Genetic Testing Market Size (2024 – 2030)
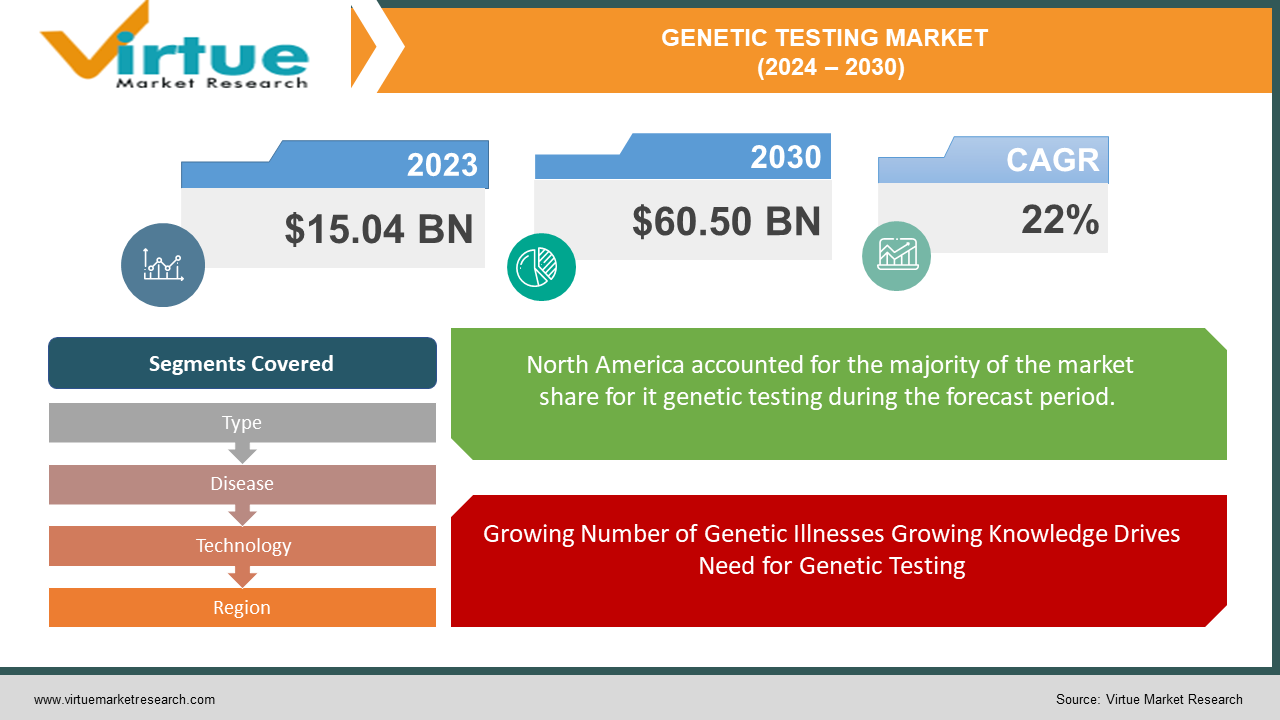
The Global Genetic Testing Market was valued at USD 15.04 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 60.50 billion by 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 22%.
Genetic testing looks for alterations associated with disease by analysing your proteins, chromosomes, or DNA. It has several purposes, including identifying carrier status, forecasting future risk, screening foetuses and infants, diagnosing genetic abnormalities, and guiding treatment choices. There are several tests available, each with unique benefits and drawbacks. The best exam for you will depend on your unique situation.
Key Market Insights:
Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from genetic abnormalities; two well-known examples are cystic fibrosis and Down syndrome. By the age of 20, one in twenty Americans will suffer from a rare hereditary illness. The need for genetic testing is being driven by rising knowledge and the frequency of genetic illnesses as individuals seek diagnoses, make plans, and make educated healthcare decisions.
