Robotic Weeder Market Size (2024 – 2030)
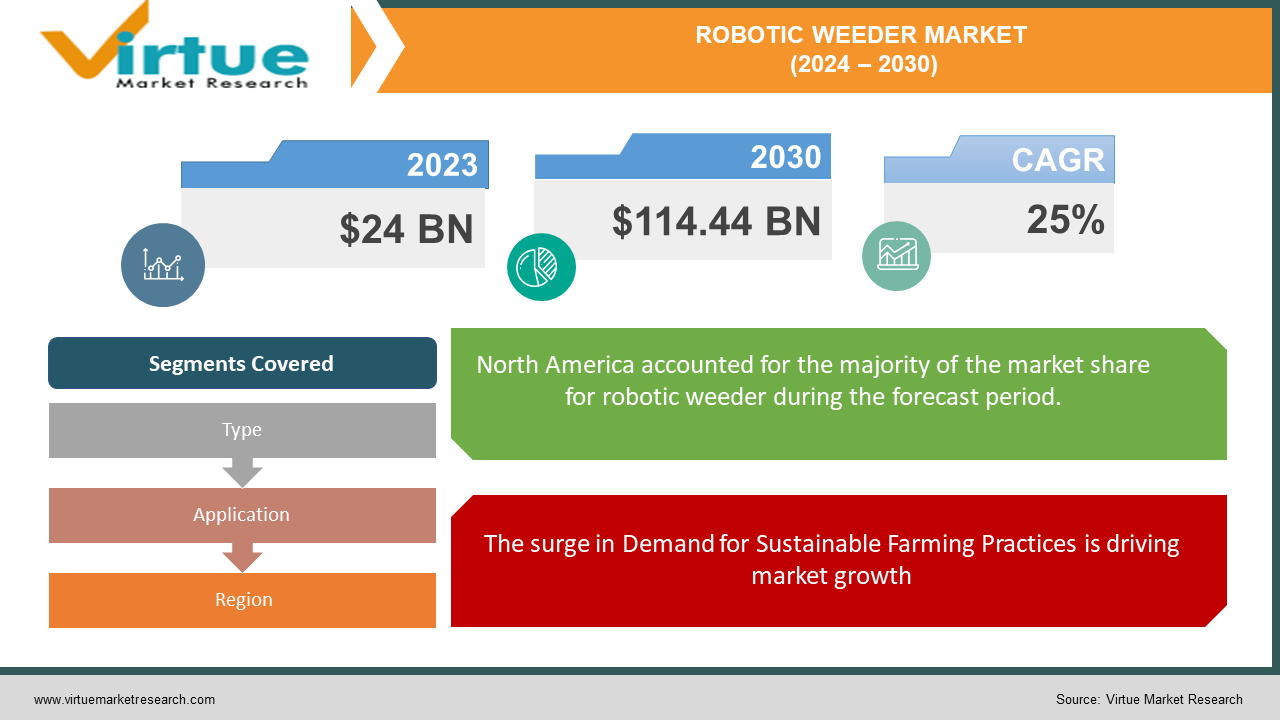
The Global Robotic Weeder Market was valued at USD 24 billion in 2023 and will grow at a CAGR of 25% from 2024 to 2030. The market is expected to reach USD 114.44 billion by 2030.
The Robotic Weeder Market is a rapidly growing sector of agricultural technology focused on developing and selling autonomous robots that eliminate weeds in fields. These high-tech machines use cameras, sensors, and AI to identify and target weeds while avoiding damage to crops. This market is driven by the need for sustainable weed control, reduced reliance on manual labor, and increased efficiency in farming, with a projected value reaching tens of billions of dollars by 2030.
Key Market Insights:
Growing demand for eco-friendly weed control methods that minimize herbicide use and environmental impact. The scarcity of agricultural labor fuels the need for automation solutions like robotic weeders.
Robotic weeders offer precise and efficient weed removal, potentially increasing crop yields. Automatic robots are expected to hold the dominant market share due to their fully autonomous operation.
Grain crops currently lead the application segment, but the market for specialty crops is anticipated to grow significantly.
High upfront investment required for purchasing and maintaining robotic weeders can be a barrier for some farmers. Continuous development is needed to improve weed identification accuracy and ensure robots can navigate diverse field conditions.
