InfiniBand Market Size (2024 – 2030)
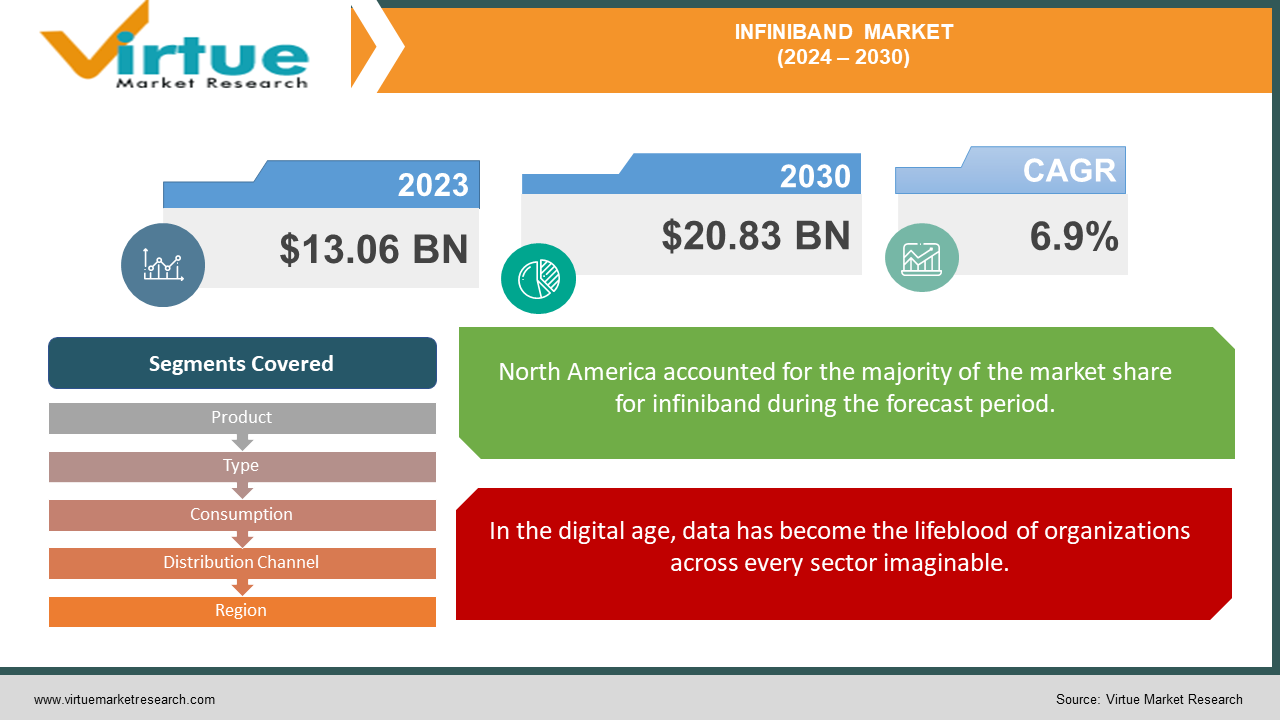
The Global InfiniBand Market was valued at USD 13.06 Billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 20.83 Billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.9%.
InfiniBand is transforming high-performance computing and data center networks. Since its introduction in the late 1990s, this advanced technology has evolved from a niche solution to a crucial part of modern computing.
InfiniBand is designed for ultra-fast data transfer between CPUs and input/output devices. With its high speed and low latency, it is ideal for industries that need rapid data processing, such as scientific research and financial services.
The InfiniBand market has grown significantly, with phases of rapid expansion and consolidation. As businesses face increasing data volumes and computing demands, InfiniBand is emerging as a key solution for faster and more efficient networking.
Key Market Insights:
- The deployment of InfiniBand technology can reduce data center power consumption by up to 30%. InfiniBand supports data transfer rates up to 200 Gbps.
- InfiniBand technology is used in more than 90% of the world’s top 25 supercomputers. The market for InfiniBand-enabled products exceeded 7 million ports in 2023.
