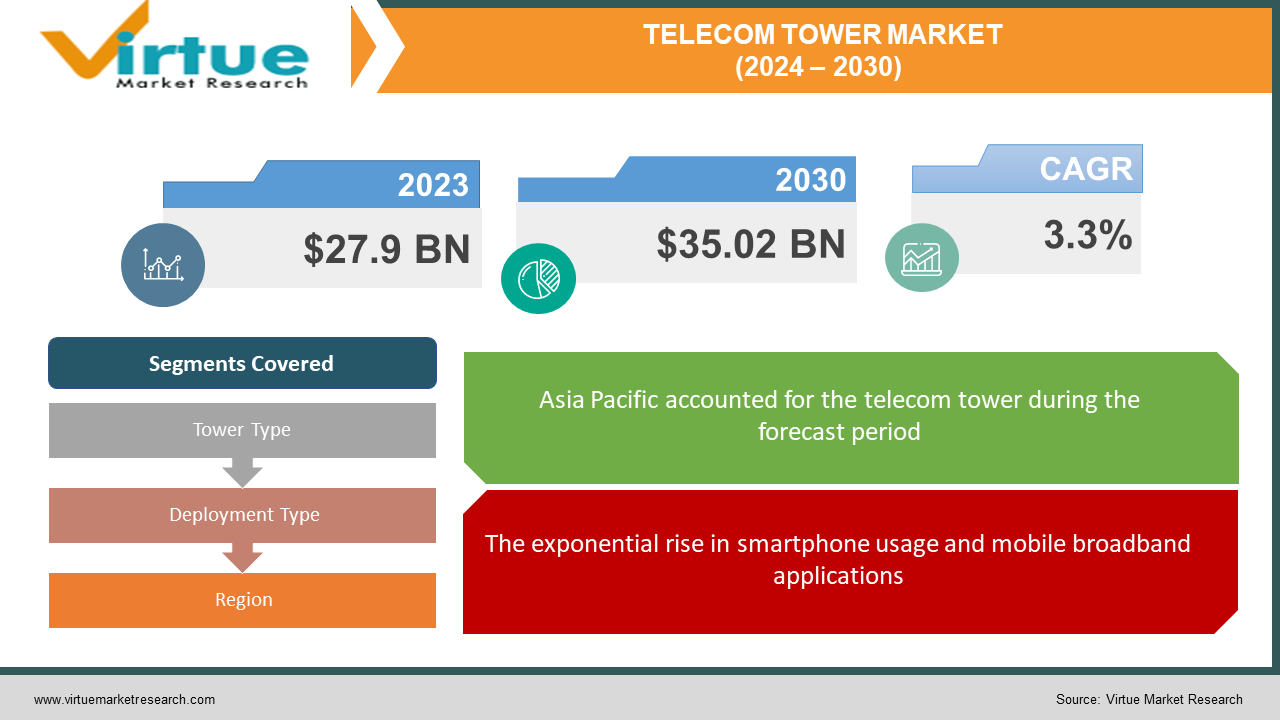
Telecom Tower Market Size (2024 – 2030)
The global telecom tower market was valued at USD 27.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 35.02 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024–2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.3%.
Tower-sharing is becoming more common since it improves network coverage while saving operators money. There is a growing need for small cell towers, which provide coverage in densely populated metropolitan areas. The proliferation of mobile networks, especially with the adoption of 5G technology, is driving up demand for additional telecom towers. Because 5G has reduced latency and greater data rates, it requires a denser network of towers and small cells to function at its best. Developing countries and regions with increasing cell penetration rates are the main drivers of the need for new telecom towers. As more people gain access to mobile phones and internet services, telecom carriers make investments in network infrastructure to meet the increasing demand. Telecom operators often enter into agreements for the pooling of infrastructure to reduce costs and boost efficiency. Because multiple operators are sharing a single tower, this may lead to increased power consumption. Laws and regulations from the government have a major role in shaping the telecom tower market. Now and then, governments offer incentives to encourage the construction of telecom infrastructure to boost economic development and connectivity. The rise of smart cities and the growing Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem are contributing factors to the need for improved connections. Telecom towers are crucial for supporting the infrastructure needed for Internet of Things devices and smart city applications.
