Telehealth Market Size (2024 – 2030)
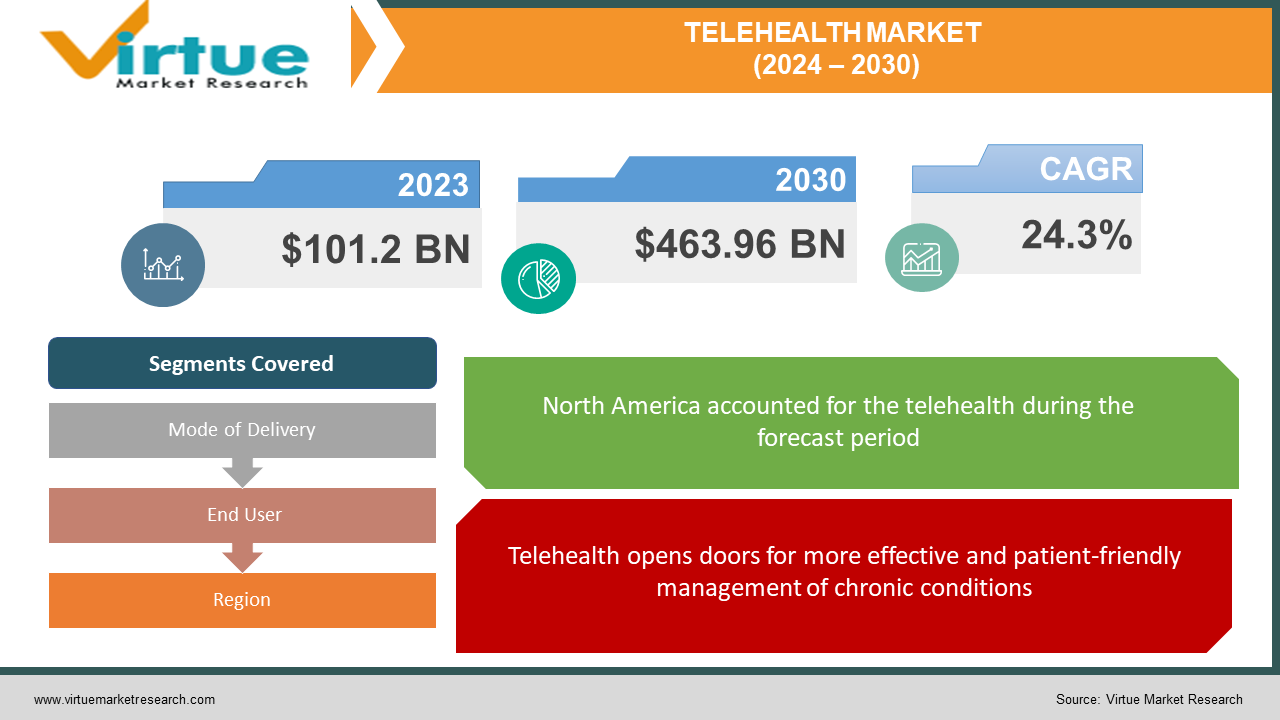
The Telehealth Market was valued at USD 101.2 Billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 463.96 Billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 24.3%.
Telehealth, the use of telecommunications and information technology to provide healthcare services over a distance, has disrupted traditional healthcare delivery models. It offers unparalleled advantages in terms of accessibility, convenience, and cost optimization. From remote consultations to virtual chronic disease management, telehealth's potential extends across the healthcare spectrum. The global telehealth market witnessed remarkable growth, especially fueled by the COVID-19 pandemic where virtual consultations became a necessity. The market was valued at a significant sum in 2023 and is projected to expand at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the coming years. Patients desire more control and convenience. Telehealth offers scheduling flexibility and eliminates travel time and waiting room delays. Telehealth helps manage chronic conditions through remote monitoring and proactive care, improving outcomes and potentially reducing hospitalizations. Telehealth extends the reach of medical care, particularly in rural or underserved areas, bridging gaps in access. Affordable smartphones, wearable devices, and reliable internet connectivity have laid the foundation for seamless telehealth experiences.