- InfiniBand products can support up to 400 Gbps in future iterations. InfiniBand contributes to reducing network overhead by up to 50%.
- The adoption of InfiniBand in data centers has increased by 15% annually over the past five years. InfiniBand technology can handle up to 1.5 million messages per second per port.
- In financial services, InfiniBand reduces transaction processing times by up to 40%.
- InfiniBand is used in over 25% of HPC (High-Performance Computing) installations worldwide. The average cost of InfiniBand switches ranges from $5,000 to $20,000.
- InfiniBand supports RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) with latencies as low as 1 microsecond.
- InfiniBand is utilized by over 50% of Fortune 500 companies in their IT infrastructure. InfiniBand technology is used in 70% of AI and machine learning data centers.
- InfiniBand’s market penetration in Europe is estimated at 20% of the total data center market.
InfiniBand Market Drivers:
In the digital age, data has become the lifeblood of organizations across every sector imaginable.
The rise of big data has changed how computing systems work. Traditional networks, which were once good enough, now struggle to handle the massive amount, speed, and variety of data businesses deal with today. This is where InfiniBand comes in—a technology designed for the big data era.
InfiniBand stands out because of its high speed and low delay. As companies process larger datasets in real-time, they need a network that can transfer data quickly and efficiently. InfiniBand meets this demand by delivering multi-gigabit speeds with microsecond-level latency, making it the perfect choice for modern data-driven organizations.
The rise of high-performance computing (HPC) and supercomputing serves as a key driver accelerating the growth of the InfiniBand market.
As the world faces complex challenges like climate modeling and drug discovery, the need for powerful computing has grown rapidly. InfiniBand has become a key technology in high-performance computing (HPC), helping to build some of the fastest supercomputers.
What makes InfiniBand so important in HPC? It provides high-speed, low-latency connections that efficiently link thousands of computing nodes. Traditional networking systems often slow down as they scale, creating bottlenecks that hurt performance. However, InfiniBand is designed specifically for high-performance environments, making it ideal for large, interconnected computing clusters.
With its ability to handle massive workloads efficiently, InfiniBand continues to drive advancements in supercomputing, supporting breakthroughs in science, technology, and industry.
InfiniBand Market Restraints and Challenges:
One of the biggest challenges in the InfiniBand market is competition from other networking technologies, especially Ethernet. Ethernet is widely used and has been a standard in enterprise networking for a long time. While InfiniBand delivers better performance for high-performance computing (HPC), many organizations prefer Ethernet because it is familiar and easier to implement.
Another major challenge is the cost. InfiniBand hardware, such as adapters and switches, is often more expensive than Ethernet alternatives. For businesses with limited budgets, this price difference can be a big barrier, especially if they don’t need InfiniBand’s full capabilities.
Additionally, InfiniBand requires specialized skills for setup and maintenance. This increases the overall cost of ownership and can make it less attractive to smaller businesses or those without dedicated HPC teams.
InfiniBand Market Opportunities:
The InfiniBand market has huge growth potential, especially in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). As AI applications become more advanced and require massive amounts of data, the demand for high-speed, low-latency networking is increasing. InfiniBand offers superior performance, making it a top choice for AI data centers and research facilities.
Beyond just networking, InfiniBand vendors have the opportunity to create specialized solutions designed for AI workloads. This could open up new market segments and drive further growth.
Another key opportunity lies in edge computing. As more computing tasks move closer to the data source, high-performance networking solutions are needed at the edge. Adapting InfiniBand for compact, energy-efficient edge deployments could significantly expand its use beyond traditional data centers.
The rise of exascale computing—the next generation of supercomputers—also presents a major opportunity. As governments and organizations compete to build the most powerful computing systems, the need for ultra-fast networking solutions will continue to grow. InfiniBand is well-positioned to become the preferred choice for these advanced systems.
With the rapid evolution of AI, edge computing, and supercomputing, InfiniBand is set to play a crucial role in the future of high-performance networking.