Key Market Insights:
More network capacity and coverage are required due to the growing use of smartphones and mobile broadband. As a result, more cell towers are being installed, and those that already exist are being upgraded. Compared to earlier mobile technology generations, the deployment of 5G networks necessitates a denser tower network. This is because 5G uses higher frequencies that have a shorter range. The need for mobile services is growing as more individuals relocate to urban areas. Telecom companies are under pressure because of this to grow their networks in cities. By giving rural areas mobile access, governments and telecoms are putting more and more effort into closing the digital divide. The market for telecom towers is seeing new chances as a result. Small cells can be used to offer coverage in places where standard towers are impractical since they are low-power, short-range base stations. In places impacted by natural catastrophes or other occurrences, drones are also utilized to temporarily blanket the area. One of the biggest energy consumers is telecom towers. Operators are investing more in energy-efficient technologies like solar panels and LED lighting as a means of lowering their operational costs and environmental effects.
Telecom Tower Market Drivers:
The exponential rise in smartphone usage and mobile broadband applications.
The surge in mobile data usage driven by the growing adoption of smartphones, increasing internet penetration, and the rise of bandwidth-intensive applications is a significant driver for the telecom tower market. With the proliferation of mobile devices and the demand for high-speed data services, telecom operators need to expand and upgrade their network infrastructure to handle the escalating data traffic. The exponential rise in usage of mobile broadband applications, from streaming video to online gaming, creates a critical need for robust network infrastructure. This translates to increased deployment of new towers and upgrading existing ones to handle higher data volumes and faster speeds. This driver fuels the demand for more telecom towers and advanced technologies like 4G and 5G to enhance network capacity and coverage. Telecom companies are compelled to invest in the deployment of additional towers and the upgrading of existing ones to meet the increasing data demands of consumers and businesses. The rise of bandwidth-intensive applications and content such as high-definition video streaming, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and large file downloads significantly contributes to the increase in mobile data traffic. Users now expect seamless and high-quality experiences, putting pressure on telecom operators to enhance their networks to meet these demands. Telecom companies are investing in advanced technologies like 4G and 5G to provide higher data speeds and lower latency. These technologies require a denser network infrastructure, including more telecom towers, to deliver the necessary bandwidth and support the performance requirements of modern applications. As a result, the demand for telecom towers is fueled by the need to accommodate these bandwidth-intensive applications. The shift towards remote work, online education, and digital lifestyles has become more pronounced, especially in recent times. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work and digital communication tools, leading to a significant increase in mobile data usage for virtual meetings, cloud-based collaboration, and online activities. The changing work and lifestyle patterns have created a sustained demand for robust and reliable mobile connectivity. Telecom operators are under pressure to optimize and expand their networks to ensure seamless connectivity for remote workers and individuals engaging in digital activities. This translates into a need for additional telecom towers to improve coverage, capacity, and network reliability, driving growth in the telecom tower market.
A denser network of towers is required for greater coverage and optimal performance with the coming of 5G, which has higher frequencies and a shorter range.
The telecom tower market is being driven in large part by the global rollout of 5G networks. 5G offers far faster data rates, reduced latency, and more connectivity for a variety of uses, such as smart cities, driverless cars, and the Internet of Things (IoT). To provide the required coverage and performance, 5G deployment calls for a denser network architecture with additional towers, including small-cell installations. To build a dense and connected network, the introduction of 5G networks is creating a huge need for telecom towers, particularly small cells and macrocells. By supplying the required infrastructure, telecom tower firms are actively supporting the 5G rollout and fostering the expansion of the telecom tower market. In contrast to earlier iterations, 5G networks necessitate a network architecture that is more densely dispersed to provide the high speeds and low latency that are promised. To supplement conventional macro cells, mini cells are being deployed in residential neighborhoods, busy intersections, and urban regions. The installation of small cells—which are frequently seen on buildings, utility poles, and streetlights—is essential to expanding the capacity and coverage of 5G networks. The need for telecom towers rises as 5G networks get denser with the installation of macro and small cells. The infrastructure required for small cell installations is provided by telecom tower firms, which helps enable the wider adoption of 5G technology. The huge connectivity demands of the Internet of Things (IoT) are supported by 5G networks, which also make Industry 4.0 technologies possible to deploy. A strong and large-capacity network infrastructure is needed to meet the connectivity requirements of a variety of IoT devices, sensors, and machines. Due to this, 5G networks are being deployed, which in turn is fueling the need for telecom towers to provide the requisite infrastructure. Infrastructure for telecom towers will see more investment as 5G networks are deployed to serve Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things applications. 5G networks' scalability and dependability make them ideal for linking many devices across numerous industries, which supports the market's general expansion for telecom towers.