Personalised medicine adjusts medical interventions based on each patient's distinct genetic profile. This programme, which aims to advance personalised medical research, has recruited over a million volunteer participants from the US. Because genetic testing may reveal how an individual's genes may react to certain drugs or therapies, it is essential to the field of personalised medicine. This enables medical professionals to recommend the best therapies with the fewest negative effects, improving patient outcomes.
Currently, North America dominates the worldwide market for genetic testing. Nonetheless, the Asia-Pacific area is expected to increase at the quickest rate in the upcoming years because of reasons including growing awareness of genetic illnesses and rising disposable income. This change demonstrates the growing popularity of genetic testing and its potential to enhance healthcare outcomes and access in Asia-Pacific's developing nations.
Global Genetic Testing Market Drivers:
Growing Number of Genetic Illnesses Growing Knowledge Drives Need for Genetic Testing
It seems that hereditary abnormalities are becoming more commonplace worldwide. There are several reasons for this. One factor is a greater understanding of these illnesses, which include Down syndrome, sickle cell disease, and cystic fibrosis. This knowledge increases the likelihood that people will seek out genetic testing, which can result in diagnosis and future planning. Still, there might be a more serious problem involved. Growing rates of genetic illnesses may also be caused by changes in lifestyle, the environment, or even postponing children. To fully comprehend the causes of this apparent rise, more investigation is required.
From Universal Size to Customised Attention Personalised medicine is growing because of genetic testing.
By focusing on therapies specific to each patient's individual biology rather than a "one-size-fits-all" approach, personalised medicine is revolutionising healthcare. Genetic testing, which reveals a person's genetic composition, is what makes this change possible. Through deciphering this code, medical professionals can forecast an individual's potential response to drugs or treatments. For example, a genetic test may identify differences that affect how a patient metabolises a certain medication. Equipped with this understanding, medical professionals may recommend the best drug at the right dosage, reducing the possibility of adverse reactions and optimising the effectiveness of therapy. This tailored strategy has great potential to enhance treatment results for a variety of illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, and mental health issues.
Global Genetic Testing Market Restraints and Challenges:
Genetic testing has a bright future, but not without challenges. Many people may not be able to afford these exams. Clear criteria and careful thought are necessary considering ethical considerations around discrimination, privacy, and the emotional impact of results. Accessibility is further limited by a lack of skilled specialists to interpret testing and by limited insurance coverage. Complications are increased by data security breaches and a constantly shifting regulatory environment. Unlocking the full potential of genetic testing and realising its promise for improved healthcare for everyone depends on overcoming these obstacles through workforce development, ethical frameworks, expanded insurance coverage, affordability, strong data protection, and navigating changing legislation.
Global Genetic Testing Market Opportunities:
The industry for genetic testing offers an abundance of opportunities. Prenatal non-invasive testing is becoming more popular, offering a safer method of checking for foetal anomalies. Another intriguing approach is pharmacogenomics, which uses genetic data to tailor medication regimens for increased efficacy and fewer adverse effects. Expanding newborn screenings and using innovative testing methods to identify genetic diseases early on provides a great chance to improve health outcomes. Another area that is ripe for development is oncology, where genetic testing is essential for risk assessment, therapy selection, and cancer diagnosis. The market for direct-to-consumer testing is anticipated to grow, and businesses that offer trustworthy and educational DTC tests stand to gain. In conclusion, the rapidly growing market for genetic testing in poor nations offers an opportunity to increase accessibility and raise knowledge, enabling people to take charge of their own health.
GENETIC TESTING MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
22% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Disease, Technology and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
23andMe (US), Abbott Laboratories (US), AncestryDNA (US), Illumina (US), Invitae (US), Myriad Genetics (US), Natera (US), QIAGEN (Germany), Roche Diagnostics (Switzerland), Thermo Fisher Scientific (US) |
Global Genetic Testing Market Segmentation: By Type
-
Carrier Testing
-
Diagnostic Testing
-
Predictive Testing
-
Prenatal Testing
-
Newborn Screening
-
Other Types
The genetic testing industry is now dominated by carrier testing, but predictive testing is expected to increase at the highest rate. Predictive testing helps people determine their risk of acquiring genetic problems in the future, so it's probable that this jump is a result of the increased focus on preventative healthcare. additional well-established areas include diagnostic testing, prenatal testing, and newborn screening; additional types include pharmacogenomics and paternity testing.
