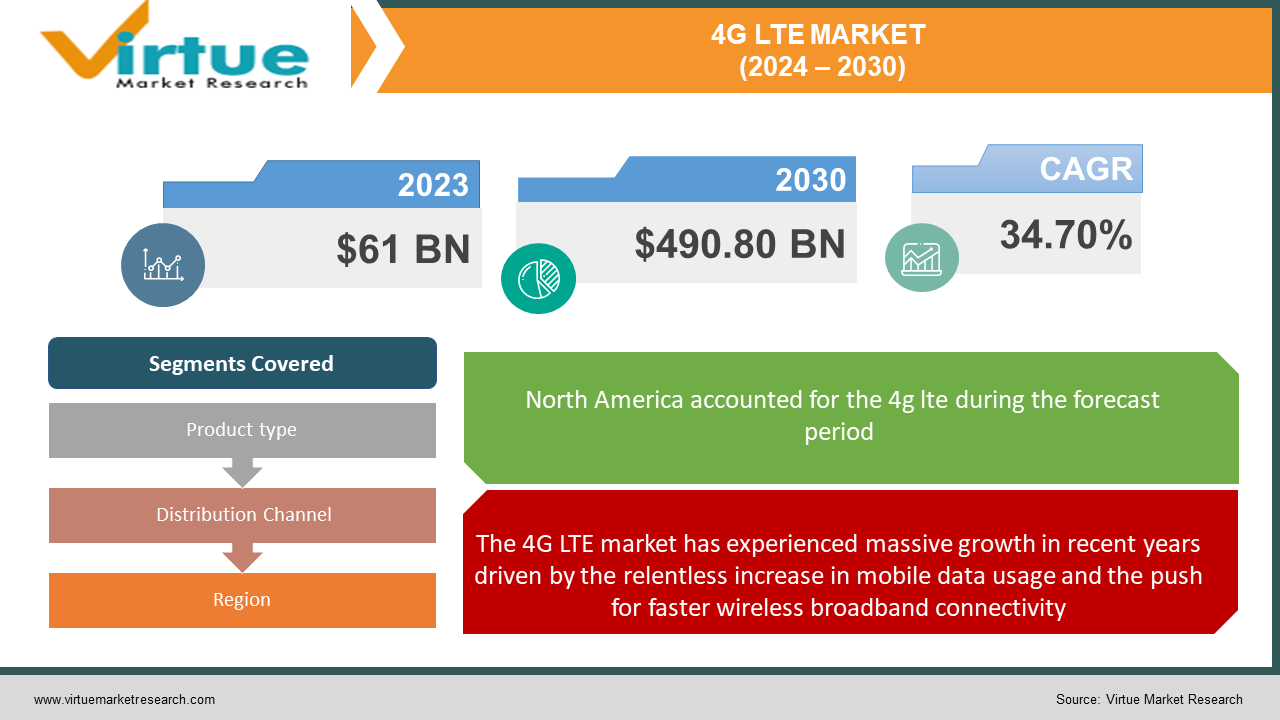
The 4G LTE Market was valued at USD 61 Billion and is projected to reach a market size of USD 490.80 Billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 34.70%.
4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) technology has become the global standard for high-speed wireless connectivity. 4G networks provide significantly faster mobile broadband speeds than legacy 3G infrastructure, supporting advanced functionality like HD video streaming, high-res interfaces, and real-time collaboration tools. The transition to 4G has enabled innovations across mobile computing, autonomous systems, industrial IoT, and immersive media. Commercial 4G networks first launched around 2010 and have expanded coverage to over 60% of the worldwide population presently. Key drivers fueling ongoing 4G investment include rising data usage from video and gaming apps, growth in connected mobile devices per subscriber, and spectrum availability at frequency bands below 6 GHz offering favorable propagation characteristics.
Key Market Insights:
- Several compelling factors are driving ongoing investment and expansion in 4G LTE networks globally including rising data usage per subscriber, growth in connected devices, spectrum availability, and rural connectivity demands. While early 5G rollouts have started, 4G remains the workhorse for reliable high-speed connectivity that will continue growing over the next 5-7 years.
