Vietnam Power EPC Market Size (2025-2030)
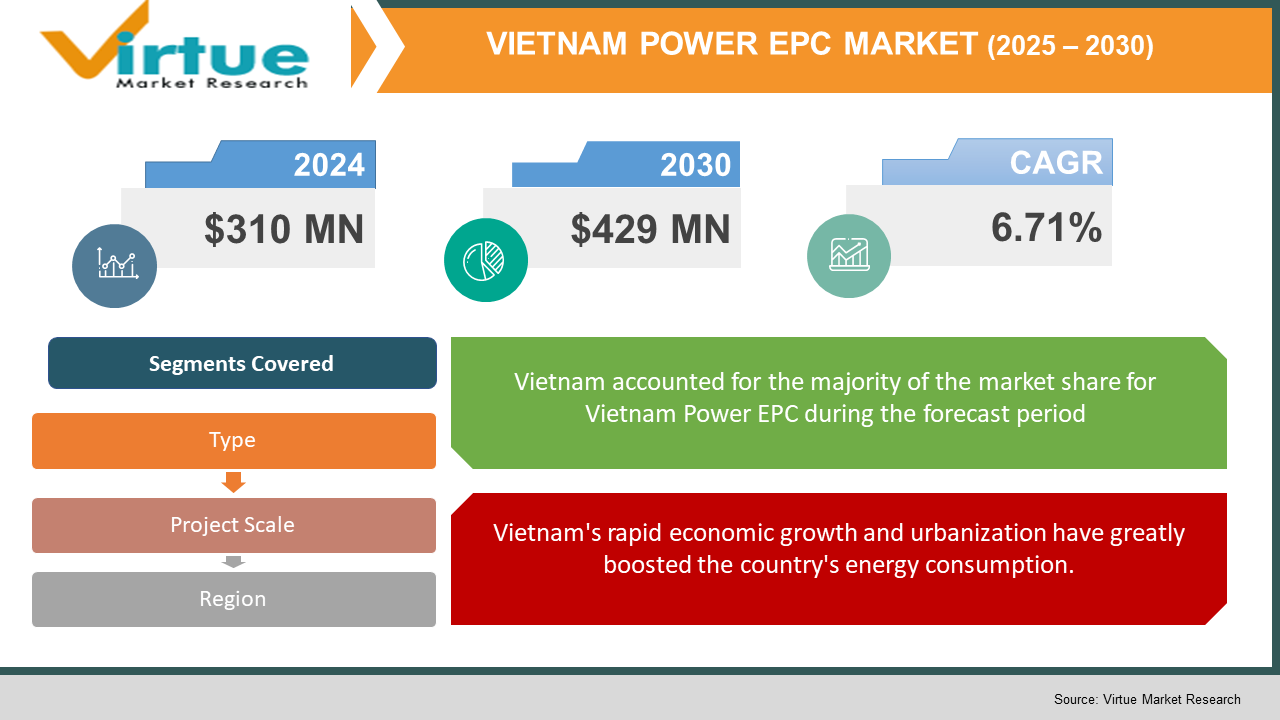
The Vietnam Power EPC Market was valued at USD 310 million in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 429 million by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.71%.
Over the last few years, Vietnam's Power EPC industry has been driven by industrialisation and urbanization, resulting in a huge increase in energy needs. To diversify the energy mix and increase the security of energy supplies, the government has been actively promoting investments in conventional energy resources, including coal and gas, as well as renewable energy resources, including solar and wind power. Major participants in the EPC space are international and domestic players with the capacity and capability to execute complex, large-scale projects. The industry also is moving towards cleaner and more sustainable energy resources, in line with the trend in the rest of the globe towards cleaner use of energy.
Key Market Insights:
- The thermal sector, comprising sources such as coal, oil, and gas, which accounted for more than 66.0% of Vietnam's total power generated in the year 2020, will thus be the market leader.
- Vietnam possesses some of the largest renewable energy resources in the world. Wind energy resources alone possess over 311 GW worth of potential. The government of Vietnam has had a vision to meet 10% of its energy requirement with renewable by the year 2030. This can provide different types of opportunities for the Vietnamese power EPC market in the long term.
- Government incentives and policies towards electricity production are likely to propel the market over the forecast period. Additionally, investments in the transmission infrastructure on a large scale are being undertaken, further propelling the power EPC market in Vietnam.
Vietnam Power EPC Market Drivers:
Vietnam's rapid economic growth and urbanization have greatly boosted the country's energy consumption.
Vietnam's economic development and urbanization at a fast rate have greatly augmented the country's energy requirements. The industrial sector, being the driver of such growth, requires a strong and stable power source to keep it productive and drive further growth. As more and more individuals flock to the cities, there arises a corresponding surge in domestic use of energy, and therefore there is a demand to enhance the power infrastructure. This surge in demand for power is a leading driver for the Power EPC market driving the construction of new power plants and the upgrading of existing infrastructures to serve a growing population and economy. As there are growing urban centres, the demand for clean and sure sources of power grows, and therefore there is ongoing investment in energy projects.
The Vietnamese government has established several regulations and incentives to upgrade the energy sector and encourage foreign investment.