The fusion of technological advancements and cost optimization strategies is revolutionizing the telecom tower market.
AI-powered solutions are transforming tower management. Predictive maintenance algorithms anticipate potential issues, preventing failures and reducing downtime. Real-time monitoring allows remote diagnosis and repair, minimizing manual inspections and travel costs. AI-driven resource optimization tools manage power consumption and network loads, leading to improved energy efficiency and lower operating expenses. Software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) are virtualizing network functions, enabling flexible and scalable networks. This reduces reliance on physical hardware, simplifies infrastructure upgrades, and lowers equipment costs. Additionally, it allows telcos to offer customized services and optimize network performance based on real-time demand. Minimal base stations and aerial platforms provide targeted coverage in areas with limited infrastructure or high user density. This eliminates the need for new towers in specific locations, reducing deployment costs and offering rapid temporary coverage for events or emergencies. Lighter and stronger materials are being used in tower construction, making them more resistant to extreme weather and reducing repair needs. Advancements in tower design are optimizing wind resistance and heat dissipation, further impacting maintenance costs. Sharing tower infrastructure among multiple operators reduces the number of towers needed, minimizing construction costs and environmental impact. This collaborative approach also simplifies permitting processes and streamlines maintenance, benefiting all stakeholders. Implementing energy-saving technologies like solar panels and LED lighting significantly reduces energy consumption and associated costs. Additionally, smart power management systems optimize energy usage based on network traffic and weather conditions, further maximizing savings. Automating mundane tasks like inventory management, site surveys, and reporting through digital platforms improves efficiency and reduces manpower requirements. This translates to lower operational costs and faster turnaround times for various processes. By adopting AI-powered predictive maintenance solutions, telcos can anticipate equipment failures and schedule preventative repairs before breakdowns occur. This minimizes downtime, avoids costly emergency repairs, and extends the lifespan of equipment, leading to significant cost savings.
Telecom Tower Market Restraints and Challenges:
Stringent regulations and permitting processes are causing delays in tower installation.
One of the significant restraints in the telecom tower market is the complex regulatory landscape and permitting challenges associated with tower deployment. Obtaining permits for tower construction or modification can be a time-consuming and intricate process, involving coordination with local governments, environmental agencies, and community stakeholders. Regulatory hurdles can result in delays and increased costs for tower deployment. Regulatory challenges can hinder the timely rollout of telecom towers, affecting the overall expansion and optimization of network infrastructure. Companies in the telecom tower market may face delays in obtaining necessary approvals, leading to project delays and increased operational costs. Additionally, stringent regulations may limit the locations where towers can be installed, impacting coverage and network efficiency. Community opposition can result in prolonged approval processes or even project cancellations. Telecom tower companies may need to invest additional resources in community engagement efforts, public awareness campaigns, or modifications to tower designs to address aesthetic concerns. NIMBY-related challenges can lead to project delays, increased costs, and limitations on the placement of towers, affecting the overall efficiency of network expansion. Regulatory authorities often require thorough environmental impact assessments (EIAs) before approving the deployment of telecom towers. These assessments evaluate the potential environmental consequences of tower installations, considering factors such as wildlife disruption, habitat destruction, and visual impact. Conducting comprehensive EIAs and obtaining environmental clearances can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. The necessity for environmental assessments adds a layer of complexity to the regulatory process. Telecom tower companies must factor in the time and costs associated with EIAs when planning deployments. Delays in obtaining environmental clearances can hinder project timelines and increase overall project costs. Balancing the need for network expansion with environmental considerations becomes crucial in addressing these regulatory challenges.
Environmental land acquisition and site availability issues are causing losses for the expansion.