- Average monthly data consumption per unique mobile subscriber now exceeds 10GB in leading countries like South Korea and China. Video streaming, conferencing, and multiplayer gaming applications underlying this demand growth perform optimally on 4G LTE’s high bandwidth throughput and low latency capabilities. Using these rich media services often requires subscribers to purchase plans with monthly data allocations of 5GB or higher.
- The proliferation of smartphones, tablets, mobile hotspots, and embedded IoT systems also continues elevating data traffic volumes. Advanced handsets integrate ever more sensors and features that require persistent connectivity. Adoption in developing regions also remains robust as device costs decline.
- Global cellular IoT connections are projected to triple to over 5 billion by 2028, predominately relying on existing 4G infrastructure for scale, reliability, and coverage.
- Expanding spectrum allocations has prevented congestion while lowering rollout barriers. Regulators are assigning more licensed and shared spectrum per carrier specifically for commercial 4G services across bands like AWS (1700/2100 MHz) and lower BRS bands under 1 GHz offering favorable signal propagation. These spectrum assignments allow operators to cost-efficiently increase 4G network capacity and density within metropolitan areas along with range to cover rural zones with sparse populations.
4G LTE Market Drivers:
The 4G LTE market has experienced massive growth in recent years driven by the relentless increase in mobile data usage and the push for faster wireless broadband connectivity.
The main factor driving the global rollout of 4G LTE networks has been the sharp increase in smartphone adoption. LTE gives smartphones the quick wireless internet access they need to offer a positive user experience. Mobile devices and wireless carriers alike benefit from the self-reinforcing loop caused by the interdependent growth of 4G networks and the smartphone industry. The usefulness and adaptability that cell phones provide have been the main drivers of this extraordinary growth pace. Smartphones have become essential digital companions because of touchscreen displays, mobile operating systems, app stores with millions of downloads, and the incorporation of capabilities like GPS and cameras. Today's advanced smartphones can reach their full potential thanks to high-speed 4G LTE connectivity. Fast, responsive mobile broadband services are essential for applications like social media, e-commerce, video streaming, web surfing, and multimedia. Due to LTE's notable speed advantage over 3G, users can now utilize their smartphones for bandwidth-intensive activities that were not consistently supported by prior networks. 3G technologies like EV-DO and HSPA are up to ten times slower than average LTE download speeds of 12–25 Mbps. Theoretically, LTE peak speeds can reach over 100 Mbps. Smartphones need this extra capacity to provide a satisfying user experience. Frustratingly slow speeds in the absence of LTE quickly cause discontent and reduce the usefulness of devices.
The rapid proliferation of bandwidth-hungry smartphones quickly overwhelmed older 3G networks. Peak download speeds for 3G standards like EV-DO and HSPA were only in the 2-5Mbps range.
The rapid proliferation of advanced smartphones and mobile devices quickly overwhelmed the limited speed capacity of legacy 3G networks. Congested 3G infrastructure struggled to deliver the broadband connectivity and responsiveness consumers expected. This frustrating user experience was a major factor motivating carriers to accelerate the deployment of higher capacity 4G LTE networks. 3G standards like EV-DO and HSPA topped out at peak download speeds between 2-5 Mbps. While an improvement from 2G networks, these speeds were barely sufficient for smoothly browsing web pages and struggled with video. Streaming HD video consistently required 4G capacity. As smartphones gained capabilities like mobile web browsing, apps, GPS, and cameras, mobile data traffic exploded. From 2008 to 2014, global mobile data traffic grew over 50 times. However the growth in data consumption far outpaced improvements in 3G network technology. Network congestion and overloaded cells became increasingly common, especially in densely populated metropolitan areas. During times of peak demand like commuting hours, data speeds slowed to a crawl. Videos would buffer endlessly, web pages stalled while loading, and apps timed out. This severely degraded user experience limited consumers’ ability to take full advantage of their smartphones’ functions. With 3G networks hampering performance, smartphone utility suffered drastically. Customer frustration and dissatisfaction soared during periods of slow data speeds. Carriers realized legacy 3G networks urgently needed capacity upgrades to handle surging smartphone traffic. Expanding 3G was an ineffective solution, as the technology was stretched to its limits and still insufficient for burgeoning mobile data usage.
4G LTE Market Restraints and Challenges:
Building out LTE networks requires huge capital investments by wireless carriers. Constructing just the radio access network portion of LTE infrastructure costs up to $70,000 per base station.
