Urban Farming Market Size (2024 – 2030)
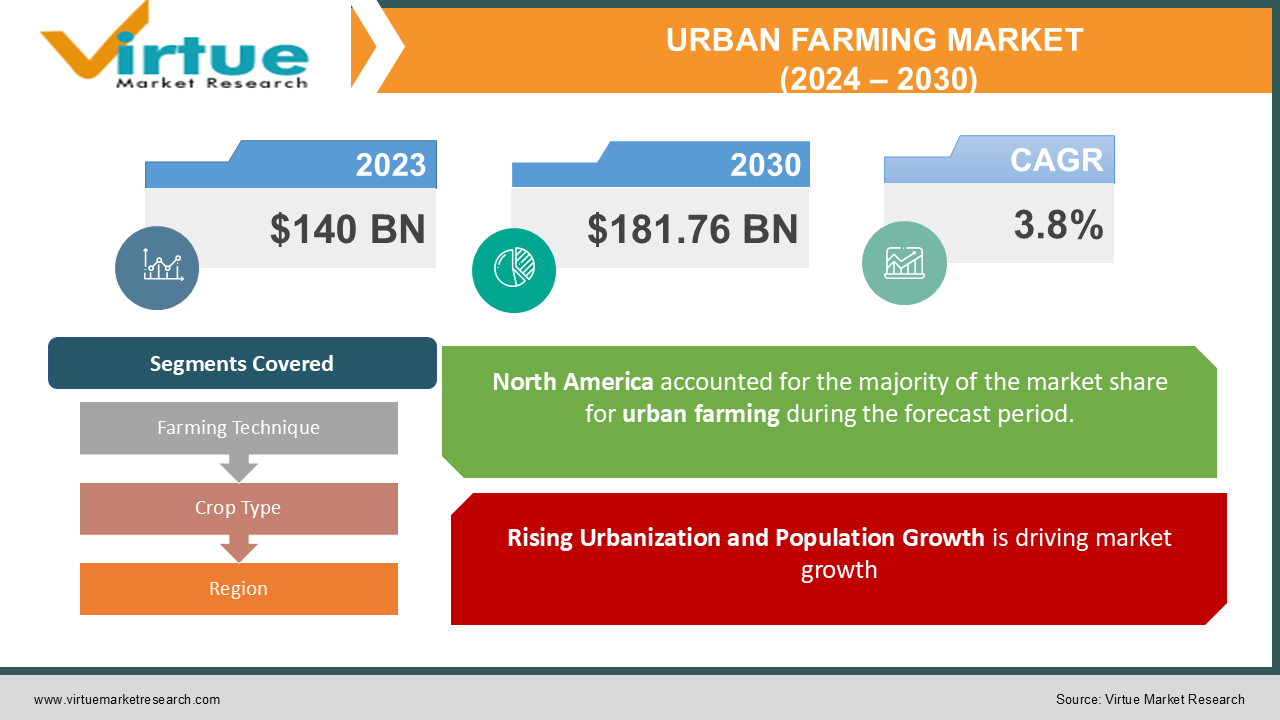
The Global Urban Farming Market was valued at USD 140 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.8% from 2024 to 2030, reaching a market size of USD 181.76 billion by 2030.
Urban farming is gaining significant momentum due to several factors, such as rapid urbanization, increasing concerns over food security, sustainability, and the environmental impact of traditional agriculture. These urban farming techniques are seen as a solution to mitigate food supply challenges while reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions associated with conventional farming. The market growth is also influenced by rising consumer interest in locally grown, organic, and sustainable food. As more cities across the globe adopt urban farming practices, this niche market is expected to grow substantially, supported by technological advancements and a growing focus on sustainable food production.
Key Market Insights
-
The global urban farming market is expected to witness significant growth due to increasing urbanization and the need to supply food to densely populated cities, with over 55% of the world’s population living in urban areas by 2024.
-
Vertical farming is one of the dominant segments of urban farming, with a projected market share of over 40%, driven by its efficient use of space and resources like water and nutrients.