GLOBAL INFINIBAND MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
6.9% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Distribution Channel and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Mellanox Technologies (acquired by NVIDIA), Intel Corporation, Xilinx Inc. (acquired by AMD), Cavium Inc. (acquired by Marvell Technology Group), Broadcom Inc., Supermicro Computer Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Dell Technologies, Lenovo Group, Inspur Group |
SEGMENTATION ANALYSIS
InfiniBand Market Segmentation: By Types
-
Single Data Rate (SDR)
-
Double Data Rate (DDR)
-
Quad Data Rate (QDR)
-
Fourteen Data Rate (FDR)
-
Enhanced Data Rate (EDR)
-
High Data Rate (HDR)
-
Next-Generation Data Rate (NDR and XDR)
QDR and FDR InfiniBand still maintain a significant market presence, particularly in mid-range HPC installations and enterprise environments. Their balance of performance and cost-effectiveness make them attractive options for organizations looking to upgrade from older networking technologies without incurring the full cost of the latest InfiniBand generations. The most dominant type in terms of installed base is likely FDR InfiniBand. Its widespread adoption in previous years, coupled with the significant investment required for upgrades, means that many organizations continue to rely on FDR InfiniBand for their high-performance networking needs. However, in terms of new deployments and revenue generation, EDR and HDR InfiniBand are rapidly gaining dominance.
EDR and HDR InfiniBand currently represent the fastest-growing segments. The relentless demand for higher performance in AI, big data analytics, and scientific computing is driving the rapid adoption of these latest generations. Organizations at the forefront of data-intensive computing are quick to embrace these technologies to gain competitive advantages and push the boundaries of what's computationally possible.
InfiniBand Market Segmentation: By Distribution Channel
-
Direct Sales
-
System Integrators
-
Value-Added Resellers (VARs)
-
Cloud Service Providers
-
Distributors and Dealers
-
Online Sales
-
Others
The most dominant distribution channel remains direct sales, particularly for high-end InfiniBand solutions. The complex nature of many InfiniBand deployments, especially in large-scale HPC environments, often necessitates direct engagement between vendors and customers. This channel allows for highly customized solutions and ensures that customers can fully leverage the advanced capabilities of InfiniBand technology.
The fastest-growing distribution channel for InfiniBand technology is likely the cloud service provider segment. As more organizations look to leverage high-performance computing capabilities without the overhead of managing physical infrastructure, cloud-based HPC services are gaining traction. This trend is opening up new opportunities for InfiniBand adoption, particularly among organizations that might not have previously considered investing in high-performance networking solutions.
InfiniBand Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Europe
-
Asia-Pacific
-
South America
-
Middle East & Africa
The worldwide InfiniBand market is dominated by North America. Numerous elements contribute to the region's prominence, such as the existence of significant technological businesses, sophisticated IT infrastructure, and significant R&D expenditures. North American businesses are always creating and implementing cutting-edge computer solutions, placing them at the forefront of technological innovation. This trend is demonstrated by the use of InfiniBand technology in data centers and HPC.