Securing suitable land for telecom tower installation can be a significant challenge. The availability of appropriate sites, especially in densely populated urban areas, can be limited due to zoning restrictions, land use conflicts, and community opposition. Additionally, negotiating with landowners for leases or acquiring land can be a complex process, leading to delays in tower deployment. The scarcity of suitable land and challenges in acquiring sites for tower installation can impede the expansion of telecom networks. This constraint may limit the coverage and capacity improvements required to meet the growing demand for mobile services. Telecom tower companies may face increased costs associated with land acquisition, and the scarcity of suitable sites may lead to suboptimal network planning. Acquiring land or securing leases for telecom tower installation involves negotiations with landowners, local communities, and other stakeholders. These negotiations can be complex due to varying landowner expectations, concerns over property values, and the need to address community opposition. Securing agreements that satisfy all parties involved can be time-consuming and may require additional incentives or concessions. Complex land acquisition negotiations can result in project delays and increased costs. Telecom tower companies may need to allocate resources for legal and negotiation experts to navigate through these complexities. Additionally, disputes with landowners or communities can further delay projects, affecting the overall efficiency of network deployment and hindering the growth of the telecom tower market. Zoning regulations and other land-use restrictions imposed by local authorities can limit the placement of telecom towers in certain areas. Some regions may have strict zoning codes that designate specific zones for residential, commercial, or industrial use, restricting the placement of towers in residential neighborhoods or other sensitive areas. Compliance with these regulations requires careful planning and coordination with regulatory bodies. Zoning and regulatory restrictions can constrain the flexibility of tower placement and limit the overall coverage and capacity of the network. Telecom tower companies may face challenges in obtaining necessary approvals for tower installations in areas crucial for network optimization. Overcoming these restrictions requires strategic planning, collaboration with regulatory authorities, and sometimes advocating for changes in local zoning policies.
Technological and infrastructure challenges in the telecom tower market are creating barriers.
The deployment of advanced technologies, such as 5G, poses technical challenges in terms of infrastructure and compatibility. Upgrading existing towers to accommodate new technologies or deploying small cells for 5G networks requires substantial investment and technical expertise. Additionally, the need for fiber connectivity to support high-speed and low-latency services can pose challenges, especially in regions with limited fiber optic infrastructure. Technological challenges can slow down the pace of network upgrades and the implementation of advanced services. Telecom tower companies may face increased capital expenditures to modernize their infrastructure, and the lack of seamless technology integration may impact the overall efficiency and performance of the telecom network. These challenges can lead to a more gradual adoption of new technologies in certain markets. The success of advanced technologies like 5G is closely tied to robust and high-capacity fiber optic connectivity. However, in certain regions, the availability of fiber-optic infrastructure may be limited. Connecting telecom towers with fiber optic cables is essential for delivering the high-speed and low-latency services promised by technologies like 5G. Overcoming challenges related to laying fiber optic cables, obtaining right-of-way permissions, and addressing last-mile connectivity issues can be complex. Inadequate fiber connectivity can hinder the full realization of the potential benefits of advanced technologies. Telecom tower companies may face delays in the deployment of 5G networks or experience suboptimal performance due to limitations in backhaul connectivity. Investment in expanding fiber optic infrastructure becomes crucial to overcoming this challenge and ensuring the seamless integration of advanced technologies. The telecom industry often faces challenges related to interoperability and standardization, especially when integrating diverse technologies and equipment from different vendors. Ensuring seamless communication between various network elements, protocols, and hardware can be a complex task. Lack of standardized practices may result in compatibility issues, leading to operational inefficiencies, network disruptions, and increased complexity in managing telecom tower infrastructure. Interoperability challenges can hinder the smooth integration of new technologies and equipment, impacting the overall performance and reliability of the telecom network. Telecom tower companies may need to invest in solutions that promote interoperability and adhere to industry standards. Standardization efforts become crucial for creating a cohesive and efficient telecom tower ecosystem.
Global Telecom Tower Market Opportunities:
The global 5G rollout necessitates a denser network of towers, unlocking significant growth opportunities for infrastructure providers. Tower companies can capitalize on this by expanding their reach, offering innovative tower solutions, and collaborating with operators for efficient network deployment. Emerging technologies offer targeted coverage solutions in high-traffic areas or remote locations. Tower companies can invest in deploying and managing small cell networks or partner with drone operators for temporary coverage, diversify their service portfolio, and cater to niche needs. Integrating AI-powered predictive maintenance and network optimization can significantly reduce operational costs and downtime for tower companies. Additionally, automating routine tasks like site monitoring and reporting can improve efficiency and free up resources for innovation. Bridging the digital divide by providing coverage in underserved rural areas holds immense potential. Tower companies can partner with governments and telcos to implement cost-effective solutions like co-location or small cells, contributing to social good and expanding their market reach. Rapidly developing economies present untapped potential for tower infrastructure deployment. Companies entering these markets early can establish a strong foothold and benefit from the burgeoning demand for mobile connectivity. Collaborating with multiple operators on tower-sharing agreements can optimize infrastructure utilization, reduce construction costs, and create win-win scenarios for all parties involved. Investing in energy-efficient towers, utilizing solar panels and wind power, and adopting green construction practices can attract environmentally conscious investors and customers. This focus on sustainability aligns with global climate goals and creates a positive brand image. Partnering with governments and educational institutions to provide digital literacy training and upskilling programs in rural areas can bridge the digital divide and empower communities. This aligns with social responsibility goals and benefits the company's image.
