Cancer Vaccines Market size (2025-2030)
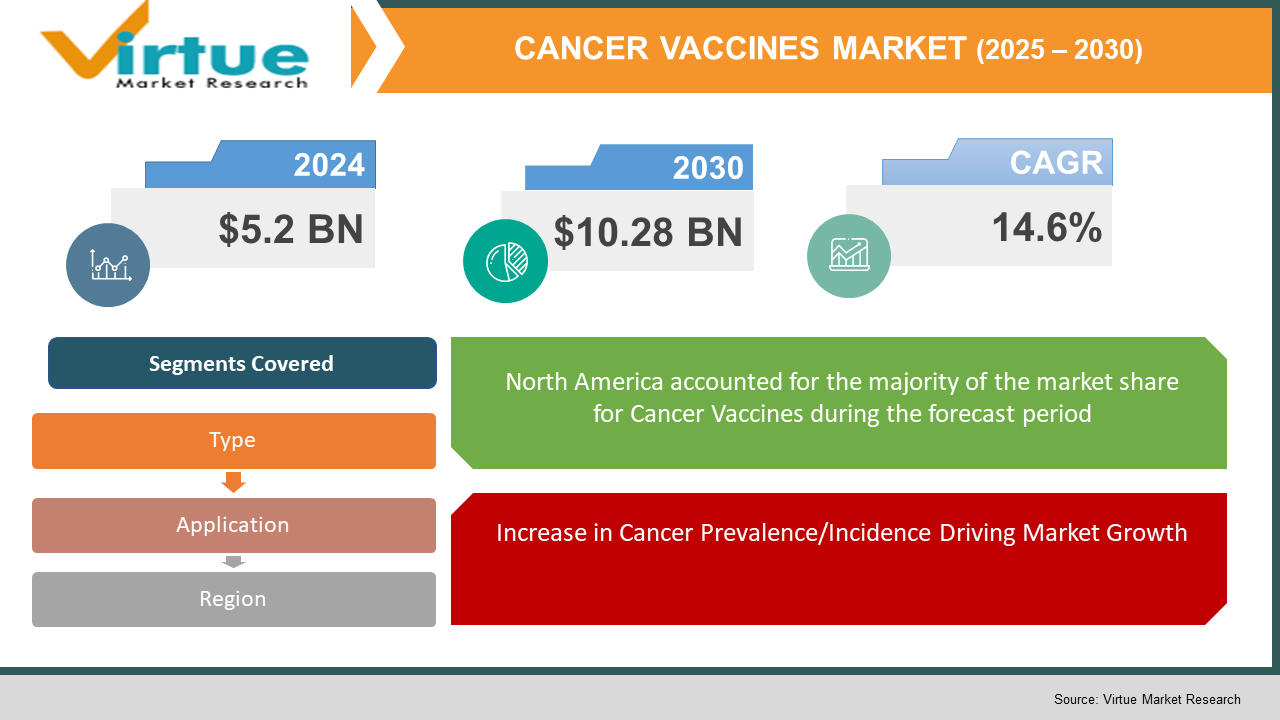
The Global Cancer Vaccines Market was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 10.28 billion, growing at a rapid CAGR of 14.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2030
Cancer vaccines are designed to treat or prevent the occurrence of any type of cancers via stimulating the immune system to identify and kill cancer cells. Cancer vaccines include preventive and therapeutic cancer treatment vaccines for patients with cancer (example HPV vaccine). The increased incidence and prevalence of cancer, advancements in vaccine technology and growing utilization of personalized medicine are the factors contributing to the growth of this market. The motivation for safe, less destructive cancer treatment therapies is expected to drive the growth of the market. Continued and ongoing research and development (R&D) operations and government support for cancer treatment programs are driving the increased demand for cancer vaccines.
Key market insights:
- The availability of preventive cancer vaccines, such as the HPV vaccine, has helped reduce the risk of certain cancers, particularly cervical cancer.
- Cancer vaccines are experiencing high demand in emerging markets, as increased healthcare awareness and improved access to medical services boost treatment options.
- Regulatory approvals for several promising cancer vaccine candidates are expected to accelerate, enhancing the availability of new treatment options in the market. High R&D investments from leading pharmaceutical companies and ongoing clinical trials are expected to open new opportunities for cancer vaccine development and market expansion.