Global Genetic Testing Market Segmentation: By Disease
-
Cancer
-
Cystic Fibrosis
-
Down Syndrome
-
Sickle Cell Disease
-
Neurological Disorders
-
Rare Diseases
-
Other Diseases
Cancer is the most common disease and has the highest market share for genetic testing because of its significance for diagnosis and treatment. But uncommon illnesses are a close race to overtake other diseases for the throne. As awareness and study of rare illnesses increase, there is potential for major development in this area, while the other disorders category continues to expand due to ongoing breakthroughs in genetic testing.
Global Genetic Testing Market Segmentation: By Technology
-
Cytogenetic Testing
-
Biochemical Testing
-
Molecular Testing
In terms of technology, molecular testing dominates the genetic testing business both now and in the future. Compared to cytogenetic and biochemical testing methods, this technology's strength is its direct analysis of DNA for anomalies, which offers excellent accuracy and adaptability across a larger variety of applications.
Global Genetic Testing Market Segmentation: By Region
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America leads the world's genetic testing industry because of its sophisticated healthcare system, high level of awareness, and significant players. But in terms of growth, the Asia-Pacific area is predicted to outpace the rest because of rising incomes, government backing, and healthcare expenditure, while Europe continues to expand at a steady rate and South America, the Middle East, and Africa have promise due to rising economic growth and more awareness.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Genetic Testing Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a variety of effects on the global market for genetic testing. Lockdowns and travel restrictions caused supply chain disruptions that resulted in temporary shortages of testing kits and reagents and delays in non-COVID genetic testing processes. On the one hand, these events occurred. Prioritising resources above other needs may have caused hospitals to delay non-urgent prenatal testing or elective carrier screening. But the epidemic also offered a few noteworthy possibilities. The market for genetic testing methods was greatly bolstered by the enormous demand for COVID-19 diagnoses. The crisis also highlighted how important genetic testing is for understanding and identifying infectious illnesses, which might spur long-term market growth in this field. The use of telemedicine, particularly telegenetic counselling, which has the potential to increase accessibility to genetic testing services, was also expedited by social distancing tactics.
Recent Trends and Developments in the Global Genetic Testing Market:
Innovation is booming in the global industry for genetic testing. Prenatal non-invasive testing is becoming more and more common, providing a safer option for identifying foetal anomalies. An age of personalised medicine is being ushered in by pharmacogenomics, which uses genetic information to customise pharmacological treatments for better outcomes and fewer adverse effects. There is an increasing focus on early detection of genetic abnormalities, leading to the development of newer diagnostics and increased newborn screening programmes. Thanks to the importance that genetic testing plays in cancer diagnosis, therapy selection, and risk assessment, oncology is another discipline that is seeing advancements. The market for direct-to-consumer testing is booming, giving people the ability to take ownership of their health data. Furthermore, as access and awareness grow, the market for genetic testing is set to grow significantly in underdeveloped nations. The pandemic's social distancing efforts have contributed to the emergence of telegenetic counselling, which provides more convenient consultations and may expand the use of genetic testing. These trends provide a clear picture of a quickly changing industry that has the potential to transform healthcare and provide people with the ability to take proactive control of their health.