Global Robotic Weeder Market Drivers:
The surge in Demand for Sustainable Farming Practices is driving market growth:
The growing consumer demand for sustainable agriculture practices is a major driving force behind the robotic weeder market. Traditional herbicide use, while effective, raises environmental concerns. Herbicides can contaminate soil and water sources, disrupt ecosystems, and even lead to the development of herbicide-resistant "superweeds." Robotic weeders offer an attractive alternative. These machines use cameras, sensors, and AI to precisely identify and target weeds, eliminating them mechanically or with minimal herbicide application. This targeted approach minimizes environmental impact and reduces the risk of herbicide resistance. As a result, robotic weeders are increasingly seen as a viable solution for achieving healthy crop yields while adhering to eco-friendly practices. This aligns perfectly with the growing public interest in sustainable food production, creating a strong market push for these innovative agricultural robots.
Labor Shortage in Agriculture are driving market growth:
The agricultural industry is grappling with a critical shortage of manual labor. This is due to a confluence of factors, including the physically demanding nature of farm work, often low wages, and the migration of younger generations towards urban opportunities. This scarcity directly impacts a farm's ability to maintain productivity and meet growing food demands. Robotic weeders offer a compelling solution by automating tedious and labor-intensive tasks like weed removal. These high-tech machines can navigate fields autonomously, utilizing image recognition and targeted tools to eliminate weeds with precision. By automating this process, robotic weeders significantly reduce the reliance on manual labor, freeing up human workers for more specialized activities. This could involve tasks requiring human judgment and dexterity, such as crop monitoring, plant maintenance, or even operating the robotic weeders themselves. Essentially, robotic weeders act as a force multiplier, allowing existing farm workforces to manage larger areas and optimize their time. This not only addresses the labor shortage but also opens doors for increased efficiency and productivity in the agricultural sector.
Focus on Precision and Efficiency are driving market growth:
Traditional weed control methods often involve a trade-off between effectiveness and precision. Broad-spectrum herbicides, for example, can be efficient at eliminating weeds but can also harm desired crops and pollute the environment. Manual weeding, while targeted, is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Robotic weeders offer a game-changer by leveraging technology for a smarter approach. Equipped with cameras, sensors, and artificial intelligence, these machines can identify weeds with incredible accuracy. Cameras capture detailed visual information, while sensors detect factors like plant height and thermal signatures. AI algorithms then analyze this data to distinguish between crops and weeds. This precise identification allows for targeted removal using mechanical tools or minimal, strategically applied herbicides. This minimizes accidental crop damage and herbicide waste compared to traditional methods. By focusing solely on the unwanted weeds, robotic weeders optimize resource utilization and reduce the environmental footprint. Furthermore, the targeted removal of weeds allows crops to thrive with less competition for water, nutrients, and sunlight. This can potentially lead to increased crop yields, making robotic weeders a win-win for both environmental sustainability and agricultural productivity.
Global Robotic Weeder Market challenges and restraints:
High upfront costs are a significant hurdle for Robotic Weeder:
A major hurdle to the wider adoption of robotic weeders is their cost. These machines are packed with advanced technology like cameras, sensors, and AI systems. This sophistication translates to a hefty price tag, making them a significant financial investment for farmers, especially smaller operations. The upfront cost of purchasing the robot itself can be a barrier, requiring a substantial initial outlay that might not be readily available for all. Additionally, ongoing maintenance adds to the financial burden. Robotic weeders require specialized technicians for repairs and software updates, which can be expensive, especially in remote areas. Furthermore, the cost of spare parts can be high due to the specialized nature of the technology. This financial strain can be particularly challenging for small-scale farmers with limited budgets. To address this challenge, the industry needs to explore solutions like leasing models, government subsidies, or creating more affordable versions of the technology targeted toward smaller farms. Making robotic weeders more financially accessible will be crucial for widespread adoption and maximizing their impact on agricultural productivity.