Global Cancer Vaccines Market Drivers:
Increase in Cancer Prevalence/Incidence Driving Market Growth:
The accelerating incidence of cancer around the world is one of the primary drivers for the growing demand for cancer vaccines. As the incidence of cancer is increasing, especially in lower and middle-income countries, the need for preventive as well as therapeutic vaccination has become important. The World Health Organization estimates that cancer led to approximately 9.6 million deaths in 2018 around the world, and that number is expected to rise moving forward. The rising cancer burden is forcing health systems to incorporate new treatment solutions, which is why vaccines are becoming more widely accepted and used. Preventive vaccines, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines (which cause cervical cancer), are gaining popularity for the prevention of other cancers including hepatitis B (liver cancer). Furthermore, therapeutic vaccines capable of treating cancers after they develop are also being invented, and hold promise for patients previously with few options for treatment. As the global burden of cancer continues to escalate, cancer vaccines are being viewed as a novel potential solution to the rising incidence and mortality rates attributed to cancer.
Advances in Immunotherapy and Personalized Medicine are fueling the market growth:
The latest scientific advancement in immunotherapy has been instrumental in establishing the growth of cancer vaccines. Immunotherapy is focused on exploiting and enhancing the immune response to fight cancer and cancer vaccines represent a significant part of this therapeutic option. With the introduction of personalized cancer vaccines, which are tailored based on the genetic make-up of a patient's tumor, the market opportunities for cancer vaccines are unprecedented. These personalized vaccines are designed to elicit an immune response to only the cancer cells, making them very effective in treating some cancers. Personalized medicine is only going to grow in the next ten years, as patients will increasingly want targeted and more individualized treatment options. Personalized cancer vaccines are being evaluated in melanoma, lung cancer, and breast cancer, and are providing new hope for patients who previously had very few options. The addition of immunotherapy, including cancer vaccines, against other treatments such as chemotherapy and targeted therapies will help transform cancer treatment plans in the near future.
Government Programs and Funding for Cancer Research will boost the growth of the market:
Governments around the globe have recognized the urgent need for cancer research and are offering substantial funding to support the development of cancer vaccines. The launch of public health programs aimed at decreasing the global burden of cancer is promoting the use of cancer vaccines. As an example, many governments have implemented national immunization programs for human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B to reduce the incidence of cervical cancer and liver cancer, respectively. Additionally, regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have supported the development of new cancer vaccines by providing fast-track approval and grant options for the conducting of clinical trials. The availability of government support will help expedite the development of vaccines and further promote the growth of the market. In addition, public private partnerships are facilitating the innovation of cancer vaccine technology to expedite access to patients. The support through government programs is likely to continue driving the cancer vaccine market for years to come.
Global Cancer Vaccines Market Challenges and Restraints:
High Development Costs and Complex Regulatory Approvals is restricting market growth:
One of the main challenges facing the market for cancer vaccines is the high costs associated with development. Cancer vaccine development can be costly because it takes a large amount of funding to complete the research studies, clinical trials, and certifications from regulators, thus making it lengthy and expensive. Pharmaceutical companies must conduct multiple rounds of clinical trials to demonstrate sufficient evidence of safety and efficaciousness of the vaccine, which can take several years. The regulatory process of getting approvals also varies by geography, adding complexity to the market. In most cases, cancer vaccines will go through extensive study to verify efficacy and safety before being available in the market, which involves regulators, such as the FDA and EMA, reviewing these studies. This all leads to prolonged time to market for one product, thus reducing the overall supply of cancer vaccines into the market. Additionally, the development cost at such high investment levels can also result in an expensive product that may be prohibitive in low income countries. For all of these reasons, while cancer vaccines carry much promise and potential, the costs associated with development and approval will continue to be a challenge to overcome until improvements can be made.
Limited Efficacy and Adverse Effects limits market growth:
Despite the great potential of cancer vaccines, they have limitations with respect to efficacy and safety. There are some cancer vaccines that may not adequately protect against all types of cancers making them of limited value as "universal" treatment options. For example, the preventative HPV vaccines have been very effective at protecting against cervical cancer but may be less effective at preventing other HPV-related cancers. Likewise, therapeutic vaccines targeting cancers at advanced stages may not achieve the intended result every time. Furthermore, cancer vaccines may also have side effects consistent with all vaccines, or medical interventions, as an automatic rule. The side effects may vary from mild symptomatology (e.g., fatigue, fever, etc.) to serious adverse events. These side effects may delay the adoption of cancer vaccines more widely and may also result in patients having second thoughts about their use. Additionally, there is still no guarantee that everyone receiving the cancer vaccine will respond as well to treatment, impacting the efficacy experience by some. Successfully addressing these issues will be key to unlocking the full potential of cancer vaccines and achieving wider utilization.
