Europe Vertical Farming Market Size (2024-2030)
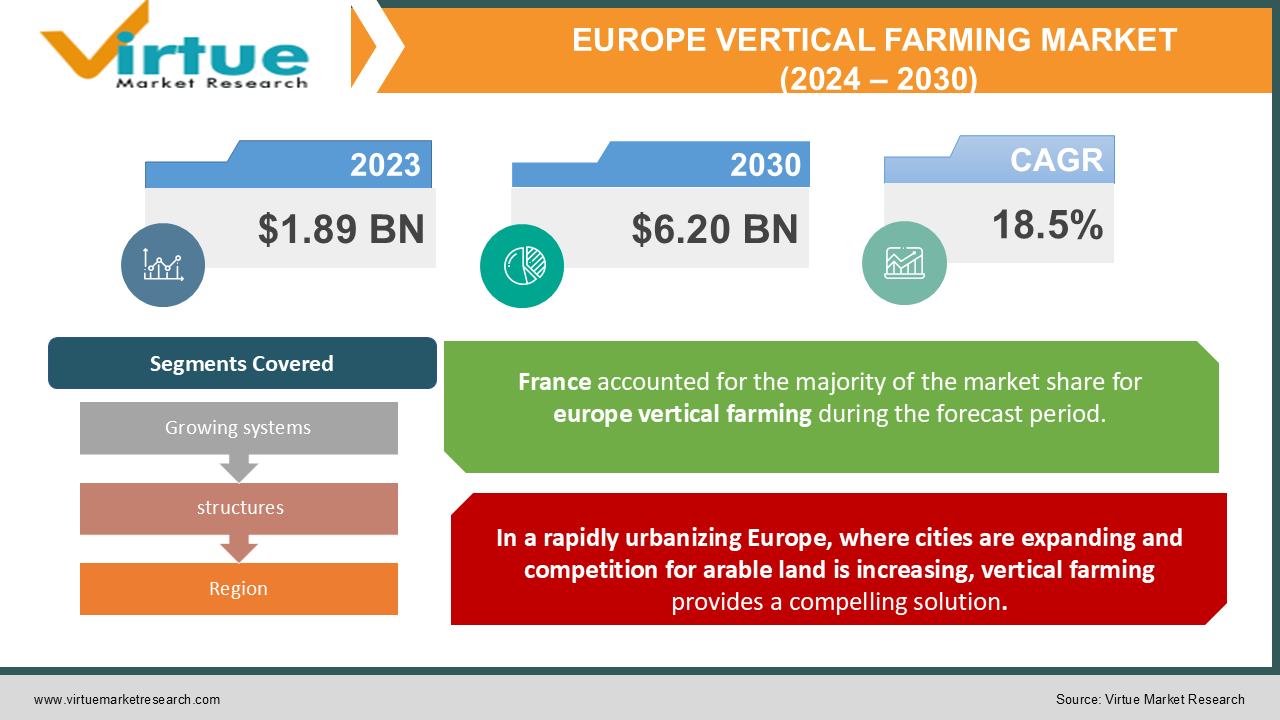
The Europe Vertical Farming Market was valued at USD 1.89 Billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 6.20 Billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.5%.
Vertical farming breaks the boundaries of traditional agriculture. It's the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often within controlled environments like warehouses or repurposed buildings. This innovative approach offers a compelling solution to challenges faced by conventional farming in Europe. As populations grow, prime agricultural land gets swallowed by urbanization. Vertical farming maximizes yield per square meter, not per acre. Indoor vertical farms are shielded from unpredictable weather events, ensuring consistent harvests year-round, crucial in the face of climate change. Controlled environments allow for precise optimization of water and nutrient delivery, often using recirculating systems that minimize waste. Advances in LED efficiency, automation, and renewable energy integration will make vertical farming more economically competitive. Research into optimizing fruiting vegetables, root crops, or even staple grains in vertical systems could revolutionize food production.
