Warehouse Robotics Market Size (2024 – 2030)
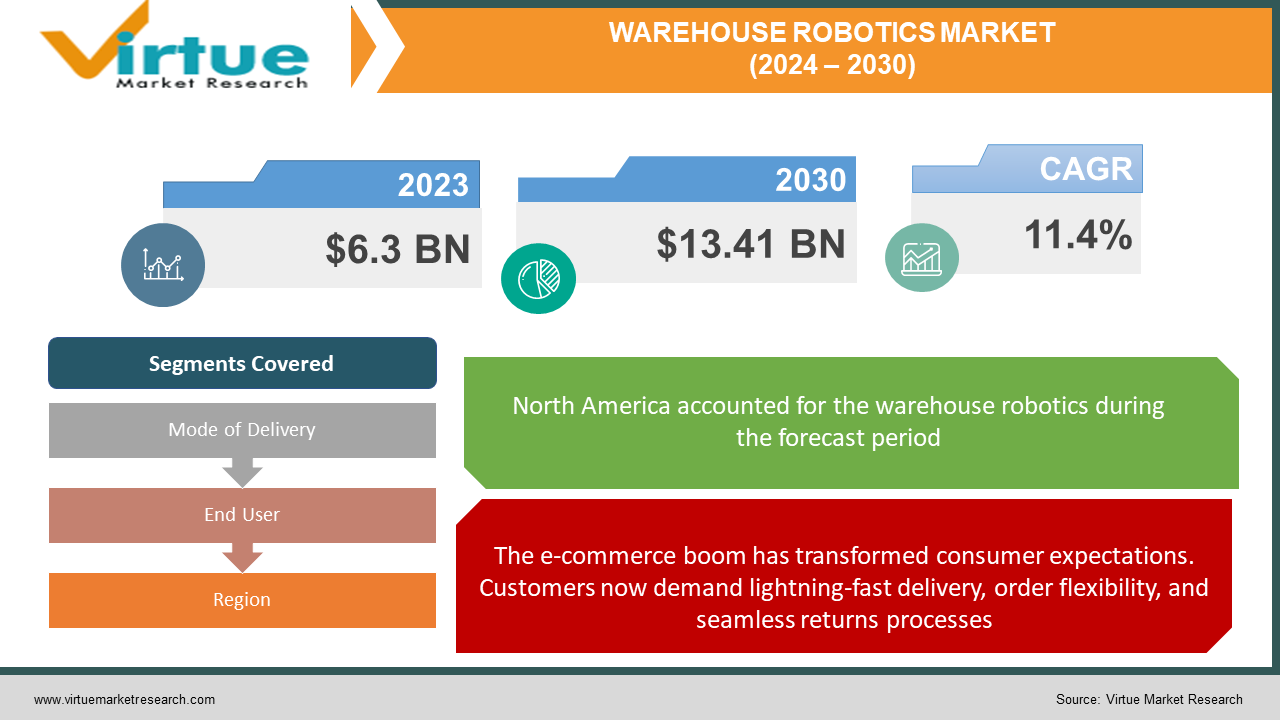
The Warehouse Robotics Market was valued at USD 6.3 Billion and is projected to reach a market size of USD 13.41 Billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.4%.
Warehouse operations are undergoing a profound transformation fueled by the integration of advanced robotics. The warehouse robotics market encompasses a broad spectrum of solutions designed to automate, streamline, and optimize tasks ranging from goods-to-person picking and packing to inventory management and transportation within warehouse environments. The exponential rise of e-commerce and the consumer demand for rapid order fulfillment puts immense pressure on warehouses. Robotics offer the speed, scalability, and accuracy necessary to meet this demand. Finding and retaining reliable warehouse labor is a persistent challenge in many regions. Robotic solutions automate repetitive, physically demanding tasks, alleviate labor shortages, and reduce dependence on a fluctuating workforce. Robotics introduce significant efficiency gains throughout the warehouse workflow. They increase picking speeds, reduce errors, optimize space utilization, and offer potential long-term cost reduction. Robotics can handle hazardous materials, heavy lifting, and work in environments that may be unsafe for human workers, enhancing workplace safety. Continuous progress in areas like robotic mobility, artificial intelligence (AI), machine vision, and collaborative robots (cobots) are expanding the capabilities and potential applications for warehouse robotics. Used for transporting goods across warehouses, these can be guided by tracks or sensors (AGVs) or leverage advanced navigation systems for greater autonomy (AMRs).