Key Players:
-
23andMe (US)
-
Abbott Laboratories (US)
-
AncestryDNA (US)
-
Illumina (US)
-
Invitae (US)
-
Myriad Genetics (US)
-
Natera (US)
-
QIAGEN (Germany)
-
Roche Diagnostics (Switzerland)
-
Thermo Fisher Scientific (US)
Chapter 1. Genetic Testing Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Genetic Testing Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Genetic Testing Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Genetic Testing Market Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Genetic Testing Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Genetic Testing Market – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Carrier Testing
6.3 Diagnostic Testing
6.4 Predictive Testing
6.5 Prenatal Testing
6.6 Newborn Screening
6.7 Other Types
6.8 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.9 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Genetic Testing Market – By Disease
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Cancer
7.3 Cystic Fibrosis
7.4 Down Syndrome
7.5 Sickle Cell Disease
7.6 Neurological Disorders
7.7 Rare Diseases
7.8 Other Diseases
7.9 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Disease
7.10 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Disease, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Genetic Testing Market – By Technology
8.1 Introduction/Key Findings
8.2 Cytogenetic Testing
8.3 Biochemical Testing
8.4 Molecular Testing
8.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Technology
8.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Technology, 2024-2030
Chapter 9. Genetic Testing Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
9.1 North America
9.1.1 By Country
9.1.1.1 U.S.A.
9.1.1.2 Canada
9.1.1.3 Mexico
9.1.2 By Type
9.1.3 By Disease
9.1.4 By By Technology
9.1.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.2 Europe
9.2.1 By Country
9.2.1.1 U.K
9.2.1.2 Germany
9.2.1.3 France
9.2.1.4 Italy
9.2.1.5 Spain
9.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
9.2.2 By Type
9.2.3 By Disease
9.2.4 By Technology
9.2.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.3 Asia Pacific
9.3.1 By Country
9.3.1.1 China
9.3.1.2 Japan
9.3.1.3 South Korea
9.3.1.4 India
9.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
9.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.3.2 By Type
9.3.3 By Disease
9.3.4 By Technology
9.3.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.4 South America
9.4.1 By Country
9.4.1.1 Brazil
9.4.1.2 Argentina
9.4.1.3 Colombia
9.4.1.4 Chile
9.4.1.5 Rest of South America
9.4.2 By Type
9.4.3 By Disease
9.4.4 By Technology
9.4.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.5 Middle East & Africa
9.5.1 By Country
9.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
9.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
9.5.1.3 Qatar
9.5.1.4 Israel
9.5.1.5 South Africa
9.5.1.6 Nigeria
9.5.1.7 Kenya
9.5.1.8 Egypt
9.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
9.5.2 By Type
9.5.3 By Disease
9.5.4 By Technology
9.5.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 10. Genetic Testing Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
10.1 23andMe (US)
10.2 Abbott Laboratories (US)
10.3 AncestryDNA (US)
10.4 Illumina (US)
10.5 Invitae (US)
10.6 Myriad Genetics (US)
10.7 Natera (US)
10.8 QIAGEN (Germany)
10.9 Roche Diagnostics (Switzerland)
10.10 Thermo Fisher Scientific (US)
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Genetic Testing Market was valued at USD 15.04 billion in 2023.
The worldwide Global Genetic Testing Market growth is estimated to be 22% from 2024 to 2030.
The Global Genetic Testing Market is segmented By Type (Carrier Testing, Diagnostic Testing, Predictive Testing, Prenatal Testing, Newborn Screening, Other Types); By Disease (Cancer, Cystic Fibrosis, Down Syndrome, Sickle Cell Disease, Neurological Disorders, Rare Diseases, Other Diseases); By Technology (Cytogenetic Testing, Biochemical Testing, Molecular Testing) and by region.
Future developments in genetic testing are anticipated to include expanded use of early detection tests, pharmacogenomics for personalised therapy, non-invasive prenatal testing, and ongoing cancer research. Furthermore, there is tremendous opportunity for development in the direct-to-consumer industry and in expanding into new markets.
The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the market for genetic testing are multifaceted. The pandemic has brought attention to the possibilities of genetic testing for infectious illnesses and personalised medicine approaches to treatment, even if certain standard genetic testing procedures may have been delayed owing to resource allocation in healthcare institutions.