-
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate during the forecast period, with countries like China, India, and Japan investing heavily in urban farming to address food security challenges in rapidly growing urban populations.
Global Urban Farming Market Drivers
Rising Urbanization and Population Growth is driving market growth: The growth driver of global urban farming is the increasing pace of worldwide urbanization. As per the estimation of the United Nations, as of 2024, more than 55% of the world population lives in urban areas and will reach nearly 68% of the world population by 2050. Urbanization means more people who live in cities and have the requirement of fresh and locally grown foods. This ever-increasing urban population cannot be met by using normal farm layouts, and the demand for fresh produces is the largest challenge that affects densely populated cities. Urban farming has been used as a solution that exploits available urban space by making use of rooftops, abandoned buildings, and vacant lots to produce food within the limits of cities. It ensures reduced transportation which contributes to food spoilage, higher prices, and carbon emissions. Besides, urban farming techniques like vertical farming and hydroponics make the best use of a small area available and produce yields in an area that is limited to small space. As the cities increase in size so does the necessity of efficient food production systems, and thus urban farming has been included as an essential tool in sustainable urban development.
Growing Consumer Preference for Sustainable and Locally Grown Food is driving market growth: As the public becomes more conscious about the environmental and ethical implications of their food, demand for locally grown organic and sustainable food continues to rise. This is met by urban farming, as fresh produce does not contain harmful pesticides or synthetic fertilizers - a common use of conventional farming. In addition, urban farms employ cutting-edge, water-saving, and land-space-saving techniques like hydroponics and aquaponics, which clearly use dramatically less water and take up dramatically less land than conventional farming. The "farm-to-table" movement has also stimulated the rise in popularity of urban farming. Consumers are getting increasingly curious about where their food comes from and how it is produced. Urban farming provides clear, sustainable ways of obtaining fresh, quality food for urban dwellers. This will impact the way consumers prefer their food; there are many consumers who today are finding a deeper connection with their food sources. These consumers' preferences are now influencing the growth of urban farming markets, especially within those cities that prioritize sustainability and environmental stewardship.
Technological Advancements in Urban Farming is driving market growth: Technological innovation has always been a driving factor for growth in the urban farming market. The new advancements made in smart farming technologies continue to evolve to make an urban farm more efficient, requiring less food production at a lower resource consumption level. For example, automated systems, IoT-enabled sensors, and artificial intelligence are being employed to monitor and control environmental factors like light, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels in real-time. These technologies ensure optimal growing conditions, improve yields and reduce waste, making urban farming more cost-effective and sustainable. For instance, vertical farming is reaping the advantages of technology in that it is possible to grow a wide variety of crops in stacked layers thus optimizing vertical space in an urban setting. AI, robotics, and automation have largely reduced labor costs and ensured efficiency in vertical farms. More importantly, innovation in the hydroponics system is now making way for urban farms to grow crops in a nutrient-rich water solution that eliminates the need for soil altogether and consumes significantly less water. The increasing developments of technology will make urban farming even more efficient and scalable, therefore increasing its scope to provide food to booming urban populations.
Global Urban Farming Market Challenges and Restraints
High Initial Investment and Operational Costs is restricting market growth: Another challenge is the set-up investment of opening up urban farms, wherein urban farming businesses require huge investments in the case of modern technologies like vertical farming and hydroponics. Quite a lot of investments are deemed necessary for infrastructures, technologies, and equipment within these farming systems. For example, vertical farming necessitates specific lighting systems, climate control systems, and irrigation systems that are automated. These can be very costly to install and maintain. Aside from this, operational costs for urban farming are also high. They occupy less land and water than a traditional farm but still require an enormous amount of energy for maintaining optimal growing conditions in controlled environments such as in greenhouses or indoor vertical farms. This is especially the case in regions that have high electricity costs, where energy-intensive farming practices might undermine the cost effectiveness of urban farming. Thus, financial entry barriers might become one of the main challenges for small-scale operations taking up urban farming activities; thus, market growth potential is severely restricted in such regions.