Key Market Insights:
The warehouse robotics market is experiencing significant growth fueled by powerful forces reshaping the way goods are stored, moved, and processed within warehouses and distribution centers. The surge in online shopping has placed immense pressure on warehouses to fulfill orders faster, more accurately, and with greater flexibility to handle fluctuations in demand. A tight labor market and challenges in attracting and retaining warehouse workers are driving the need for automation solutions to maintain productivity. Businesses seek operational efficiency gains to stay competitive. Warehouse robotics offers ways to streamline processes, reduce costs, and optimize space utilization. Rapid advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine vision, and sensor technology are enabling more sophisticated and versatile warehouse robots. AGVs are autonomous vehicles used to transport goods throughout a warehouse, often following pre-programmed paths. They enhance efficiency and safety by reducing manual material handling. A more advanced type of robot, AMRs use sensors and AI to navigate warehouse environments dynamically. They offer flexibility in adapting to changes in layouts or processes. These can be used for picking, packing, sorting, and palletizing tasks. Advancements in gripper technology and machine vision enhance their precision and ability to handle diverse items. These systems automate retrieval of stored items, bringing them to a worker station. G2P systems significantly improve picking efficiency and reduce worker travel time within the warehouse. While still in the earlier stages, drones show potential for inventory cycle counting, particularly in warehouses with high ceilings and hard-to-reach storage areas
Warehouse Robotics Market Drivers:
The e-commerce boom has transformed consumer expectations. Customers now demand lightning-fast delivery, order flexibility, and seamless returns processes.
E-commerce empowers consumers with unmatched convenience, limitless product choices, and price transparency at their fingertips. This shift has fundamentally altered consumer expectations for how they want to shop. Online shopping is a 24/7 activity. Consumers expect the ability to place orders anytime and receive those orders with rapid delivery turnaround times. E-commerce platforms collect rich data on consumer preferences. This fuels a desire for personalized product recommendations, targeted promotions, and a curated shopping experience. The ease of online buying has led to a higher volume of returns. Consumers expect free and frictionless return processes, unlike traditional brick-and-mortar experiences. E-commerce means fulfilling individual orders of varying sizes and quantities rather than sending full pallets of goods to stores. This necessitates rethinking warehouse layouts and processes.
Finding, attracting, and retaining sufficient warehouse workers is a persistent challenge for many businesses, especially in economies with low unemployment rates.
Aging populations in many countries result in a shrinking pool of available workers for physically demanding warehouse jobs. Repetitive tasks like picking, packing, or loading/unloading goods, often under time pressure and in potentially noisy environments, aren't appealing to everyone. Warehouses increasingly need to operate round-the-clock to meet e-commerce demands, requiring night shifts and weekend hours that many workers are reluctant to accept. Other industries, like logistics and transportation, also require similar skill sets, creating competition and driving up labor costs. E-commerce driven demand spikes during holidays leave warehouses desperately scrambling for temporary labor, often of inconsistent quality. Failure to ship orders on time has a cascading effect on customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and can even lead to financial penalties in some e-commerce models. Overburdened existing employees can suffer from burnout, negatively impacting productivity and safety within the warehouse.
Warehouse Robotics Market Restraints and Challenges:
In order to implement warehouse robotics, a significant upfront capital investment may be necessary for the acquisition of robots, related equipment, and frequently, layout changes to already-existing warehouses.
Implementing warehouse robotics can require substantial upfront capital expenditure for acquiring robots, supporting infrastructure, and often modifications to existing warehouse layouts. While the potential for reduced labor costs and efficiency gains is clear, calculating a precise return on investment (ROI) can be complex. It involves factoring in longer-term aspects like robot maintenance, adaptability, and workforce skillset adjustments. Implementing and maintaining warehouse robotics demands either on-staff technical expertise or strong partnerships with technology providers for ongoing support and troubleshooting. To fully utilize robot-generated data and enable integrated workflows, data standardization and compatibility between different systems are crucial. While warehouse robotics creates new types of jobs and augments existing roles, it also necessitates a concerted effort toward reskilling and retraining the workforce to manage the evolving technological landscape. While improving, robots still struggle to perfectly replicate the dexterity and fine motor control of humans for certain complex tasks, especially with a diverse range of products. Programmed robots can lack the adaptability to handle unexpected situations, sudden SKU changes, or major process disruptions as effortlessly as humans can adapt. For many real-world warehouse scenarios, a hybrid approach combining robots with human judgment and problem-solving currently yields the most optimal results.