For wireless operators, the large capital costs associated with constructing nationwide 4G LTE networks have presented financial difficulties. The enormous expense of building hundreds of additional cell sites and modernising the core network infrastructure has slowed the rollout of LTE. The cost of deploying a new LTE cell site ranges from $150,000 to $300,000. These costs consist of spectrum licensing fees, base station radios and antennas, towers, and site leases, core network routers and switches, installation and testing personnel, and radio access network equipment. Building and connecting tens of thousands of LTE-capable cell sites with fiber backhaul links is necessary for a carrier to attain countrywide coverage. These Greenfield end-to-end networks easily have total capital expenditures (capex) in the tens of billions of dollars. Following the first deployment, there are also significant ongoing costs. Network hardware needs to be updated often. Over time, the costs of system upkeep, electricity, backhaul bandwidth, and labour for running LTE infrastructure accumulate. Enhancing capacity regularly is necessary to keep up with the growing data needs of subscribers. The significant cost associated with widespread LTE coverage has hindered carrier installations that lack strong financial resources. Particularly smaller regional carriers have trouble gathering enough money to pay for LTE construction. Additional limitations arise from the incapacity to allocate expenses among a substantial clientele.
4G LTE Market Opportunities:
Beyond smartphones and tablets, LTE's transmission capability supports an ever-widening range of connected devices. This opens up the possibility of new sources of income from developing gadget categories. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, digital health monitors, automotive fleet management systems, and industrial IoT sensors are a few examples. All of these gadgets are mobile thanks to cellular connectivity. The "Internet of Things" ecosystem, which connects everything from infrastructure to consumer devices, is made possible by LTE. Essential foundations for the next generation 5G standard have been established by LTE improvements and infrastructure enhancements. By utilizing existing cell sites, spectrum, and architecture, operators can accelerate 5G rollouts while making an amortization of their LTE expenditures. Numerous 5G features expand upon innovations made possible by LTE networks. In the 2020s, the worldwide 5G market is expected to expand quickly. Gaining traction quickly will be essential to carriers' competitive positioning. With a lot of the LTE core elements currently in place, wireless companies can focus on new opportunities and ease the transition to 5G.
4G LTE MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
34.70% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product type, Distribution Channel and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, Verizon Wireless, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint |
4G LTE Market Segmentation: By Product Type
-
LTE-FDD
-
LTE-TDD
-
LTE-Advanced
-
LTE-Advanced Pro
LTE-FDD holds the largest market share within the 4G LTE umbrella. The reason for its dominance is due to wider spectrum availability in the initial wave of LTE deployments and favorable propagation characteristics. LTE-TDD is Gaining traction, especially in regions with limited spectrum availability or where operators seek additional network capacity. It's well-suited for asymmetrical traffic where the downlink needs are greater than the uplink (e.g., streaming content).
LTE-Advanced, is the technology of choice for most providers when upgrading LTE networks due to techniques like carrier aggregation. It's widespread and considered standard for delivering the faster speeds consumers and businesses expect from 4G LTE. LTE-Advanced Pro Focuses on niche deployments or bleeding-edge use cases requiring peak data speeds (gigabit speeds). It represents the technological potential of 4G LTE but faces hurdles due to device compatibility and the rising dominance of 5G.
4G LTE Market Segmentation: By Distribution Channel
-
Smartphones
-
Tablets
-
Mobile Hotspots
-
Routers
-
M2M Devices
Smartphones: Account for approximately 70-80% of the market share. They are the driving force behind LTE adoption and data consumption globally. Tablets: Represent roughly 10-15% of the market share. While widespread, their demand generally follows behind smartphones.
Mobile Hotspots: Hold about 5-8% of the market, playing a niche but essential role in providing on-the-go connectivity. Routers: Represent a smaller, but steady segment, often used in rural or underserved areas. M2M Devices: This rapidly growing segment holds a share that's increasing alongside diverse IoT applications. Smartphones are by far the most dominant devices in the 4G LTE market.M2M (Machine-to-Machine) devices represent the fastest-growing segment in the 4G LTE market.
4G LTE Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America is driven mostly by the region's high LTE adoption rate and plenty of sophisticated LTE-enabled devices, the region holds a sizeable part of the market—roughly 30% to 35% in 2023.
