Global Water Pressure Management Market Size (2023 – 2030)
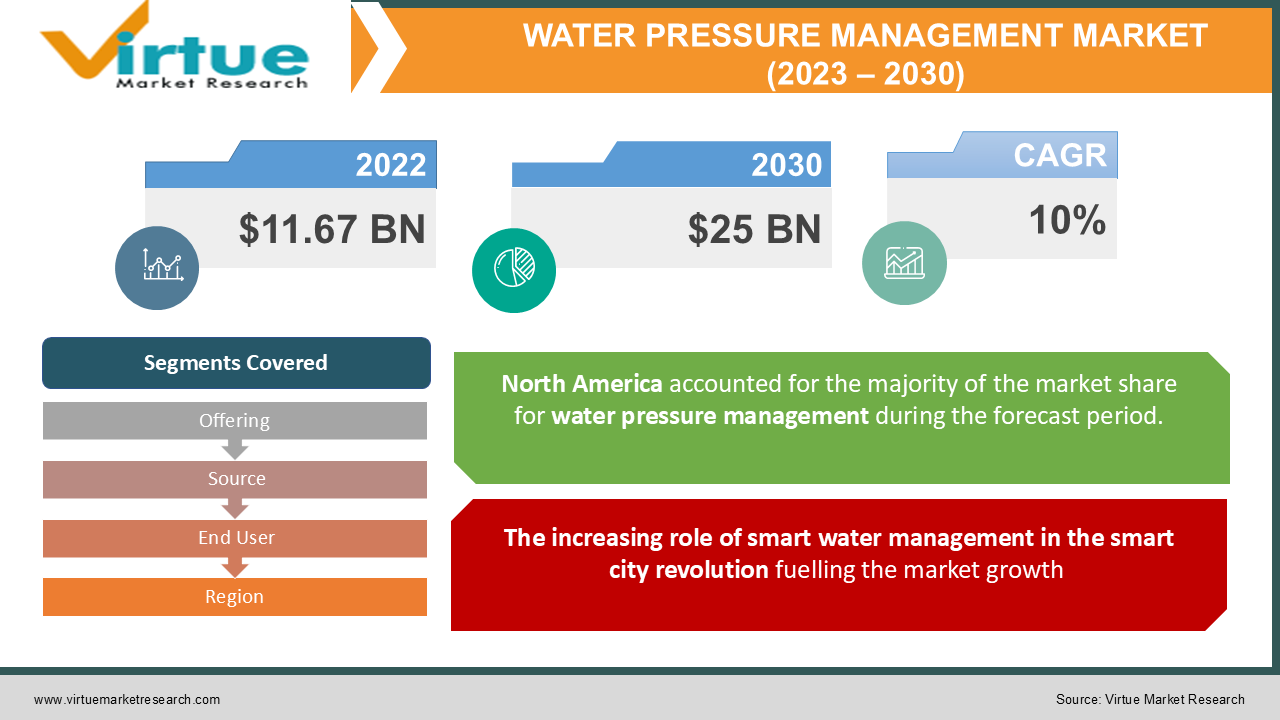
In 2022, the Global Water Pressure Management Market was valued at USD 11.67 billion and is projected to reach a market size of USD 25 billion by 2030. Over the forecast period of 2023-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10%.
Industry Overview
The most advantageous and economical method of leakage management is pressure management. The majority of pipe bursts are caused less by high pressure and more by persistent pressure variations that cause the pipes to repeatedly expand and contract, leading to stress fractures. However, there is a physical connection between pressure and leakage flow rate. The rate of leaking will increase or decrease depending on the pressure.
As a result, the pressure should be kept to a minimum without compromising the needs of the customers. Whether there is enough pressure on the consumer is one way that water providers gauge their quality. To guarantee that consumers have enough pressure at all times of the day, utilities frequently use a constant intake pressure to the individual zones/districts. The main factors are rapid urbanization, which puts a lot of pressure on water utilities to provide quality and continuous water supply and related services; rapid adoption of advanced technologies; growing concern for sustainable living; creation of rules and laws by governments around the world to reduce water consumption; and the development of water treatment technologies.
The traditional approach to water pressure management relies on a centralized system with few management options. Due to the disparity in freshwater supply and demand, the system's low operating efficiency, the high energy costs associated with production and distribution, and the high cost of treatment. A new smart water management system is needed to handle these problems. One of the main drivers of the market growth for smart water management is the development of technology. Numerous potentials for market expansion are emerging as a result of the development of the Advanced Metering System (AMS) and the integration of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) into the water management system.