Key Market Insights:
The telehealth market experienced a surge fueled by the COVID-19 pandemic, which exposed the need for remote care solutions. This substantial growth is expected to continue in the years to come. Patients and providers alike are increasingly embracing telehealth for its convenience, accessibility, and potential cost savings. Governments are recognizing telehealth's benefits and revising regulations to support its integration into mainstream healthcare. This includes expanded reimbursement coverage and relaxed rules around interstate telehealth practice. Regulatory changes are ongoing, and both providers and technology vendors must stay updated to ensure compliance and capitalize on new opportunities. Telehealth expands access for underserved populations in rural areas, those with mobility issues, and those facing healthcare provider shortages. Remote monitoring tools allow for better management of conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension, potentially reducing complications and hospitalizations. Telehealth lowers the barrier to access for mental health services, providing a more convenient and sometimes less intimidating option for patients. While telehealth initially gained popularity for basic consultations, its applications now extend to specialties like dermatology, radiology, behavioral health, physical therapy, and urgent care. The proliferation of wearables (fitness trackers, smartwatches) and medical-grade devices allow for real-time patient data collection, enhancing virtual care. AI assists in diagnosis, triage, personalized care plans, and even virtual companions, streamlining processes for providers and improving patient experience. Cloud computing facilitates secure data storage, enables real-time communication, and supports scalability in telehealth services.
Telehealth Market Drivers:
Telehealth opens doors for more effective and patient-friendly management of chronic conditions.
The cost of chronic diseases is immense, putting strain on healthcare systems, impacting productivity, and contributing to financial hardship for individuals and families. Chronic diseases are rising rapidly in developing nations, often overwhelming healthcare systems that are ill-equipped to handle the complex, long-term management these diseases demand. The traditional healthcare model, often centered around episodic care and in-person visits, struggles to effectively address the unique challenges posed by chronic disease management. Connected medical devices like blood pressure monitors or wearable glucose sensors transmit patient data directly to healthcare providers. This empowers proactive intervention, preventing potential crises and ensuring better disease control. Effective chronic disease management frequently involves a team of providers – physicians, nurses, nutritionists, physical therapists, etc. Telehealth facilitates convenient virtual consultations with various specialists, streamlining care coordination and helping patients navigate their treatment plans.
Patients increasingly expect the same convenience and personalization they experience in other aspects of their lives in their healthcare interactions.
Consumers have easy access to health information online, fostering a desire for a more informed and collaborative approach to healthcare decisions. Busy lifestyles and long commutes make traditional in-person appointments challenging. Patients crave flexible scheduling options and convenient access to care. Rising healthcare costs make affordability a major concern. Patients value solutions that offer quality care without sacrificing financial well-being. Certain telehealth solutions offer access to basic consultations or nurse hotlines 24/7, addressing concerns and potentially avoiding unnecessary emergency room visits. Telehealth platforms can often provide upfront pricing estimates for consultations, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare expenditures. Telehealth platforms can facilitate secure communication channels with healthcare providers, allowing for asynchronous communication and personalized guidance. Robust safeguards are essential to ensure the privacy and security of sensitive patient data transmitted over virtual platforms. The rise of telehealth isn't just about technology; it's about empowering patients and ensuring that quality healthcare is accessible to all.
Telehealth Market Restraints and Challenges:
Adapting to regulatory changes demands flexibility from providers and telehealth platforms. The lack of consistent policies across regions could hinder seamless cross-border telehealth practices.
Limited access to broadband internet, especially in rural and low-income communities, creates a barrier to telehealth adoption for a significant segment of the population. Many individuals may not have access to suitable smartphones, computers, or webcams necessary for telehealth consultations. Varying levels of comfort with technology, particularly among older adults, can impede their ability to confidently use telehealth platforms and devices. Reimbursement models for telehealth services by both private and public insurers vary widely. This inconsistency introduces complexity and financial risks for providers. Certain types of telehealth consultations may not be eligible for reimbursement, restricting the range of service offerings via telehealth. Some states or payers may place limitations on telehealth reimbursement based on the patient's location or place limitations on providers who practice across state lines. Reimbursement challenges can disincentivize providers from adopting telehealth services, hinder sustainability for telehealth platforms, and limit access for patients, particularly those in areas with less robust coverage. Technological limitations impede a seamless telehealth experience, introduce data vulnerabilities, and may hinder integration with broader healthcare systems. Some healthcare providers may be reluctant to shift established workflows or invest time in learning new technology for telehealth implementation. Certain medical examinations and procedures intrinsically require a hands-on physical examination by a healthcare provider, limiting the scope of issues that telehealth can fully address. Telehealth may make it harder to pick up subtle clinical cues a provider might observe during an in-person visit, potentially impacting diagnostic accuracy in certain cases.