Asia Pacific holds another significant portion, about 30% in the same year, driven by robust smartphone markets, rising demand for mobile broadband access, and policies that encourage the expansion of LTE networks.
Europe due to its advanced LTE infrastructure and extensive use in the majority of its countries, Europe accounts for 20–25 percent of the market. The remaining region, which is made up of Africa, the Middle East, and Latin America, has greater degrees of regional variation. Because so many nations encourage the development of LTE infrastructure, which increases accessibility, the Asia Pacific region stands out as having the fastest-growing 4G LTE market.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on 4G LTE Market:
The COVID-19 epidemic and the lockdowns that followed brought about behavioral changes that have had a variety of effects on the 4G LTE industry. Despite brief hiccups, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a greater reliance on mobile connectivity, which has expedited the deployment of LTE.
Early in 2020, when lockdowns initially occurred, consumer mobility drastically decreased. As a result, the number of new LTE subscribers decreased slightly as market activity slowed. This effect, though, was fleeting since vital movement soon resumed.
As employment, education, social interactions, and leisure activities moved online, data traffic on LTE networks increased concurrently. Customers used mobile devices and apps more frequently since they were spending more time at home. The reasons behind the surge in usage were video streaming, gaming, e-commerce, and video conferencing. During peak lockdowns, several carriers reported an increase in data volumes of more than 50%.
The increase in traffic from urbanites who were teleworking remotely put a specific burden on rural networks. The capacity and performance of LTE were impeded by this unforeseen congestion. Operators increased their investments in spectrum and cell sites to strengthen networks to make up for the loss. Years-long plans to expand LTE coverage and capabilities have to be finished in a matter of months. COVID forced operators to accelerate LTE capacity optimization.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
LTE-Advanced Pro represents the latest evolution of 4G technology standards. Key features include higher-order MIMO, 3D beamforming, and aggregation of up to 32 component carriers for download speeds exceeding 1 Gbps.
Carriers are deploying advanced antennas and upgrading backhaul to unlock extreme data rates. Densification of networks is increasing through small cell rollouts in urban areas to add targeted capacity. Small cells shrink LTE coverage footprints to light poles, buildings, or street posts.
Millimeter wave small cells are beginning to emerge for localized gigabit speeds. Edge computing will enable low-latency services. Dedicated enterprise and industrial private LTE networks are also on the rise. Verticals like manufacturing, transportation, utilities, mining, and ports are deploying on-site LTE for secure, high-performance connectivity. Private LTE networks are estimated to grow at over 15% CAGR through 2025 and expand the LTE ecosystem.
Key Players:
-
Nokia
-
ZTE
-
Samsung
-
Verizon Wireless
-
AT&T
-
T-Mobile
-
Sprint
Chapter 1. 4G LTE Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. 4G LTE Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. 4G LTE Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. 4G LTE Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. 4G LTE Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. 4G LTE Market – By Product Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 LTE-FDD
6.3 LTE-TDD
6.4 LTE-Advanced
6.5 LTE-Advanced Pro
6.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Product Type
6.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Product Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. 4G LTE Market – By Distribution Channel
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Smartphones
7.3 Tablets
7.4 Mobile Hotspots
7.5 Routers
7.6 M2M Devices
7.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Distribution Channel
7.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Distribution Channel, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. 4G LTE Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Product Type
8.1.3 By Distribution Channel
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Product Type
8.2.3 By Distribution Channel
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Product Type
8.3.3 By Distribution Channel
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Product Type
8.4.3 By Distribution Channel
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Product Type
8.5.3 By Distribution Channel
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. 4G LTE Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Nokia
9.2 ZTE
9.3 Samsung
9.4 Verizon Wireless
9.5 AT&T
9.6 T-Mobile
9.7 Sprint
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
Consumers rely on 4G LTE for high-speed mobile connectivity to their phones and tablets. Video streaming (Netflix, YouTube), social media, gaming, and rich online content drive demand for fast downloads and seamless browsing.
4G LTE relies on finite radio spectrum bands, and the explosion of data use strains capacity in densely populated areas. As more users flock to LTE networks, speeds can decline during peak hours, hampering experiences for applications like streaming and gaming.
Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, Verizon Wireless, AT&T, T-Mobile, Sprint
North America currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 35%.
Asia Pacific exhibits the fastest growth, driven by its increasing population, and expanding economy.