Key Market Insights:
Europe's vertical farming market is still relatively nascent, with significant room for growth and evolution in the coming years. While its overall economic impact remains smaller than traditional agriculture, interest and investment are rapidly increasing. As cities expand and arable land faces competing uses, vertical farms offer a space-efficient solution for food production near population centers. Vertical farming's reduced water usage, minimal pesticide reliance, and potential for lowering food transport emissions align with sustainability goals. The ability to produce crops year-round in controlled environments insulates against weather disruptions and bolsters local food security. In Europe, leafy greens, herbs, and certain types of berries are particularly well-suited and commonly grown in current vertical farming systems. Advancements hold the potential for a wider crop range. Vertical farms are intrinsically dependent on innovations in LED lighting, sensor systems, automation, and data analytics for optimization and cost-efficiency. Vertical farming is best suited for certain crops and market segments. It complements, rather than fully replaces, traditional farming practices. The significant initial investment in setting up vertical farming infrastructure, from specialized growing systems to climate control technology, creates a barrier to entry, especially for smaller-scale operations. Powering artificial lighting and maintaining precise environmental conditions requires substantial energy. Optimizing energy efficiency and utilizing renewable sources will be crucial for both cost reduction and the sector's environmental footprint.
Europe Vertical Farming Market Drivers:
In a rapidly urbanizing Europe, where cities are expanding and competition for arable land is increasing, vertical farming provides a compelling solution.
Growing upwards rather than outwards to maximize yields in a smaller footprint is the fundamental idea behind vertical farming. Because of this, metropolitan communities with limited land resources find it very enticing. Vertical farms should be positioned inside or close to urban areas to minimize "food miles," shorten delivery times, and guarantee that customers may obtain locally cultivated, ultra-fresh produce. Urban areas could be redefined by vertical farming. Imagine vertical farming enterprises bringing a little bit of nature into busy commercial districts, or rooftop farms providing communal green spaces. Real estate developers and property management firms investigating the possibility of incorporating vertical farming into urban revitalization initiatives should show interest. Because they grow quickly and are in great demand in urban markets, leafy greens, herbs, and microgreens will probably continue to be the main emphasis of urban-based vertical farms. Vertical farms provide chances for education and engagement for urban consumers who are becoming more disengaged from traditional agriculture, which could increase the adoption of this new production style.
Concerns about the environmental impact of traditional agriculture and the vulnerability of food supply chains due to climate change are fueling the search for more sustainable solutions.
Vertical farms use sophisticated hydroponic or aeroponic systems, often with closed-loop water recycling. This results in dramatically lower water consumption compared to field cultivation. The controlled environment of vertical farms drastically reduces pest and disease pressure, significantly decreasing or even eliminating the need for chemical crop protection. Vertical farms aren't at the mercy of unpredictable weather patterns. This ensures consistent harvests year-round, improving local food security and offering resilience in the face of climate disruptions that impact traditional farming. By producing food closer to where it's consumed, vertical farming reduces the need for long-distance transport, lowering the carbon footprint associated with moving food from farm to plate. Vertically farmed products positioned with a strong emphasis on sustainability resonate with a growing segment of European consumers who make purchasing choices based on environmental impact. Vertical farms partnering with restaurants or retailers committed to sustainable sourcing can create powerful models and strengthen their market position.
Europe Vertical Farming Market Restraints and Challenges:
One of the most substantial hurdles facing vertical farming operations is the issue of energy consumption. The economic realities of vertical farming present a significant barrier, particularly for smaller-scale operations.
Artificial lighting is essential for year-round, consistent crop production in vertical farms. However, the energy cost of running LED systems for optimal plant growth can be significant. Maintaining precise temperatures, humidity, and air circulation within the enclosed environment requires additional energy inputs. While technological advancements are steadily improving energy efficiency, vertical farming still consumes substantially more energy per unit of output compared to traditional field cultivation that relies on sunlight. Unless vertical farms make significant strides in transitioning to renewable energy sources, their environmental benefits may be overshadowed by their energy footprint. Constructing the specialized growing infrastructure that allows for vertical stacking, and outfitting it with precision climate control, lighting, and automation systems necessitates a sizable upfront investment. The reliance on sensors, data analytics platforms, and ongoing technological advancements translates into both initial costs and the need for continual upgrades. The higher production costs associated with vertical farming mean crops must be sold at premium prices to achieve a profit margin, potentially impacting their competitiveness within the broader market.