Impact of Covid-19 on the industry
The IT and telecom sector has been crucial in supporting national digital infrastructures around the world during the COVID-19 epidemic. Every person and government have been in continual communication with one another to supply and receive real-time information on COVID-19, regardless of whether they are at the federal, state, central, local, or provincial levels. Currently, the government, telecommunications, utilities, and healthcare sectors are working nonstop to calm the situation and provide essential services to everyone. The number of COVID-19 cases is increasing daily as a result of an increase in instances that are infected. Like with people, COVID-19 has had a significant impact on businesses of all sizes. Due to national-level policies, key industries like manufacturing, automotive, textile, transportation and logistics, travel and hospitality, and consumer goods have all been closed.
Market Drivers
With metropolitan areas becoming more intelligent and technologically savvy, there is a growing need for innovative techniques to manage natural water resources
Population increase, economic expansion, increasing urbanization, and rising per-capita food consumption are all contributing factors to the worldwide challenge of meeting the growing demand for (renewable) water resources. In water-stressed areas, there are over 2 billion people, according to the UN World Water Development Report 2021. 45 % of the world's population, or almost 3.4 billion people, lack access to safe sanitation facilities. By 2030, the world would have a global water shortage of 40%, they predicted. Countries are unable to deliver water in sufficient amounts and of acceptable quality by employing conventional water management techniques because of the limited water resources and the growing demand. Additionally, the overuse or improper management of the current water resources is posing problems for water utilities, including NRW losses, water contaminants, and the difficulty to provide a continuous water supply. This situation prompts water companies to look into creative ways to use the available water supplies effectively and sustainably.
The increasing role of smart water management in the smart city revolution fuelling the market growth
Globally, governments are putting a lot of effort into making smart technologies for economic development a central part of their urban planning strategy. Initiatives to create "smart cities" were launched in 2013, and they include several different elements, including smart energy, smart buildings, smart mobility, smart technology, smart infrastructure, and smart healthcare. One of the key elements that characterize a smart city is smart water. Digital water and wastewater treatment technologies are deployed as part of the smart infrastructure component, which includes SWM. With the rising population, fast urbanization, soaring food consumption, and overexploitation of resources, smart city projects present enormous commercial prospects for SWM solution suppliers. By 2050, 68 % of the world's population will reside in urban areas, according to the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
It is therefore crucial that consumption and water use projections be assessed precisely because this has opened up a big market for producers of smart water solutions. As a result, there is a need for smart water systems that can collect useful information on the flow, pressure, and distribution of water inside a metropolis. For instance, the IWRA worked together on its Smart Water Management (SWM) initiatives from July 2020 to December 2023 with K-water (the Korea Water Resources Corporation), the Asia Water Council (AWC), and water specialists from around the world.
Market Restraints
The lack of a skilled workforce will challenge the market growth
Over the next ten years, the energy and utility skills company Energy & Utility Skills predicts a 221,000-person labor need in the water utility sector. The aging workforce, a competitive labor market, and a lack of technical skills in the workforce are the causes of the shortage. There has been an instant need to upskill every employee in the water utility industry, whether new or current, due to the integration of technologies like smart networks and IoT (in the utility sector) at every level. The COVID-19 outbreak, however, has made it more crucial than ever for utility firms to interact with their most vulnerable customers, anticipate their requirements, and offer proactive support, including payment choices for cash users and those in financial hardship.
The utilities sector's resilience mechanisms have been put to the ultimate test by this epidemic, opening the door for more adaptable, quick-response work styles that fully make use of modern technologies. The lack of digitally skilled workers in the water utility industry is one of the main constraints in this technological age. The lack of knowledge among millennials about the expansion of the water utility sector for pursuing a career is another factor. These elements further limit market expansion.
Difficulty in technology implementation over the legacy infrastructure
The water utility sector is changing to deal with the water sector challenges brought on by climate change, infrastructural problems, and droughts that are causing water scarcity to fulfil the demand of the highly dynamic and competitive market. Due to the promise of optimizing trends in water usage and providing sustainable solutions, water utilities have resorted to digital transformation. However, one of the difficulties water utilities confront in adapting to new technological and economic requirements over aging systems is change management. It can be difficult for solution providers to persuade water utilities to implement SWM solutions because numerous technological elements, including hardware, software, and network components, call for integration with sensors, smart meters, network switches, and valves over the legacy system infrastructure.
WATER PRESSURE MANAGEMENT MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2022 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2022 |
|
Forecast Period |
2023 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
10% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Offering, source, end user, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
IBM Corporation, nationalwell International Inc., ABB Limited, Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG |
This research report on the global water pressure management market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on, and Geography & region.