Market opportunities:
The cancer vaccination sector presents numerous prospects, particularly in prevention, treatment, and personalized medicine. Preventive vaccines will escalate in share as additional countries implement vaccination campaigns targeted to viral cancers such as HPV and hepatitis B. These vaccination campaigns will help reduce the worldwide burden of cancer, particularly burden in countries with higher rates of cancer. With a worldwide increase in the incidence of cancer, the therapeutic cancer vaccination sector is also anticipated to see strong growth, particularly for new indications such as melanoma, lung cancer, and breast cancer. In addition, the emphasis in practice and drug development in personalized medicine provides new potential revenue opportunities in the marketplace through the development of personalized vaccines. Personalized vaccinations targeted to the genetic profile of each patient showed promising results in clinical trials. Additionally, combination therapies and immunotherapy will continue to pave the way for cancer vaccination development. The incorporation of cancer vaccines into conjunction with therapies, such as targeted therapies and chemotherapy, can improve cancer vaccination outcomes and grow its appeal as part of a treatment regime. In addition to this steady development is the greater number of novel cancer vaccine candidates in clinical tests which will support innovation and the introduction of cancer vaccinations to market in the near future.All these factors contribute to the cancer vaccines market being a dynamic and fast-growing sector with huge growth prospects.
CANCER VACCINES MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
14.6% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Merck & Co., GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, and BioNTech. |
Cancer Vaccines Market segmentation:
Cancer Vaccines Market Segmentation By Type:
- Preventive Vaccines
- Therapeutic Vaccines
The preventive cancer vaccines segment is expected to dominate because of the recent increase in adoption of vaccines including vaccines for HPV which prevent cervical cancer, and are proven safe and efficacious in preventing certain malignancies that develop from a viral infection. The prevalence of success of preventative vaccines, as well as the promotion of government-sponsored vaccine campaigns, continues to greatly contribute to the growth of this segment of the market.
Cancer Vaccines Market Segmentation By Application:
- Cervical Cancer
- Hepatitis B-related Cancer
- Melanoma
- Lung Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
At this moment, cervical cancer represents the single most common indication for cancer vaccines, driven by the widespread implementation of the HPV vaccine. The vaccine is highly effective against the most common types of cervical cancer, and global vaccination campaigns have resulted in decreased incidence of those forms of cervical cancer, especially in younger people. With increasing awareness and vaccine acceptance, preventing cervical cancer is the focus of the cancer vaccine market.
Cancer Vaccines Market Regional Segmentation:
• North America
• Asia-Pacific
• Europe
• South America
• Middle East and Africa
Due to factors like strong healthcare investment, a sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, and a plethora of pharmaceutical companies invested in cancer vaccine development, North America represents the leading continent for the cancer vaccine market. North America's robust regulatory trajectory (e.g., FDA) enables approval and commercialization of new drugs. Moreover, North America has seen higher-than-ever levels of adoption of preventive cancer vaccines (e.g., HPV), helping their position as global market leaders. Strong universities and healthcare providers have contributed to innovated therapies, helping North America lead the global cancer vaccines market.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Cancer Vaccines Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic had a two-fold impact on the cancer vaccines market. On the one hand, many healthcare systems worldwide were interrupted by the pandemic and experienced delays in approval and development of cancer vaccines. There were pauses in clinical trials, and access to cancer care -including vaccines- was curtailed in most areas so as to deal with the pandemic. On the other hand, successful COVID-19 vaccines have expedited vaccine development technologies and this has a positive impact on the cancer vaccines market. Lessons learned in developing and distributing COVID-19 vaccines have sped up applications of these technologies to develop cancer vaccines. In addition, the pandemic will have raised the profile for vaccines and demonstrated the potential benefits of new technologies to develop vaccines for different areas of disease, such as cancer. As the world comes out of this pandemic, the demand for cancer vaccines will bounce back, as governments and healthcare systems turn their attention to the next wave of vaccine technologies and innovation.