Technological limitations are throwing a curveball at the Robotic Weeder market:
Even with ongoing advancements, robotic weeders aren't perfect weed warriors just yet. A major hurdle lies in their ability to consistently identify weeds in real-world fields. The sheer variety of weeds throws a curveball at AI systems. Different weed types with unique shapes, sizes, and colors can be mistaken for crops. Early-stage weeds, appearing as tiny sprouts, can be particularly tricky to distinguish from desired crops, especially for machines under development. Even some crops can closely resemble weeds, further confounding the AI. Beyond identification, navigating uneven fields can be physically challenging for the robots. Bumpy terrain, slopes, or unexpected holes can hinder their movement and stability. Similarly, wet soil conditions can cause the robots to lose traction and struggle to maneuver effectively. These limitations restrict the robots' weed-whacking abilities and highlight the need for ongoing development to create more robust and adaptable machines that can handle the diverse conditions of a real farm.
Limited operational range is a growing nightmare for Robotic Weeder:
A current Achilles' heel of robotic weeders is their limited operational range. Unlike their tireless human counterparts, these machines can only operate for a set amount of time before needing a recharge. This significantly impacts their efficiency, especially in vast agricultural fields. Imagine a robotic Sisyphus, perpetually battling weeds but tethered to a charging station like a modern-day mechanical vine. The need for frequent recharging disrupts the workflow and limits the area a single robot can cover in a day. For large fields, this translates to deploying multiple robots or a single robot making numerous return trips to the charging station, wasting valuable time and effort. Another constraint is the tether itself. Some robotic weeders rely on a physical tether to a power source, further restricting their movement and potentially creating entanglement hazards. While promising advancements in battery technology are on the horizon, overcoming this range limitation is crucial for robotic weeders to reach their full potential and become efficient weed-fighting machines for large-scale agriculture.
Market Opportunities:
The Robotic Weeder Market is fertile ground for opportunities that promise to cultivate a more sustainable future for agriculture. Fueled by the demand for eco-friendly food production, these high-tech machines offer a precise alternative to herbicides, minimizing environmental impact and fostering healthier crops. This resonates with a global shift towards sustainable practices, creating a vast market for robotic weeders. They also address the critical labor shortage plaguing agriculture by automating tedious weeding tasks, freeing up human workers for more specialized activities, and boosting farm productivity. Furthermore, robotic weeders leverage AI and advanced sensors to identify weeds with laser focus, eliminating unnecessary damage to crops and optimizing resource utilization. This focus on precision translates to higher crop yields while minimizing environmental impact. Beyond their current capabilities, the future holds promise for even greater versatility. Advancements in navigation and maneuverability will allow these machines to conquer diverse terrains, large fields, and even specialty crop environments. Additionally, research is exploring the integration of robotic weeders with broader agricultural automation systems, paving the way for a future where robots seamlessly collaborate with seeders and harvesters within a larger intelligent farming network. The commitment to sustainability doesn't stop there. The research delves into integrating targeted, low-impact herbicide applications or even natural weed-suppression techniques alongside the robots. In essence, the Robotic Weeder Market is not just about eliminating weeds; it's about cultivating a future where agriculture thrives on innovation, efficiency, and a deep respect for the environment.
ROBOTIC WEEDER MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
25% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Ecorobotix, Naio Technologies, Vision Robotics Corporation, Harvest Automation, Soft Robotics Inc., Abundant Robotics, Bosch Deepfield Robotics, Blue River Technology, Saga Robotics, VitiBot |
Robotic Weeder Market Segmentation - By Type
-
Automatic Robotic Weeders
-
Semi-Automatic Robotic Weeders
In the Robotic Weeder Market, automatic robotic weeders are poised to be the dominant sector. These high-tech machines operate entirely on their own, navigating fields, identifying weeds with cameras and sensors, and eliminating them with AI-powered precision. This eliminates the need for constant human oversight compared to semi-automatic models. While semi-automatic options might be a more affordable entry point, the complete autonomy and efficiency of automatic robotic weeders are expected to win favor in the long run, especially for large-scale farms seeking to maximize productivity and minimize labor costs.