Telehealth Market Opportunities:
Telehealth is progressively moving beyond basic urgent care consultations. We're seeing early-stage success in virtual emergency triage, remote post-surgical monitoring, and some forms of tele-hospitalist programs. Specialists in fields like dermatology, cardiology, neurology, and even some surgical consults are increasingly integrating telehealth into their practice. This expands access for patients seeking specialized care who face geographic or mobility challenges. The success of telehealth for mental health consultations has opened doors for wider access to therapy, virtual support groups, and even management of chronic mental health conditions. This expansion into various specialties addresses the shortage of healthcare access in underserved areas, improves care coordination, and offers more comprehensive services for patients with complex conditions. The future of telehealth likely lies in seamless integration with in-person care. Patients may have initial consultations virtually, with necessary follow-ups, testing, or procedures done in person. Hybrid models leverage the best of both virtual and in-person care, optimizing healthcare delivery while retaining the essential elements of the in-person doctor-patient interaction. AI-powered platforms analyzing this telehealth-generated data could enable early detection of worsening conditions, timely interventions, and even predict potential health risks.
TELEHEALTH MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
24.3% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Mode of Delivery, End User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Teladoc Health, Amwell (American Well), Doctor on Demand, MDLive, Doximity, Talkspace, BetterHelp, CVS Health, Walgreens |
Telehealth Market Segmentation: By Mode of Delivery
-
Web-based telehealth
-
Mobile App-Based Telehealth
-
Telephone-Based Telehealth
Web-based telehealth holds a substantial market share, potentially around 40-50%. It is accessed through secure websites or online portals via computers, tablets, or smartphones. Mobile apps represent a rapidly growing segment, potentially capturing around 30-40% of the market. It emphasizes portability, and convenience, and may feature integrated health tracking or appointment scheduling tools. Telephone-based telehealth holds a smaller share (perhaps 10-20%), but it remains relevant, especially for addressing technology access limitations. Particularly useful for basic follow-ups, mental health support, or situations where video may not be essential. Mobile app-based telehealth is the segment experiencing the most explosive growth. Smartphones are increasingly prevalent across demographics, making access to telehealth extremely convenient. Apps often prioritize intuitive design and ease of navigation, enhancing patient experience.
Telehealth Market Segmentation: By End User
-
Providers (Hospitals and Healthcare Systems, Individual Practitioners & Clinics, Other Healthcare Facilities)
-
Consumers
-
Payers (Private Health Insurers, Government Programs)
-
Employers (Large Corporations, Small and Medium-Sized Businesses)
Hospitals and Healthcare Systems: Utilizing telehealth to expand service offerings, reach patients in underserved areas, and enhance care coordination. This may include virtual urgent care, specialist consultations, and post-discharge follow-up. Individual Practitioners & Clinics: Doctors and specialists in private practices adopting telehealth to offer convenient consultations, manage chronic conditions, and improve patient engagement. Other Healthcare Facilities: Skilled nursing facilities, long-term care, and rehabilitation centers leveraging telehealth for remote consultations with specialists, medication management, and resident monitoring. Individuals seeking Convenience: People seeking accessible care for non-emergency conditions, prescription refills, or general health consultations outside of traditional in-person appointments. Those with Limited Mobility: Patients with disabilities, chronic conditions limiting travel, or those living in geographically remote areas rely on telehealth for essential healthcare access. Mental Health Support Seekers: Telehealth eliminates some barriers and stigma around seeking therapy and mental health consultations. Private Health Insurers: Major insurers are increasingly incorporating telehealth coverage and reimbursement policies to varying degrees, influencing market growth. Government Programs: Medicare, Medicaid, and other public healthcare programs in many countries have evolving policies on telehealth reimbursement, which plays a crucial role in accessibility and adoption rates. Large Corporations: Many large businesses offer telehealth as an employee benefit to improve access to care, potentially reduce absenteeism, and contribute to a sense of overall employee well-being. Small and Medium-Sized Businesses: Partnering with dedicated telehealth platforms offers a wider range of healthcare options to employees in smaller companies.