In the worldwide InfiniBand market, Asia-Pacific is the region with the quickest rate of growth. The high market growth rate of the area may be attributed to its rapid economic expansion, rising investments in technology, and developing IT infrastructure. The Asia-Pacific region is embracing more and more cutting-edge technologies, such as cloud computing and HPC, which call for InfiniBand's effective and fast interconnects.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the InfiniBand Market:
Global lockdowns and travel restrictions disrupted the intricate supply chains that feed the InfiniBand market. Shortages of critical components like semiconductors and disruptions in manufacturing caused delays in the production and delivery of InfiniBand equipment. With businesses facing economic uncertainty, many data center expansion projects and HPC deployments were put on hold. This led to a decline in demand for InfiniBand solutions, impacting both hardware vendors and software developers in the ecosystem. The pandemic fueled research efforts into vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments. This, in turn, increased the demand for HPC resources to analyze massive datasets, simulate complex models, and accelerate scientific breakthroughs. InfiniBand's ability to connect high-performance computing clusters efficiently played a crucial role in these endeavors. Businesses are re-evaluating their data center needs and prioritizing investments in technologies that enable scalability, remote management, and efficient handling of ever-growing data volumes. InfiniBand, with its inherent strengths in these areas, is well-positioned to benefit from this shift.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
The introduction of High Data Rate (HDR) InfiniBand is a game-changer. This next-generation technology boasts speeds of up to 200 Gbps (gigabits per second), doubling the bandwidth of the previous generation. Imagine HPC applications processing complex simulations or artificial intelligence models at an unprecedented pace, facilitated by the lightning-fast data exchange enabled by HDR InfiniBand. HDR InfiniBand isn't operating in isolation. It's designed to seamlessly integrate with cutting-edge technologies like NVIDIA In-Network Computing acceleration engines. This powerful combination unlocks a new level of performance for applications like scientific discovery, big data analytics, and machine learning. Cloud computing is revolutionizing how we access and utilize computing power. InfiniBand is finding its way into cloud data centers, enabling high-performance computing as a service (HPCaaS). The rise of AI and machine learning applications demands robust communication infrastructure. InfiniBand's ability to handle massive data transfers with minimal latency makes it ideal for supporting these data-hungry applications. Imagine AI algorithms processing vast datasets for facial recognition or natural language processing, all fueled by the efficient data exchange facilitated by InfiniBand.
Key Players:
-
Mellanox Technologies (acquired by NVIDIA)
-
Intel Corporation
-
Xilinx Inc. (acquired by AMD)
-
Cavium Inc. (acquired by Marvell Technology Group)
-
Broadcom Inc.
-
Supermicro Computer Inc.
-
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
-
Dell Technologies
-
Lenovo Group
-
Inspur Group
Chapter 1. InfiniBand Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. InfiniBand Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. InfiniBand Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. InfiniBand Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. InfiniBand Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. InfiniBand Market – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Single Data Rate (SDR)
6.3 Double Data Rate (DDR)
6.4 Quad Data Rate (QDR)
6.5 Fourteen Data Rate (FDR)
6.6 Enhanced Data Rate (EDR)
6.7 High Data Rate (HDR)
6.8 Next-Generation Data Rate (NDR and XDR)
6.9 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.10 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. InfiniBand Market – By Distribution Channel
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Direct Sales
7.3 System Integrators
7.4 Value-Added Resellers (VARs)
7.5 Cloud Service Providers
7.6 Distributors and Dealers
7.7 Online Sales
7.8 Others
7.9 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Distribution Channel
7.10 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Distribution Channel, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. InfiniBand Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Type
8.1.3 By Distribution Channel
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Type
8.2.3 By Distribution Channel
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Type
8.3.3 By Distribution Channel
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Type
8.4.3 By Distribution Channel
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Type
8.5.3 By Distribution Channel
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. InfiniBand Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Mellanox Technologies (acquired by NVIDIA)
9.2 Intel Corporation
9.3 Xilinx Inc. (acquired by AMD)
9.4 Cavium Inc. (acquired by Marvell Technology Group)
9.5 Broadcom Inc.
9.6 Supermicro Computer Inc.
9.7 Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
9.8 Dell Technologies
9.9 Lenovo Group
9.10 Inspur Group
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The amount of data generated globally is exploding, driven by factors like social media, the Internet of Things (IoT), and scientific research. This necessitates high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructure that can handle massive datasets and complex calculations efficiently.
Implementing an InfiniBand network can be expensive compared to traditional Ethernet solutions. The cost of InfiniBand hardware, software licenses, and qualified personnel for installation and maintenance can be a significant barrier for some potential users, particularly smaller organizations.
Mellanox Technologies (acquired by NVIDIA), Intel Corporation, Xilinx Inc. (acquired by AMD), Cavium Inc. (acquired by Marvell Technology Group), Broadcom Inc., Supermicro Computer Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Dell Technologies, Lenovo Group, Inspur Group.
The market is dominated by North America, which commands a market share of around 35%.
With a market share of about 15%, Asia Pacific is expanding the quickest.