Robotic Weeder Market Segmentation - By Application
-
Grain Crops
-
Orchard Weeders
Grain crops currently hold the leading position in the Robotic Weeder Market application segment. This dominance is driven by the vast, open fields characteristic of grain production (corn, wheat, etc.) These large, uniform areas are perfectly suited for autonomous robotic weeders to navigate efficiently. While orchard weeders offer a promising solution for targeted weed control around trees, their need for maneuverability and more complex weed identification in a non-uniform environment limits their current market share. As robotic weeder technology matures, orchard weeders have the potential to grow significantly, but for now, grain crops reign supreme due to their ideal compatibility with current robotic capabilities.
Robotic Weeder Market Segmentation - Regional Analysis
-
Asia-Pacific
-
North America
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
While data is still emerging, analysts predict that North America is currently the most dominant region in the Robotic Weeder Market. This lead is likely driven by a combination of factors: a strong focus on precision agriculture, a relative abundance of large-scale farms well-suited for these machines, and government support for adopting new technologies. However, Asia, particularly China and Japan, is expected to be a strong competitor in the coming years due to their significant agricultural sectors and growing emphasis on automation.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Robotic Weeder Market
The COVID-19 pandemic presented a mixed bag for the Global Robotic Weeder Market. On the one hand, supply chains faced disruptions due to lockdowns and travel restrictions, leading to shortages of raw materials and components needed for manufacturing robotic weeders. This resulted in production delays and increased costs for some market players. Additionally, the economic downturn caused by the pandemic might have led to decreased investment in new agricultural technologies for some farms. However, the pandemic also highlighted the importance of automation in the agricultural sector. Labor shortages became more acute due to social distancing measures and restrictions on migrant workers. This created a surge in demand for technologies like robotic weeders that could address these labor gaps and maintain agricultural productivity. Furthermore, the growing focus on hygiene and minimizing human contact during the pandemic might have made robotic weeders a more attractive option for some farmers. Overall, the COVID-19 pandemic's impact on the Robotic weed market was multifaceted. While it caused some initial challenges, it also accelerated the need for automation solutions in agriculture, potentially positioning the market for stronger growth in the post-pandemic era.
Latest trends/Developments
The Robotic Weeder Market is experiencing a wave of innovation. AI advancements are leading to more accurate weed identification, while developers focus on creating versatile robots suited for various terrains and crops. Collaboration between robotics and agricultural equipment companies is paving the way for integrated farming systems. The focus on sustainability remains strong, with research exploring eco-friendly weed removal methods beyond just mechanical tools. This points towards a future where robotic weeders become smarter, more adaptable, and part of a larger network of automated, sustainable farming practices.
Key Players:
-
Ecorobotix
-
Naio Technologies
-
Vision Robotics Corporation
-
Harvest Automation
-
Soft Robotics Inc.
-
Abundant Robotics
-
Bosch Deepfield Robotics
-
Blue River Technology
-
Saga Robotics
-
VitiBot
Chapter 1. Robotic Weeder Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Robotic Weeder Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Robotic Weeder Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Robotic Weeder Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Robotic Weeder Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Robotic Weeder Market – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Automatic Robotic Weeders
6.3 Semi-Automatic Robotic Weeders
6.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Robotic Weeder Market – By Application
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Grain Crops
7.3 Orchard Weeders
7.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Application
7.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Application, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Robotic Weeder Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Type
8.1.3 By Application
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Type
8.2.3 By Application
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Type
8.3.3 By Application
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Type
8.4.3 By Application
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Type
8.5.3 By Application
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Robotic Weeder Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Ecorobotix
9.2 Naio Technologies
9.3 Vision Robotics Corporation
9.4 Harvest Automation
9.5 Soft Robotics Inc.
9.6 Abundant Robotics
9.7 Bosch Deepfield Robotics
9.8 Blue River Technology
9.9 Saga Robotics
9.10 VitiBot
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Robotic Weeder Market was valued at USD 24 billion in 2023 and will grow at a CAGR of 25% from 2024 to 2030. The market is expected to reach USD 114.44 billion by 2030.
A surge in Demand for Sustainable Farming Practices, Labor Shortage in Agriculture, and Focus on Precision and Efficiency are the reasons that are driving the market.
Based on Application it is divided into two segments – Grain Crops, Orchard Weeders.
North America is the most dominant region for the luxury vehicle Market.
Ecorobotix, Naio Technologies, Vision Robotics Corporation, Harvest Automation