Europe Vertical Farming Market Opportunities:
Optimizing light spectrum, nutrients, and environmental factors can enhance the flavor profile of leafy greens, herbs, and specialty crops. This appeals to consumers tired of bland, mass-produced options. Vertical farms situated within or near cities can deliver freshly harvested produce to retailers and restaurants. This ensures unmatched freshness and a longer shelf-life. The controlled environment of vertical farming typically eliminates the need for pesticides. This aligns with strong European consumer demand for clean, safe produce. Vertical farms can craft compelling narratives about their tech-forward approach, sustainability, and connection to local communities, appealing to values-conscious shoppers willing to pay more. Vertical farms can easily meet organic standards, and some are exploring even more rigorous growing practices such as biodynamic or regenerative, catering to those seeking the highest environmental and ethical standards in their produce. Vertical farms can grow heirloom varieties, lesser-known herbs, or exotic microgreens that excite chefs and adventurous home cooks, offering something traditional farms cannot. Research suggests the potential to manipulate growing conditions in vertical farms to increase levels of specific nutrients or phytonutrients in crops. Think higher-antioxidant greens or specialty herbs tailored for nutraceutical uses. Vertical farms can offer subscriptions for a curated selection of fresh produce delivered directly to consumers, tapping into the desire for convenient access to unique and premium options.
EUROPE VERTICAL FARMING MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
18.5% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Growing systems, structures, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
UK, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Rest of Europe |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Infarm, Plenty, Aero Farms, Nordic Harvest , Jones Food Company, Agricool, Let us Grow |
Europe Vertical Farming Market Segmentation:
Europe Vertical Farming Market Segmentation: By Growing System -
- Hydroponics
- Aeroponics
- Aquaponics
Hydroponics is the most widely used technology in the European vertical farming industry, accounting for 60-70% market share. Instead of soil, plants are grown directly in nutrient-rich water. This technique is known for its adaptability to a variety of crops. Aeroponics: This is a smaller but quickly expanding market that could account for 20–30% of the total. Airborne plant roots are misted with a nutritional solution regularly. This technique provides superior root zone oxygenation and may require even less water than hydroponics. Aquaponics: A small but extremely specialized market segment that accounts for less than 10% of the total. It creates a symbiotic system by combining plant agriculture and aquaculture, or fish farming. Plants receive nutrients from fish feces, and the plants, in turn, filter the fish's water.
Europe Vertical Farming Market Segmentation: By Structures -
- Building-Based Farms
- Shipping Container Farms
- In-Store Installations
Building-Based Farms: Currently hold the dominant market share, often estimated between 60-70%. This is driven by established players with larger-scale operations and ongoing investments in this model. These utilize either repurposed structures (warehouses, abandoned factories) or newly constructed spaces specifically designed for vertical farming. They offer the potential for scalability but also often involve significant upfront capital investment. Shipping Container Farms: Represent a sizeable and rapidly growing segment, sometimes estimated around 20-30% of the market. Their flexibility and lower initial investment compared to large-scale building-based systems appeal to many entrants. Self-contained, prefabricated vertical farming units housed within retrofitted shipping containers. These prioritize modularity and the ability to be deployed in various locations. In-Store Installations: Make up a smaller, yet noteworthy niche, often estimated below 10% of the market. Their success is tied to consumer desire for visible, ultra-local food production integrated into their shopping experience. Smaller-scale vertical farms integrated directly within grocery stores, restaurants, or other retail environments. Here, the emphasis is on demonstrating hyper-freshness and transparency to consumers.
