Power Market Size (2025-2030)
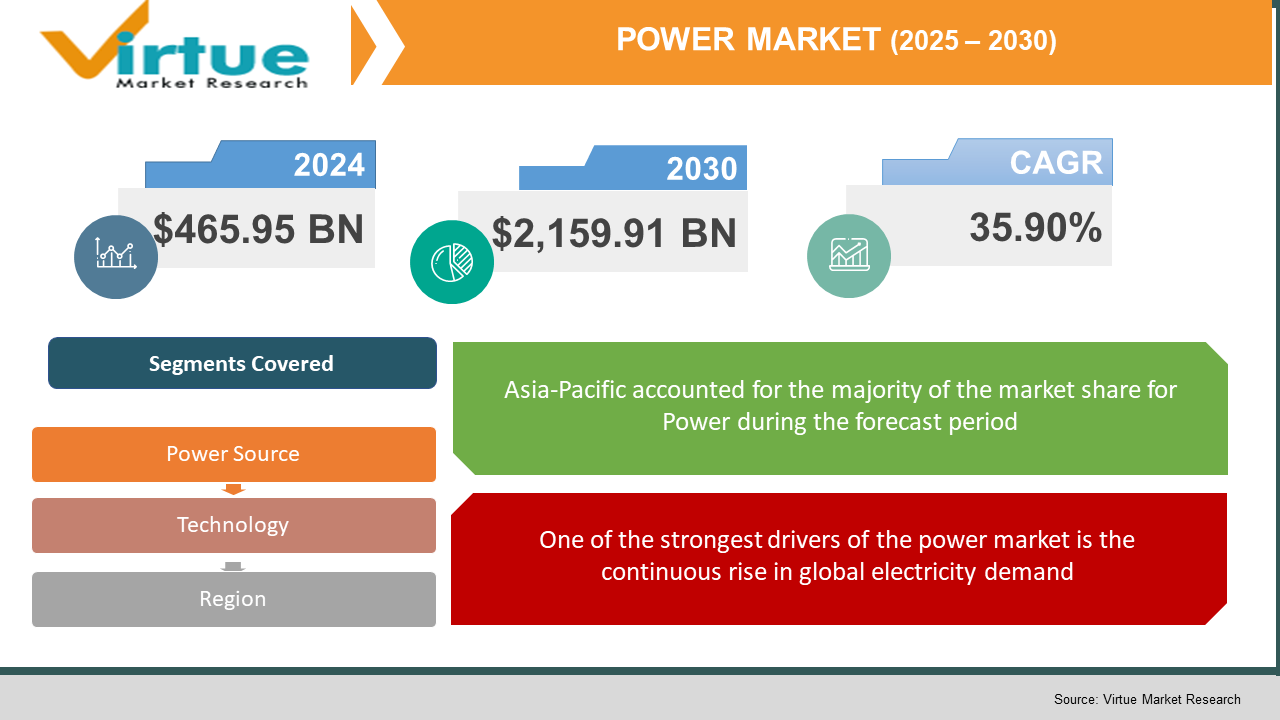
The Power Market was valued at USD 465.95 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 2,159.91 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 35.90%.
The Power Market has gone through some major changes as various new technologies continue emerging, the adoption of renewable energy by many people worldwide is increasing, coupled with the increasing worldwide demand for electricity that is sustainable. Nations have been attempting to decarbonize their energy systems; therefore, investments are flowing into smart grids, energy storage, and clean generation methods, including solar, wind, and hydro sources. Furthermore, policy support, digitalization, and electrification of industries and transport sectors are all increasing. The world turns to focus on and build a low-carbon future, further placing the power market at the front of the global energy transition.
Key Market Insights:
Over 85% of new global power capacity in 2023 came from renewable sources, led by solar and wind. This marks a major turning point in the global shift away from fossil fuels.
Worldwide electricity demand is expected to grow by 3.4% annually until 2030, driven by population growth, urbanization, and electrification of transport and industries. Emerging economies are contributing the most to this surge.
Power Market Drivers:
One of the strongest drivers of the power market is the continuous rise in global electricity demand.
Global electricity demand is the most prominent driving force of power markets. Urbanization and improved living standards in the growing population increase the need for continuous and clean power. Besides, other sectors such as transport (i.e., EVs), heating, and industrial processes are now transitioning from fossil fuels to electricity, thus creating a shift in energy consumption. As countries now strive to achieve net-zero emissions, the use of electricity in replacing conventional energy sources is prescribed. The need for reliable and scalable power solutions is exacerbated by smart homes, digital devices, and data centers. Rapid industrialization in emerging economies, coupled with electrification in rural areas, is significantly creating demand for power infrastructure. In addition, increases in cooling and heating needs due to climate change lead to additional demand for electricity. As per the IEA, global electricity demand is expected to increase by over 25% by 2030. This large upcoming growth puts huge pressure on both governments and the private sector to invest in expanding and modernizing power generation and transmission networks.
The global push toward clean energy and carbon neutrality is a powerful force driving the transformation of the power market.