Global Water Pressure Management Market- By Offering
- Water Meters
- Solutions
- Services
Water utilities are implementing smart solutions to combine multiple business operations as technology advances, increasing their growth. Even with minimal physical investment, they can boost the operating efficiency of the entire water network by integrating a variety of cutting-edge technology with the current processes. The smart water sector uses these technologies and smart infrastructure to create cutting-edge solutions for clients. Due to growing consumer demands, a shortage of natural freshwater resources heightened awareness of water quality, and technological improvements, the use of smart solutions is anticipated to soar during the forecast period.
Global Water Pressure Management Market- By End User
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Residential
In every nation, the municipal authorities are directly in charge of managing the supply and distribution of water. The effectiveness of water supply systems is hampered by the lack of privatization in the sector. Because the water supply networks are not consistently inspected by the public sector worldwide, there are a lot of leakage and water loss events.
Industries must address a variety of water-related issues, such as maintaining suitable water pressure and quality, disposing of industrial wastewater safely and by regulations, and preventing process downtime and production interruptions caused by faulty equipment, such as pumps that supply cooling water or pump wastewater. Commercial and industrial end users are anticipated to increasingly use smart water solutions to address issues including optimizing water consumption, reducing billing errors, putting in place cost-effective fixes, and lowering water costs. Inefficient wastewater disposal systems and practices, including forcibly dumping industrial waste into natural water bodies, are common in many developing economies, making it extremely difficult for local authorities to handle wastewater in these areas.
Global Water Pressure Management Market- By Geography & Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
The projection period is estimated to have the highest CAGR growth in APAC.
The rapid growth can be largely attributed to several factors, including an increase in the adoption of smart grid solutions, an increase in urbanization levels leading to an increase in water demands, agricultural production, technological integration in the utility sector, and an exponential increase in population. Due to these elements, the region's industrial activities are expanding and government laws are favorable, leading to the large-scale deployment of technologies compared to the western regions. The increased need for water efficiency and reusable water resources in APAC is anticipated to fuel the expansion of the SWM market there.
The region's growing number of smart cities is anticipated to generate considerable economic prospects for providers of smart water management technologies. By 2022, India intends to invest around $500,000 in the construction of over 100 smart cities, which are estimated to benefit close to 1 billion people. Additionally, Singapore spent more than USD 1 billion on smart city programs in 2019. The adoption of enhanced metering infrastructure is anticipated to have a major opportunity because of these smart city projects in the area. Asian nations including Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, and others have made significant efforts to construct smart water infrastructure, demonstrating the market's potential for expansion. Japan has made investments in infrastructure for water management despite having a comparatively low NRW (US-24 %).
Global Water Pressure Management Market- By Companies
- IBM Corporation
- nationalwell International Inc.
- ABB Limited
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
NOTABLE HAPPENINGS IN THE GLOBAL WATER PRESSURE MANAGEMENT MARKET IN THE RECENT PAST:
- Business Partnership: - In 2022, To offer water utility customers an integrated and improved central event/asset management solution, Takadu teamed up with Asystom, a leader in universal smart monitoring for preventive maintenance.
- Product Launch: - In 2022, The ABB Ability Smart Solution for Wastewater is a new offering from ABB. The difficulty faced by operators of wastewater treatment plants in achieving the highest operating standards while using the least amount of energy is resolved by this computerized technology. Advanced process control (APC) and digital twin and simulation technologies to predict future operational needs are the two primary pillars of the creative solution.
Chapter 1.Global Water Pressure Management Market– Scope & Methodology
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Assumptions
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Sources
1.5. Secondary Sources
Chapter 2.Global Water Pressure Management Market– Executive Summary
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2022 – 2026) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.3. COVID-16 Impact Analysis
2.3.1. Impact during 2022 - 2026
2.3.2. Impact on Supply – Demand
Chapter 3.Global Water Pressure Management Market– Competition Scenario
3.1. Market Share Analysis
3.2. Product Benchmarking
3.3. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.4. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.5. Supplier - Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4.Global Water Pressure Management Market - Entry Scenario
4.1. Case Studies – Start-up/Thriving Companies
4.2. Regulatory Scenario - By Region
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4. Porter's Five Force Model
4.4.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.4.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.4.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.4.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.4.5. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Global Water Pressure Management Market- Landscape
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6.Global Water Pressure Management Market– By Offering
6.1.Water Meters
6.2. Solutions
6.3. Services
Chapter 7.Global Water Pressure Management Market– By End- User
7.1. Commercial
7.2. Industrial
7.3. Residential
Chapter 8.Global Water Pressure Management Market– By Region
8.1. North America
8.2. Europe
8.3. The Asia Pacific
8.4. Latin America
8.5. The Middle East
8.6. Africa
Chapter 9.Global Water Pressure Management Market– Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Developments)
9.1. IBM Corporation
9.2. nationalwell International Inc.
9.3. ABB Limited
9.4. Schneider Electric SE
9.5. Siemens AG
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900