Telehealth Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America often commands around 60-70% of the global telehealth market. Widespread technology adoption, an aging population, favorable reimbursement policies in some areas, and a strong presence of telehealth providers. Europe typically holds around 15-20% of the global market share. Aging demographics, government initiatives in some countries to promote telehealth, and a focus on improving healthcare access in less populated areas. APAC's share can range from 10-15%, though it's on a strong growth trajectory due to large populations with varying levels of healthcare access across the region. Rising mobile device usage and improving connectivity. Latin America holds around 5% of the global market. Growing adoption with a focus on addressing healthcare access in remote or underserved regions. The Asia Pacific (APAC) region holds massive potential for rapid telehealth growth fueled by large populations, particularly in countries like China and India, that have unmet healthcare needs that telehealth could partially address. Telehealth bridges gaps in rural areas with limited access to specialized care. Several countries within APAC have proactive policies and programs promoting telehealth development.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Telehealth Market:
With social distancing measures in place and concerns around in-person contact, patients readily embraced telehealth consultations to access necessary healthcare services. Telehealth alleviated the strain on overwhelmed hospitals and clinics by enabling remote consultations and follow-ups, freeing up resources for critical care needs. Telehealth ensured continuity of care for patients with chronic conditions who could receive virtual check-ins and medication management without risking exposure to the virus. Governments and insurance companies loosened restrictions on telehealth reimbursements, making virtual consultations financially viable for both providers and patients. The scope of services covered by telehealth broadened, enabling virtual consultations for a wider range of health concerns beyond initial triage or urgent care. Some regulations regarding where providers could practice telehealth were temporarily relaxed, improving access for patients in underserved areas. Security and privacy concerns are amplified with the rise in virtual consultations. This led to a focus on developing secure platforms and strong data encryption protocols. The pandemic highlighted the value of remote patient monitoring (RPM) for chronic condition management. Integration between telehealth platforms and RPM devices became a priority.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
AI-driven chatbots and symptom checkers collect patient information and offer preliminary assessment, helping route them to suitable care or providing self-care guidance. AI is being used in specialties like radiology and dermatology to analyze medical images for diagnosis, improving efficiency and potentially enhancing diagnostic accuracy. AI-powered companions offer mental health support, reminders, and personalized guidance to promote medication adherence and healthy behaviors. The rise of connected medical devices, wearables, and in-home testing kits empowers remote monitoring of vital signs and lab results at home. Wearables, remote monitoring devices, and telehealth interactions generate a massive amount of patient health data. Personalized virtual coaching, educational resources, and real-time feedback loops promote adherence and empower patients to take ownership of their health. From AI-powered self-help apps to virtual reality exposure therapy and online peer support groups, telehealth opens new avenues for mental health care delivery.
Key Players:
-
Teladoc Health
-
Amwell (American Well)
-
Doctor on Demand
-
MDLive
-
Doximity
-
Talkspace
-
BetterHelp
-
CVS Health
-
Walgreens
Chapter 1. TELEHEALTH MARKET – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. TELEHEALTH MARKET – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. TELEHEALTH MARKET – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. TELEHEALTH MARKET - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. TELEHEALTH MARKET – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. TELEHEALTH MARKET – By Mode of Delivery
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Web-based telehealth
6.3 Mobile App-Based Telehealth
6.4 Telephone-Based Telehealth
6.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Mode of Delivery
6.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Mode of Delivery , 2024-2030
Chapter 7. TELEHEALTH MARKET – By End User
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Providers (Hospitals and Healthcare Systems, Individual Practitioners & Clinics, Other Healthcare Facilities)
7.3 Consumers
7.4 Payers (Private Health Insurers, Government Programs)
7.5 Employers (Large Corporations, Small and Medium-Sized Businesses)
7.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End User
7.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End User , 2024-2030
Chapter 8. TELEHEALTH MARKET , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.1.3 By End User
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.2.3 By End User
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.3.3 By End User
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.4.3 By End User
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Mode of Delivery
8.5.3 By End User
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. TELEHEALTH MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Teladoc Health
9.2 Amwell (American Well)
9.3 Doctor on Demand
9.4 MDLive
9.5 Doximity
9.6 Talkspace
9.7 BetterHelp
9.8 CVS Health
9.9 Walgreens
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The growing prevalence of chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses puts ongoing strain on traditional healthcare systems. Telehealth enables convenient remote monitoring, medication adjustments, and proactive interventions, reducing complications and potentially preventing hospitalizations.
Limited access to broadband internet, reliable devices, and digital literacy skills in certain populations perpetuates healthcare disparities.
Teladoc Health, Amwell (American Well), Doctor on Demand, MDLive.
North America currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 60%.
The Asia Pacific exhibits the fastest growth, driven by its increasing population, and expanding economy.