Regulatory and Zoning Challenges is restricting market growth: Urban farming often experiences regulatory and zoning obstacles since urban environments do not usually have policies as well as infrastructure that supports agriculture. Zoning laws or building codes in local areas often limit how one can farm urban land, especially in the case of rooftop or indoor agriculture. In some cases, permits may not be issued for urban farmers or, more importantly, it may not be readily available to obtain them easily since their farming processes may involve large equipment or generate voluminous waste. Subsidies, grants, or other financial assistance for such an operation may not be readily accessible to reduce or pay for the setting-up costs of these urban farms. Without an enabling regulatory climate, the urban farmers may then not be positioned to scale up to meet the improved demand in the locally available fresh produce. Such governments, which become unwilling to change the zoning and land-use policies before the appearance of urban agriculture, will definitely stifle the long-term growth of the market.
Market Opportunities
There is tremendous scope for growth in the global urban farming market, more so with growth in urbanization and demand from consumers for locally sourced sustainable food. One of the biggest opportunities pertains to smart farming technologies. Adding AI, IoT, automation, and other digital technologies to the mainstream of urban farming operations will revolutionize the way food is produced in cities. These technologies help urban farms optimize resource use, monitor the health of crops, and improve yields, thus opening opportunities for businesses in improving productivity and profitability. In that vein, vertical farming has been another area seeing substantive growth, especially in very high-density urban areas. The vertical farming model concentrations on the use of space that can be found inside buildings and warehouses. It is, therefore ideal for cities as land becomes scarce. This method reduces land usage because production capacity increases greatly. This is essential because most cities are always faced with issues of space. Growing demand for organic and sustainable food presents a great opportunity for urban farmers. Urban farming, as one that is typically done using organic growing methods, is poised to meet demand. As consumers have increasingly focused on food grown in a way that minimizes environmental impact, urban farming provides an appealing alternative to conventional agriculture. The availability of local restaurants, grocery stores, and farmers' markets means supply chains between the urban farmer and consumer can be shorter. Finally, with continuously growing support from governments and municipalities for initiatives in urban farming, more cities realize their potential to enhance food security, reduce emission loads from transportation, and create green jobs in urban agriculture. The strong government incentives, grants, and policy changes that promote urban farming will keep supporting the market growth environment.
URBAN FARMING MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
3.8% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Farming Technique, Crop Type, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
AeroFarms, Vertical Harvest Farms, Gotham Greens, Plenty, UrbanFarmers, Green Spirit Farms, Bowery Farming, Farm.One |
Urban Farming Market Segmentation - By Farming Technique
-
Vertical Farming
-
Hydroponics
-
Aquaponics
-
Rooftop Farming
-
Community Gardens
-
Other Techniques
Vertical farming is the most dominant segment in the global urban farming market. This farming technique offers the highest potential for growth in urban areas due to its ability to maximize food production in limited spaces. By stacking layers of crops vertically, urban farmers can cultivate more food per square foot compared to traditional farming methods. Vertical farming is particularly popular in cities with high population density and limited available land, where maximizing space is crucial. This farming method is also highly efficient in terms of water and nutrient use, making it ideal for urban environments where resource conservation is a priority.
Urban Farming Market Segmentation - By Crop Type
-
Vegetables
-
Fruits
-
Herbs
-
Flowers and Ornamentals
-
Others
Vegetables are the most dominant crop type grown in urban farming systems. Leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, kale, and herbs are commonly cultivated in hydroponic and vertical farms due to their rapid growth cycles and high market demand. These crops also have relatively low space and resource requirements compared to fruits, making them well-suited to urban farming systems that focus on maximizing yield while minimizing resource consumption.