The Vietnamese government has put in place various regulations and incentives to develop the energy sector and attract foreign investment. These include tax incentives, faster approval of power projects, and subsidies for renewable energy. The National Power Development Plan, which outlines the energy strategy of the country, emphasizes the development of renewable energy and grid improvement. These policies provide a positive environment for EPC contractors by ensuring a steady stream of projects and reducing risks of long-term investments. The trend of renewable energy, in particular, provides significant stimulus to the industry, supporting the growth of solar, wind, and other green energy projects.
Vietnam Power EPC Market Restraints and Challenges:
Navigating Vietnam's regulatory framework is complicated and time-consuming. Bureaucratic delays in acquiring permits and approvals can cause project delays and expense increases.
One of the major challenges in Vietnam's power EPC market is navigating the complicated regulatory environment, which tends to cause bureaucratic delays in obtaining permits and approvals. Power project approvals involve several government departments, necessitating lengthy documentation and adherence to changing policies. Such regulatory obstacles have the potential to greatly prolong project timelines and costs for investors and EPC contractors. Also, recurrent policy amendments and opaque decision-making make it uncertain for both local and overseas stakeholders. Due to this, firms need to spend more money on legal and administrative procedures, making project implementation time-consuming and costly. Combating these regulatory inefficiencies is key to fast-tracking Vietnam's power infrastructure growth and securing further foreign investment.
Vietnam Power EPC Market Opportunities:
Vietnam's power EPC market is a compelling opportunity fueled by Vietnam's increasing energy requirements, supportive government policies, and rising foreign investments. The shift to renewable energy, especially solar and wind power, presents tremendous opportunities for EPC contractors as Vietnam is set to become carbon neutral by 2050. The incentives of the government, including feed-in tariffs and tax incentives, are drawing both local and foreign players to invest in big-ticket clean energy projects. At the same time, growing LNG infrastructure and gas-to-power projects also give rise to new business opportunities with Vietnam placing itself as the anchor of the Southeast Asian region's energy transformation. Smart grid and digitalization progress also make new opportunities possible for EPC companies to advance the power infrastructure in Vietnam. Rural electrification schemes and small-scale renewable installations, such as rooftop solar and microgrids, are emerging, providing entry points for small businesses and local start-ups. The demand for energy storage options, such as battery systems, is another growth opportunity to improve grid stability and renewable energy integration. In addition, Vietnam's geographical benefits, including robust coastal winds and high solar irradiance, position it as a favourable location for offshore wind and large-scale solar farms.
VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
6.71% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, project sale, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Power Construction Corporation of China, Toyo Engineering Corporation, Siemens Energy, GE Renewable Energy, Samsung C&T Corporation, Marubeni Corporation, and Vietnam Electricity |
Vietnam Power EPC Market Segmentation:
Vietnam Power EPC Market Segmentation: By Type
- Thermal
- Gas
- Renewable
- Nuclear
- Others
Vietnam's power EPC industry is divided into thermal, gas, renewable, nuclear, and other new and emerging energy sources. Thermal power remains a widespread source of energy, even though growing environmental issues are promoting the transition to cleaner and more efficient technologies. Gas-based power generation, especially with the help of LNG imports, is becoming popular as the nation is looking for a transition fuel to get from coal to renewables. Renewables such as solar, wind, and hydropower are seeing growth based on government subsidies and foreign investments. Vietnam put its nuclear energy on hold in 2016 but plans to revive nuclear power for long-term energy security continue to be debated. Other alternative sources such as biomass and waste-to-energy are also surfacing as strong contenders to Vietnam's sustainable energy plan.
Vietnam Power EPC Market Segmentation: By Project Scale
- Large
- Medium
- Small
Vietnam's power projects are categorized by size into large, medium, and small sizes. Large-scale projects like big thermal plants, hydroelectric dams, and offshore wind farms involve huge financial outlays and global cooperation. Medium-scale projects like onshore wind and solar farms are growing fast to meet regional energy needs and grid stability. Small-scale projects like rooftop solar panels and decentralized microgrids are especially useful for rural and far-flung communities, providing access to energy and supporting sustainability. Every project size has an important role to play in meeting Vietnam's long-term energy objectives.