Latest trends/Developments:
The personalized medicine approach is one of the most important trends in the landscape of cancer vaccines. Personalized cancer vaccines are developed based on a person's genotype and have shown high success in clinical trials. These vaccines have the potential to provide more personalized and effective treatment options that are designed specifically by targeting each patient's unique cancer characteristics. Another trend is the recent combination of cancer vaccines with immunotherapy. The addition of cancer vaccines to other treatments provides potentially enhanced treatment options at improved results, similar to other therapies in cancer treatment. Additionally, mRNA technology has received recent attention, especially in the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic, and is being explored further to develop vaccines for different cancer indications. This approach may allow for vaccines that are easier to manufacture and are more flexible in targeting various cancers. Finally, ongoing collaborations among academic institutions, drug development companies, and research institutes continue to provide innovative opportunities related to cancer vaccines. Together, these advances are resulting in the identification of new candidates for cancer vaccines and treatments.
Key Players:
- Merck & Co.
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Pfizer
- Novartis
- Roche
- Sanofi
- BioNTech
- MedImmune
- Inovio Pharmaceuticals
- Moderna
Chapter 1. CANCER VACCINES MARKET – SCOPE & METHODOLOGY
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Sources
1.5. Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. CANCER VACCINES MARKET – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2025 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. CANCER VACCINES MARKET – COMPETITION SCENARIO
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. CANCER VACCINES MARKET - ENTRY SCENARIO
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes Players
4.5.6. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. CANCER VACCINES MARKET - LANDSCAPE
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. CANCER VACCINES MARKET – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Preventive Vaccines
6.3 Therapeutic Vaccines
6.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2025-2030
Chapter 7. CANCER VACCINES MARKET – By Application
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Cervical Cancer
7.3 Hepatitis B-related Cancer
7.4 Melanoma
7.5 Lung Cancer
7.6 Breast Cancer
7.7 Prostate Cancer
7.8 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Application
7.9 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Application , 2025-2030
Chapter 8. CANCER VACCINES MARKET - By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1. North America
8.1.1. By Country
8.1.1.1. U.S.A.
8.1.1.2. Canada
8.1.1.3. Mexico
8.1.2. By Application
8.1.3. By Type
8.1.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2. Europe
8.2.1. By Country
8.2.1.1. U.K.
8.2.1.2. Germany
8.2.1.3. France
8.2.1.4. Italy
8.2.1.5. Spain
8.2.1.6. Rest of Europe
8.2.2. By Type
8.2.3. By Application
8.2.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3. Asia Pacific
8.3.1. By Country
8.3.1.1. China
8.3.1.2. Japan
8.3.1.3. South Korea
8.3.1.4. India
8.3.1.5. Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2. By Type
8.3.3. By Application
8.3.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4. South America
8.4.1. By Country
8.4.1.1. Brazil
8.4.1.2. Argentina
8.4.1.3. Colombia
8.4.1.4. Chile
8.4.1.5. Rest of South America
8.4.2. By Type
8.4.3. By Application
8.4.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5. Middle East & Africa
8.5.1. By Country
8.5.1.1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2. Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3. Qatar
8.5.1.4. Israel
8.5.1.5. South Africa
8.5.1.6. Nigeria
8.5.1.7. Kenya
8.5.1.8. Egypt
8.5.1.8. Rest of MEA
8.5.2. By Type
8.5.3. By Application
8.5.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. CANCER VACCINES MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Packaging Type, Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Merck & Co.
9.2 GlaxoSmithKline
9.3 Pfizer
9.4 Novartis
9.5 Roche
9.6 Sanofi
9.7 BioNTech
9.8 MedImmune
9.9 Inovio Pharmaceuticals
9.10 Moderna
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Cancer Vaccines Market was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 10.28 billion by 2030.
Key drivers include rising cancer incidence, advancements in immunotherapy, and government funding for cancer research and vaccines
The market is segmented by product (preventive vaccines, therapeutic vaccines) and application (cervical cancer, hepatitis B-related cancer, melanoma, lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer).
North America is the dominant region due to strong healthcare infrastructure, high spending, and rapid adoption of preventive vaccines
Leading players include Merck & Co., GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, and BioNTech.