Europe Vertical Farming Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis:
- UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
France, UK, Germany: These countries each hold sizeable shares, potentially ranging around 14%, 16%, and 20% each, reflecting both established vertical farms as well as a robust pipeline of new ventures. Italy, and Spain: These nations represent smaller yet growing segments of the European market, likely holding 12%, and 10% shares, with the potential for expansion driven by unique regional factors. Rest of Europe: While the rest of the countries are a collection of smaller, yet significant contributors to the overall picture, some countries making notable strides, potentially representing a combined market share upwards of 28%. While the Netherlands often holds the "innovation hub" title, several regions might vie for dominance in the European vertical farming landscape, depending on the metric used. The Netherlands likely leads in research & development, patents, and spearheading cutting-edge advancements within the field. Countries with larger populations and dense urban centers, like Germany, the UK, or France, have the potential for the most significant overall market size for vertically farmed produce in the long run.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Europe Vertical Farming Market:
Restaurant closures and a general shift towards home cooking caused a temporary dip in demand from the food service sector, a key customer base for some vertical farms. The overall economic uncertainty led some investors to postpone or scale back their commitments to vertical farming ventures, hindering growth plans. As concerns about food security and supply chain vulnerability grew, consumers turned towards local, sustainable options. Vertical farms, with their emphasis on controlled environments and reduced reliance on traditional supply chains, benefited from this shift in consumer priorities. The rise of online grocery shopping provided a new sales channel for vertical farms, enabling them to reach customers directly and mitigate the impact of restaurant closures. Vertical farms explored innovative delivery models such as box subscriptions and partnerships with local retailers to ensure fresh produce reached consumers efficiently. Labor shortages experienced during lockdowns highlighted the value of automation in vertical farming. Investment in automation technologies like robotic harvesting and climate control systems gained momentum. Vertical farms, with their inherently controlled environments, were well-positioned to implement stringent biosecurity protocols. This reassured consumers concerned about food safety during a pandemic.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
Strawberries were once seen as a "holy grail" for vertical farming. Developments in specialized LED lighting spectrums, tailored nutrient blends, and the breeding of cultivars suited to indoor cultivation are making them commercially viable. Expect an increasing focus on other berries and even vine crops like cherry tomatoes. Vertical farms cater to high-end restaurants seeking unique ingredients, expanding into edible flowers that add both flavor and visual flair to dishes. These command premium prices and offer differentiation in a competitive market. While less immediate, research projects are exploring the potential to adapt crops like dwarf varieties of legumes (lentils, beans, etc.), certain root vegetables, or even grains to stacked vertical farming systems. Success here could significantly impact the sector's ability to provide a wider range of calories and nutrients. Algorithms can analyze vast datasets from sensors monitoring temperature, humidity, nutrient levels, and plant growth patterns. This enables the AI system to fine-tune the environment in real-time for maximum yield, quality, and even specific flavor attributes.
Key Players:
- Infarm
- Plenty
- Aero Farms
- Nordic Harvest
- Jones Food Company
- Agricool
- Let us Grow
Chapter 1. Europe Vertical Farming Market– Scope & Methodology
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Product Growing System
1.5. Secondary Product Growing System
Chapter 2. Europe Vertical Farming Market – Executive Summary
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Europe Vertical Farming Market– Competition Scenario
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Europe Vertical Farming Market - Entry Scenario
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Europe Vertical Farming Market- Landscape
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Europe Vertical Farming Market– By Growing System
6.1. Introduction/Key Findings
6.2. Hydroponics
6.3. Aeroponics
6.4. Aquaponics
6.5. Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Growing System
6.6. Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Growing System , 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Europe Vertical Farming Market– By Structures
7.1. Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Building-Based Farms
7.3. Shipping Container Farms
7.4. In-Store Installations
7.5. Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Structures
7.6. Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Structures , 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Europe Vertical Farming Market, By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1. Europe
8.1.1. By Country
8.1.1.1. U.K
8.1.1.2. Germany
8.1.1.3. France
8.1.1.4. Italy
8.1.1.5. Spain
8.1.1.6. Rest of Europe
8.1.2. By Growing System
8.1.3. By Structures
8.1.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Europe Vertical Farming Market– Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1. Infarm
9.2. Plenty
9.3. Aero Farms
9.4. Nordic Harvest
9.5. Jones Food Company
9.6. Agricool
9.7. Let us Grow
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
3400
3900
4600
Related Reports
Frequently Asked Questions
Vertical farms can reduce water usage by up to 95% compared to traditional agriculture through closed-loop systems and precise irrigation. This is a major draw in regions facing water stress or seeking to minimize agriculture's environmental footprint.
Building vertical farms requires substantial upfront investments in infrastructure (lighting systems, climate control, growing structures) and technology (automation, sensors
Infarm, Plenty, Aero Farms, Nordic Harvest, Jones Food Company
Agricool, Let Us Grow.
Germany currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 20%.
The Netherlands market, while mature, has significant room for growth in specific segments, like online sales of herbal supplements and formats targeting stress and sleep support.