Vietnam Power EPC Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis:
Vietnam's power EPC market geographical segmentation emphasizes differences in energy development between regions. The industrial centres of northern Vietnam, with their available coal-fired and hydroelectric generation, are aiming to incorporate a greater renewable energy supply and improve transmission infrastructure. Central Vietnam, rich in coastal wind and high levels of solar irradiation, is emerging as a renewable energy hotspot with growing investment in wind farms and solar parks. Southern Vietnam, the location of Ho Chi Minh City, the country's economic behemoth, bears the greatest electrical demand and is quickly developing LNG-to-power operations and solar parks to serve industry and commerce energy requirements. Every region's specific energy profile is shaping Vietnam's overall power infrastructure plan. Vietnam's power EPC market will also expand substantially in the period between 2025 and 2030 due to rising energy needs, policies by the government, and investment in cleaner and more efficient power generation equipment.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Vietnam Power EPC Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic hugely affected Vietnam's power EPC market by disrupting supply chains, pushing back project schedules, and impacting workforce availability. Lockdowns and travel bans resulted in shortages of workforce and logistics, leading to delays in the construction of ongoing power projects. The supply of crucial equipment and raw materials, particularly for renewables and LNG facilities, was disrupted by global supply chain bottlenecks. Financial instability during the pandemic period also resulted in conservative investment strategies, delaying new project approvals and finance. Nevertheless, Vietnam's post-pandemic strong economic rebound and government initiatives toward infrastructure development had kept the power sector in high gear. The crisis also sped up digitalisation in energy management and remote monitoring technologies, driving operational efficiency for EPC contractors. While Vietnam moves towards an increasingly resilient and sustainable energy future, pandemic lessons are fueling more emphasis on supply chain diversification, automation, and risk management practices for Vietnam's power EPC industry.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
Vietnam's power EPC industry is experiencing various upcoming trends and developments fueled by the nation's energy diversification, sustainability, and technology drives. The quick growth of renewable energy, such as offshore wind and solar power, is one major trend, with large-scale initiatives enjoying firm government support and foreign investment. The use of smart grid technology and digital energy management solutions is also picking up speed, enhancing grid stability and efficiency. LNG infrastructure development, in the form of new import terminals and gas-fired power plants, is also gaining momentum as Vietnam makes the shift towards cleaner forms of energy. Battery energy storage systems (BES) are also being considered to improve the integration of renewable energy and mitigate intermittency issues. The growing influence of public-private partnerships (PPPs) in developing power infrastructure is also creating increased cooperation between local and foreign players. In addition, developments in hydrogen energy and waste-to-energy initiatives reflect Vietnam's efforts to diversify the power generation mix. With Vietnam progressing toward a 2050 net-zero emissions target, green finance and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) activities are contributing significantly to raising funds for clean energy projects.
Key Players:
- Power Construction Corporation of China
- Toyo Engineering Corporation
- Siemens Energy
- GE Renewable Energy
- Samsung C&T Corporation
- Marubeni Corporation
- Vietnam Electricity
- PetroVietnam Power Construction
Chapter 1. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET – SCOPE & METHODOLOGY
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Sources
1.5. Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2025 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET – COMPETITION SCENARIO
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET - ENTRY SCENARIO
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes Players
4.5.6. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET - LANDSCAPE
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Thermal
6.3 Gas
6.4 Renewable
6.5 Nuclear
6.6 Others
6.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2025-2030
Chapter 7. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET – By Project Scale
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Large
7.3 Medium
7.4 Small
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Project Scale
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Project Scale , 2025-2030
Chapter 8. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET - By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1. North America
8.1.1. By Country
8.1.1.1. U.S.A.
8.1.1.2. Canada
8.1.1.3. Mexico
8.1.2. By Project Scale
8.1.3. By Type
8.1.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2. Europe
8.2.1. By Country
8.2.1.1. U.K.
8.2.1.2. Germany
8.2.1.3. France
8.2.1.4. Italy
8.2.1.5. Spain
8.2.1.6. Rest of Europe
8.2.2. By Type
8.2.3. By Project Scale
8.2.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3. Asia Pacific
8.3.1. By Country
8.3.1.1. China
8.3.1.2. Japan
8.3.1.3. South Korea
8.3.1.4. India
8.3.1.5. Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2. By Type
8.3.3. By Project Scale
8.3.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4. South America
8.4.1. By Country
8.4.1.1. Brazil
8.4.1.2. Argentina
8.4.1.3. Colombia
8.4.1.4. Chile
8.4.1.5. Rest of South America
8.4.2. By Type
8.4.3. By Project Scale
8.4.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5. Middle East & Africa
8.5.1. By Country
8.5.1.1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2. Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3. Qatar
8.5.1.4. Israel
8.5.1.5. South Africa
8.5.1.6. Nigeria
8.5.1.7. Kenya
8.5.1.8. Egypt
8.5.1.8. Rest of MEA
8.5.2. By Type
8.5.3. By Project Scale
8.5.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. VIETNAM POWER EPC MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Packaging Type, Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Power Construction Corporation of China
9.2 Toyo Engineering Corporation
9.3 Siemens Energy
9.4 GE Renewable Energy
9.5 Samsung C&T Corporation
9.6 Marubeni Corporation
9.7 Vietnam Electricity
9.8 PetroVietnam Power Construction
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
3400
3900
4600
Frequently Asked Questions
The Vietnam Power EPC Market was valued at USD 310 million in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 429 million by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.71%.
The Vietnamese government has established several regulations and incentives to upgrade the energy sector and encourage foreign investment
Based on Service Provider, the Vietnam Power EPC Market is segmented into Government-Owned Companies, Private Domestic EPC Contractors, Independent Power Producers & Project Developers, and Equipment & Technology Providers.
The southern region of Vietnam is the most dominant region for the Vietnam Power EPC Market.
Power Construction Corporation of China, Toyo Engineering Corporation, Siemens Energy, GE Renewable Energy, Samsung C&T Corporation, Marubeni Corporation, and Vietnam Electricity are the key players in the Vietnam Power EPC Market.