TELECOM TOWER MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
3.3% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Tower Type, Deployment Type, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
American Tower Corporation, AT&T Inc, Bharti Infratel Limited, China Tower Corporation, Crown Castle International Corporation, GTL Infrastructure Ltd, Helios Tower Africa, SBA Communications Corporation, T-Mobile Tower, Viom Networks, Verizon Networks |
Telecom Tower Market Segmentation: By Tower Type
-
Lattice Towers
-
Guyed Towers
-
Monopole Towers
-
Stealth Towers
Lattice Towers dominates globally, holding around 45% of the market share. Their affordability, reliability, and suitability for high-capacity networks make them the go-to choice for rural areas and initial network deployments. Lattice towers currently reign supreme as the most dominant tower type due to their widespread applicability, as they work well in diverse terrains and network settings, they're relatively cheaper to build and maintain compared to other types, and they can accommodate various antenna configurations and network capacities. Guyed Towers capture roughly 20% of the market. Their cost-effectiveness and impressive wind resistance make them ideal for remote locations and areas with strong winds. Monopole towers are the fastest-growing segment, driven by rising populations and data demand in cities, which translates to an increased need for space-efficient towers. Their sleek design blends well with urban landscapes, minimizing visual clutter, simplifying cable management and antenna mounting, and streamlining network integration. Monopole towers comprise approximately 15% of the market. Their sleek design and space-saving features make them popular in urban areas, allowing for easier integration with existing infrastructure.
Telecom Tower Market Segmentation: by Deployment Type
-
Ground-based towers
-
Greenfield towers
-
Rooftop towers
Ground-based towers lead the pack with approximately 65% of the market share in 2023. Their flexibility in location and height caters to diverse coverage needs across rural, urban, and remote areas. Ground-based towers currently dominate the market due to their versatility, as they can be built almost anywhere, offering flexibility in network planning and coverage reach; they easily accommodate additional antennas and equipment as network capacity demands increase; and they provide a stable and reliable base for tower infrastructure, especially in challenging weather conditions. Greenfield towers hold around 25% of the market. Establishing towers in new locations is crucial for initial network deployment and expanding coverage in underserved areas. Rooftop towers are the fastest-growing segment, driven by increasing demand for mobile coverage in densely populated areas, making rooftop installations a space-saving option. Sharing existing infrastructure reduces construction costs compared to building new towers. Rooftop towers minimize visual clutter compared to ground-based structures in urban landscapes. Rooftop towers utilizing existing infrastructure in urban areas provide space-efficient coverage solutions and reduce visual impact.
Telecom Tower Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
Asia-Pacific holds the crown with a dominant 35% market share in 2023, fueled by rapid urbanization, booming mobile data demand, and government infrastructure initiatives in countries like China and India. North America captures roughly 25% of the market and is the fastest-growing region. Mature networks and a focus on 5G upgrades drive demand for tower infrastructure in this region. The success of this area is spurred by increasing smartphone adoption and mobile internet accessibility, driving infrastructure expansion, stable economies, and increasing investments in technology to create a favorable environment for tower companies, governments, and operators to collaborate to extend coverage to underserved rural areas, boosting market growth. Europe comprises approximately 30% of the market, with diverse regulatory environments and a mix of mature and developing areas influencing tower deployment strategies. South America holds around 5% of the market, experiencing significant growth with increasing mobile penetration and infrastructure investments in countries like Brazil and Mexico. The Middle East and Africa represent the smallest share at around 5% but boast high potential for future growth due to rapidly developing economies and increasing mobile adoption.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Telecom Tower Market.