Warehouse Robotics Market Opportunities:
Manufacturers are increasingly turning to robotics for streamlining raw materials handling, assembly line support, and finished goods packaging. The rise of online grocery and demand for temperature-sensitive goods drives automation needs even in environments traditionally less conducive to robots. Advances in end-effectors (grippers) are enabling robots to handle a wider range of items with varying shapes, textures, and weights. AI-powered vision systems and sensor advancements allow robots to better perceive complex warehouse environments and navigate with increased autonomy. Machine learning allows robots to adapt to changing conditions, 'learn' new tasks, and improve performance over time. This widens their potential use cases. The RaaS model allows businesses to obtain warehouse robotics solutions without major upfront capital investment, shifting costs primarily to operational expenses. RaaS offers flexibility to scale robotic systems up or down based on demand, manage seasonal fluctuations, and more easily incorporate new technology as it emerges. Warehouse robotics can automate the most physically demanding, repetitive, or hazardous tasks that are difficult to fill with human workers. Robotics solutions ease the burden on an aging warehouse worker population. Robots work alongside them, reducing strain and extending productivity throughout their careers. Analytics derived from this data empowers businesses to optimize warehouse layouts, inventory management, and predict bottlenecks before they disrupt operations.
WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
11.4% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Mode of Delivery, End User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
ABB, KION Group, KUKA, FANUC, Yaskawa Motoman, Fetch Robotics, Locus Robotics , 6 River Systems, Geek+ |
Warehouse Robotics Market Segmentation: By Mode of Delivery
-
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
-
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
-
Robotic Arms
-
Goods-to-Person (G2P) Systems
-
Drones
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)- AGVs navigate using pre-determined paths often marked by wires, magnetic strips, or visual markers. They offer a reliable solution for repetitive, high-volume material movement. AGVs historically held the largest market share due to their maturity and reliability. However, their share is gradually being challenged by the rise of AMRs. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)- AMRs leverage advanced sensors, AI, and mapping technology to navigate independently. They dynamically adjust routes based on real-time warehouse conditions. It is the fastest-growing segment, with AMRs increasingly gaining market share, driven by their flexibility and adaptability. Potentially higher initial cost than AGVs, reliance on sophisticated software and sensors. Robotic Arms- A significant and steadily growing segment. Advancements in gripper technology and AI-powered vision systems are expanding their use cases. Precision, speed, ability to handle a wide range of item shapes and sizes, well-suited for repetitive tasks. Can be stationary or mounted on mobile bases. It is used for picking, packing, sorting, palletizing, and machine tending tasks. Goods-to-Person (G2P) Systems- These systems automate the retrieval of stored items, bringing them directly to a picking station, minimizing worker travel time. A substantial segment, particularly driven by e-commerce needs for fast and accurate order fulfillment of diverse inventory. Significantly improves picking efficiency, reduces errors, optimizes storage space, scalable for demand fluctuations. Drones- Aerial drones are primarily used for inventory cycle counting, especially in warehouses with high racks and complex storage areas. The smallest current segment and still primarily in earlier adoption stages. Potential for growth as technology matures and regulations around drone usage in warehouses evolve. Regulatory hurdles, battery life constraints, payload limits, and ongoing safety considerations.
Warehouse Robotics Market Segmentation: By End User
-
Retail and E-commerce
-
Manufacturing
-
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
-
Food and Beverage
-
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Retail and E-commerce- The relentless rise of e-commerce fuels a massive demand for warehouse automation to cope with high order volumes, speed expectations, and labour challenges. Robots assist with goods-to-person systems, picking and packing, sorting, returns processing, and inventory management. The retail and e-commerce segment commands a significant share of the warehouse robotics market, often exceeding a 30-40% share. Manufacturing- Robotics in manufacturing warehouses extends beyond finished goods handling. Robots support inbound raw materials management, assembly line tasks, packaging, and quality control. The manufacturing segment holds a substantial share, often around 20-30%, with significant room for further growth. Third-Party Logistics (3PL)- 3PL providers need flexible, adaptable robotics solutions to handle varying order profiles and inventory fluctuations across their clientele. Robotics offer 3PLs a competitive edge by optimizing labour usage, minimizing errors, and maximizing throughput. While smaller than retail or manufacturing, the 3PL segment represents a sizeable and growing market, often around 15-20%. Food and Beverage- Warehouse robotics in this sector addresses tasks like handling fresh produce, sorting packaged goods, cold-chain management, and palletizing for distribution. Specialized solutions are required for handling food safely and meeting hygiene standards. A smaller yet significant market share, often ranging from 5-10% with a growth trajectory fueled by online grocery demand. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals- A niche but steadily growing market, approximately 5-10%, offering significant potential as healthcare logistics prioritizes accuracy and efficiency. Robotics integrated with inventory systems aids in ensuring traceability of medications and medical supplies. Robotics enables accurate order fulfilment, management of temperature-sensitive products, and sterile inventory handling, crucial in this sector.