Urban Farming Market Segmentation - By Region
-
North America
-
Europe
-
Asia-Pacific
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
The most common region in the international urban farming market is North America, which has captured around 40% of the market. There has been significant growth in this region since cities like New York, Los Angeles, and Toronto have been willing to embrace vertical farming, hydroponics, and other urban agricultural techniques. Coupled with the growing trend of living greenly and with a growing desire from consumers for locally grown and organically sourced food, the current state of food production calls upon urban farming to play a meaningful role within North American cities. Infrastructure and technology are also highly developed and supportive of urban agriculture in North America. The region hosts various technology firms interested in developing solutions related to smart farming, hence a rate of hi-tech farming in urban centers.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Urban Farming Market
The global urban farming market took a great hit from the pandemic. On one hand, food supplies were disrupted within the traditional channels, raising how vulnerable global food systems can be. The response, on the other hand, showed in the interest in the production of local food items. Lockdowns and travel restrictions upset the food supply chains of consumers, and they start perceiving the value of their food coming from local sources-which has helped to a positive effect on the markets of urban farming. On the other hand, the pandemic further added problems to many companies in urban farming, more so those that mainly focus on labor for the handling and operation of the farm. Social distancing measures or the restriction of in-person operation affected most of the urban farms, especially the small-scaled and community-based type. The challenges have been overcome, however, as online grocery shopping and direct-to-consumer sales provide urban farms with opportunities to reach the consumers directly and bypass the traditional channels of distribution.
Latest Trends/Developments
Smart farming technologies, involving the use of IoT, AI, and robots, are dominant in the current trends for urban farming. These technologies enable remote monitoring of crops and control environmental conditions and will automate farming to increase efficiency and lower costs. Other related trends are sustainable farming methods, which are attracting ever-increasing percentages of urban farmers that have increasingly accepted organic and environmentally friendly growing methods. Urban agriculture is fast becoming the answer to cities' food security challenges as it allows the opportunity to grow food locally and in low environmental cost. Last but not least, community-led urban agriculture initiatives are on the rise as local governments and organizations increasingly support grassroots efforts to grow food in urban areas. These initiatives not only promote access to food but also empower and educate the community on sustainable farming techniques.
Key Players
-
AeroFarms
-
Vertical Harvest Farms
-
Gotham Greens
-
Plenty
-
UrbanFarmers
-
Green Spirit Farms
-
Bowery Farming
-
Farm.One
Chapter 1. Urban Farming Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Urban Farming Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Urban Farming Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Urban Farming Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Urban Farming Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Urban Farming Market – By Farming Technique
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Vertical Farming
6.3 Hydroponics
6.4 Aquaponics
6.5 Rooftop Farming
6.6 Community Gardens
6.7 Other Techniques
6.8 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Farming Technique
6.9 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Farming Technique, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Urban Farming Market – By Crop Type
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Vegetables
7.3 Fruits
7.4 Herbs
7.5 Flowers and Ornamentals
7.6 Others
7.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Crop Type
7.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Crop Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Urban Farming Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Farming Technique
8.1.3 By Crop Type
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Farming Technique
8.2.3 By Crop Type
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Farming Technique
8.3.3 By Crop Type
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Farming Technique
8.4.3 By Farming Technique
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Farming Technique
8.5.3 By Crop Type
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Urban Farming Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 AeroFarms
9.2 Vertical Harvest Farms
9.3 Gotham Greens
9.4 Plenty
9.5 UrbanFarmers
9.6 Green Spirit Farms
9.7 Bowery Farming
9.8 Farm.One
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Urban Farming Market was valued at USD 140 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.8% from 2024 to 2030, reaching a market size of USD 181.76 billion by 2030.
Key drivers include rapid urbanization, consumer preference for sustainable and locally grown food, and advancements in smart farming technologies.
The market is segmented by farming technique (vertical farming, hydroponics, aquaponics, etc.) and crop type (vegetables, fruits, herbs, etc.).
North America is the most dominant region, accounting for nearly 40% of the global urban farming market.
Leading players include AeroFarms, Vertical Harvest Farms, Gotham Greens, Plenty, UrbanFarmers, and others.