The COVID-19 pandemic undeniably shaped the landscape of the telecom tower market, both in the short term and with lasting implications. Lockdowns and supply chain disruptions hampered tower construction and equipment deliveries, causing delays in deployment projects. Economic slowdowns and lockdowns impacted mobile data usage in certain sectors, leading to temporary dips in demand for tower infrastructure expansion. Operators prioritized network maintenance and upgrades over new deployments, focusing on ensuring existing infrastructure could handle the surge in mobile data traffic. The pandemic highlighted the vital role of strong connectivity, governments, and telcos partnering to accelerate digital infrastructure investments, boosting long-term demand for towers. Remote work, e-commerce, and online education relied heavily on mobile internet, fostering a sustained need for network capacity and coverage expansion. The digital divide became more apparent during the pandemic, prompting government initiatives and partnerships to extend coverage to underserved rural areas, creating new market opportunities. The need for efficient and flexible network solutions encouraged the adoption of technologies like small cells and network virtualization, impacting tower infrastructure design and deployment strategies. The initial slowdown due to the pandemic was eventually countered by the increased reliance on mobile connectivity and long-term digital transformation efforts.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
The rollout of 5G networks continues to be a major trend in the telecom tower market. Telecom operators are actively investing in the deployment of 5G infrastructure, including microcells and small cells, to meet the growing demand for high-speed and low-latency connectivity. Small cells play a crucial role in 5G networks by enhancing coverage and capacity, especially in densely populated urban areas. The trend involves the deployment of small cells on street furniture, utility poles, and buildings to create a more distributed and dense network. Telecom towers are increasingly becoming key components in edge computing networks. Edge computing helps reduce latency by processing data closer to the source, and telecom towers, with their strategic locations, are being leveraged to host edge computing infrastructure. Sustainability is gaining importance in the telecom tower industry. There is a growing focus on adopting environmentally friendly practices, including the use of renewable energy sources, energy-efficient technologies, and eco-friendly tower designs, to reduce the environmental impact of tower operations. Telecom operators are increasingly opting for infrastructure sharing to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Tower companies that specialize in owning, operating, and leasing out telecom towers continue to play a significant role in facilitating this trend. NFV and SDN technologies are being implemented in telecom towers to enhance network flexibility and manageability. This allows for a more dynamic allocation of resources and the introduction of new services without significant hardware changes. There is a growing trend towards the deployment of private 5G networks, especially for industrial and enterprise applications. Telecom towers are used to provide dedicated and secure connectivity for businesses looking to deploy their networks.
Key Players:
-
American Tower Corporation,
-
AT&T Inc
-
Bharti Infratel Limited
-
China Tower Corporation
-
Crown Castle International Corporation
-
GTL Infrastructure Ltd
-
Helios Tower Africa
-
SBA Communications Corporation
-
T-Mobile Tower
-
Viom Networks
-
Verizon Networks
Chapter 1. Telecom Tower Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Telecom Tower Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Telecom Tower Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Telecom Tower Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Telecom Tower Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Telecom Tower Market – By Tower Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Lattice Towers
6.3 Guyed Towers
6.4 Monopole Towers
6.5 Stealth Towers
6.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Tower Type
6.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Tower Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Telecom Tower Market – By Deployment Type
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Ground-based towers
7.3 Greenfield towers
7.4 Rooftop towers
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Deployment Type
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Deployment Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Telecom Tower Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By By Tower Type
8.1.3 By Deployment Type
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By By Tower Type
8.2.3 By Deployment Type
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By By Tower Type
8.3.3 By Deployment Type
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By By Tower Type
8.4.3 By Deployment Type
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Type
8.5.3 By Deployment Type
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Telecom Tower Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 American Tower Corporation,
9.2 AT&T Inc
9.3 Bharti Infratel Limited
9.4 China Tower Corporation
9.5 Crown Castle International Corporation
9.6 GTL Infrastructure Ltd
9.7 Helios Tower Africa
9.8 SBA Communications Corporation
9.9 T-Mobile Tower
9.10 Viom Networks
9.11 Verizon Networks
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The telecom tower market was valued at USD 27.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 35.02 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024–2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.3%.
Rising disposable incomes and increased urbanization, technology-driven personalization, increasing mobile data traffic, the rollout of 5G networks, and rural and remote connectivity initiatives are the main drivers in this market.
Asia-Pacific is the most dominant region.
North America holds the title of the fastest-growing region.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning, 5G rollout, small cells and drones, green tower initiatives, tower sharing, and colocation, a focus on rural connectivity, and public-private partnerships are the potential future trends.