Warehouse Robotics Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America holds the largest market share. This is often attributed to early technology adoption, the dominance of major e-commerce players, a strong tech innovation ecosystem, and a focus on optimizing warehouse operations to address labor challenges. Market share is often estimated at around 60-70%. Europe commands a sizable share of the global market. Key drivers include a need to optimize existing warehouse infrastructure in many countries, focus on efficiency, and government initiatives promoting robotics adoption. European market share is typically around 15-20%. APAC is the fastest-growing market for warehouse robotics. Massive population centers, booming e-commerce in countries like China and India, and government support for automation fuel this expansion. APAC's share usually ranges from 10-15%, though is on a strong upward trajectory. Latin America is a growing region for warehouse robotics adoption with a focus on addressing logistical challenges in expanding consumer markets. Market share is approximately around 5%.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Warehouse Robotics Market:
The initial outbreak and subsequent lockdowns disrupted global supply chains, impacting the availability of components needed for warehouse robot manufacturing. This led to delays in robot deployments and project postponements. Early pandemic lockdowns caused labor shortages in warehouses, prompting initial interest in automation. However, concerns about worker safety and maintaining social distancing initially limited robot deployments. The pandemic triggered a surge in e-commerce as people shifted towards online shopping. This increased demand for efficient warehouse operations and order fulfillment, accelerating investment in warehouse robotics. The pandemic exacerbated pre-existing labor shortages in warehouses. Warehouse robotics offered a solution to address these challenges, particularly for repetitive, physically demanding tasks. The pandemic exacerbated pre-existing labor shortages in warehouses. Warehouse robotics offered a solution to address these challenges, particularly for repetitive, physically demanding tasks. Warehouse robots enabled social distancing and reduced the need for close human interaction within warehouses, contributing to a safer work environment. The pandemic highlighted the need for resilient and adaptable supply chains. Warehouse robotics solutions offered greater efficiency, improved inventory management, and better order fulfillment capabilities. AMRs offer greater flexibility and adaptability compared to traditional AGVs, making them ideal for navigating dynamic warehouse environments with changing layouts. This flexibility was particularly valuable during the pandemic as businesses adjusted workflows and layouts.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
AI is no longer just about driving robot navigation. It's transforming how robots perceive their environments, make decisions, and adapt to unforeseen situations. Machine learning (ML) enables some robots to learn from past experiences, improving their accuracy and efficiency over time in tasks like grasping objects or optimizing picking patterns. AI-powered warehouse software analyzes data from robots, inventory levels, and order patterns to forecast demand, predict potential bottlenecks, and recommend preemptive actions. The shift is away from rigid automation designed for a single task towards robots easily reconfigurable to handle new SKUs, process changes, or layout adjustments. More intuitive interfaces and programming tools aim to make it easier for warehouse staff, without extensive robotics expertise, to set up, control, and modify robot operations. Customized robotics solutions are emerging to address the unique challenges of diverse sectors like cold storage, apparel handling, or hazardous material management. Robot designs increasingly prioritize energy efficiency, reducing operational costs and aligning with corporate sustainability goals. Robotics-driven warehouse layouts enable higher storage density, potentially reducing the need for construction of new warehouses and its environmental impact. Advancements in 5G networks and virtual reality have the potential to allow remote experts to 'tele-operate' complex warehouse robots or oversee operations from afar.
Key Players:
-
ABB
-
KION Group
-
KUKA
-
FANUC
-
Yaskawa Motoman
-
Fetch Robotics
-
Locus Robotics
-
6 River Systems
-
Geek+
Chapter 1. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – By Mode of Delivery
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
6.3 Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
6.4 Robotic Arms
6.5 Goods-to-Person (G2P) Systems
6.6 Drones
6.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Mode of Delivery
6.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Mode of Delivery , 2024-2030
Chapter 7. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – By End User
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Retail and E-commerce
7.3 Manufacturing
7.4 Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
7.5 Food and Beverage
7.6 Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
7.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End User
7.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End User , 2024-2030
Chapter 8. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.1.3 By End User
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.2.3 By End User
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.3.3 By End User
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.4.3 By End User
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.5.3 By End User
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. WAREHOUSE ROBOTICS MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 ABB
9.2 KION Group
9.3 KUKA
9.4 FANUC
9.5 Yaskawa Motoman
9.6 Fetch Robotics
9.7 Locus Robotics
9.8 6 River Systems
9.9 Geek+
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
E-commerce has transformed the way people shop. Customers now expect lightning-fast delivery, order flexibility, and seamless return processes, putting immense pressure on warehouses to meet these demands.
Implementing warehouse robotics can involve substantial upfront costs for robots, supporting infrastructure, and often modifications to existing warehouse layouts.
ABB, KION Group, KUKA, FANUC, Yaskawa Motoman, Fetch Robotics.
North America currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 60%.
The Asia Pacific exhibits the fastest growth, driven by its increasing population, expanding economy.