The transition to renewable energy and carbon neutrality is rapidly becoming entrenched as the force propelling the transition of the power market. With countries committing to climate agreements such as the Paris Accord and setting legally binding net-zero targets, these clean energy mechanisms phase out fossil fuels. Solar energy, wind energy, hydro, and geothermal energy are seeing a rapid shift toward very low prices, with solar photovoltaic systems seeing a drop of over 80% in price in the last decade. They are not just cleaner but are also more adaptable to deploy, with a far greater capacity for scaling across different geographies. Tax incentives, subsidies, and mandates are being provided by different governments, while the investment community is decommissioning its coal and oil-based assets. Another significant driver includes these companies' goals of sustainability, demanding green energy to power their operations and those of their supply chain. Added to that, public apprehension about and concern regarding climate change is exerting pressure on utilities to decarbonize their portfolios. This clean energy transition is shaping the generation mix and opening up new avenues for investment in grid upgrades, energy storage, and green hydrogen.
Power Market Restraints and Challenges:
One of the key restraints in the power market is the high upfront capital required for deploying renewable energy systems, upgrading grid infrastructure, and integrating advanced technologies like smart grids or battery storage.
An enormous upfront capital requirement for deployment of renewable energy systems, upgrading of grid infrastructures, and the inclusion of very advanced technologies such as smart grids or battery storage remains one of the restraints in the power market. The operational cost of renewables is relatively low; however, the initial costs for solar farms, offshore wind, transmission lines, and substations remain prohibitively high, particularly in developing economies. Financing of these enormous projects is often through complex public-private partnership schemes and long regulatory approvals. In many locations, aging infrastructure further compounds the problem, as the existing grids cannot accommodate variable renewable inputs or the rising demand. The lack of a skilled workforce and technical expertise also delays deployment. Also, private investors are dissuaded, especially given that the payback period for investments in some clean technologies could take years. Any integration of decentralized energy sources would thus require substantial upgrading of real-time monitoring and grid management systems. In the absence of proper funding mechanisms and a policy framework, these challenges related to finance and infrastructure would ultimately delay the power transition, in addition to preventing access to affordable electricity among underserved communities.
Power Market Opportunities:
There are transformative opportunities in the power market nowadays, stemming from innovation, sustainability goals, and changing consumer requirements. Rapid growth in renewable energy technologies- solar, wind, and green hydrogen slowly but surely becoming more commercially viable with increased economy and globally accepted scale. Energy storage systems in lithium-ion and flow battery technology will eventually offer even more opportunities to balance the intermittent output of renewables to enable grid stability. Smart grid technologies, AI-driven energy management systems, and IoT solutions now facilitate real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced efficiency for utility providers. Development in Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) models also presents increasing promise; this way, consumers can access clean power without heavy upfront investments. The electrification of transport is the building up of the EV charging infrastructure, then creating economies of scale across the mobility and power sectors. Emerging markets in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America have unquenched appetites for off-grid and microgrid solutions. On top of this, decentralized energy systems and peer-to-peer power trading platforms based on blockchain are opening new business models and revenue streams for startups and established energy companies alike.
POWER MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
35.90% |
|
Segments Covered |
By POWER SOURCE, TECHNOLOGY, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
General Electric, Siemens Energy, EDF Group, Enel S.p.A., Duke Energy Corporation, NextEra Energy, Iberdrola, Vestas Wind Systems, First Solar, and Canadian Solar |
Power Market Segmentation:
Power Market Segmentation: By Power Source
- Renewables
- Non-renewables
- Nuclear
Restructured comments concerning the divisions within the power market; they include Renewables, Non-renewables, and Nuclear sources, along with which each plays its role in the international energy palette. Rapid growth in renewable energy sources is due to the decarbonization targets, falling prices, and other favorable political decisions. This includes solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass sources. Record installations have been made for solar and wind energy due to their scalability and very low marginal costs. Non-renewables include coal, oil, and natural gas as the sources of base-load power in varying degrees and different regions. However, they are increasingly pressed by climate regulations and carbon taxes; coal has continually waned in use, while natural gas is still fundamentally important for grid flexibility and backup power. With its controversies in some regions, nuclear energy is experiencing a resurgence, as many countries are now turning to it for an affordable energy supply with low emissions and stable delivery. Expansion plans for nuclear capacity to meet long-term security and net-zero targets are being rolled out by some nations such as France, China, and India. This trend in the source of power will shape investment patterns, regulatory framework, and infrastructure needs from now through 2030.
Power Market Segmentation: By Technology
- Smart Grids
- Traditional Grids
- Energy Management Systems
Technological segmentation of the power market includes Smart Grids, Traditional Grids, and Energy Management Systems(EMS). Smart grids change power distribution to one that monitors energy flows and manages supply and demand in real time, using sensors and automation, and data analytics. These systems support two-way communications between utilities and consumers, enhance grid resilience, and integrate distributed energy resources like rooftop solar and EVs. In essence, these legacy grids depended on centralized generation and one-way transmission that minimized flexibility and efficiency. Many developing countries are still relying on these older systems, which absorb high transmission losses and regular outages. For grid modernization, EMS technologies are being deployed to optimize energy consumption in homes, commercial settings, and industrial setups. This platform uses AI and IoT to handle forecasting load, peak demand management, and energy saving. The technologies are expected to play an important role in the modernization and sustainability of the grids as power systems digitally gain a greater level of decentralization.
Power Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
The world power market presents distinct regional dynamics formed by energy policies, industrial growth, and technological adoption. The Asia-Pacific region constitutes the largest share of the market due to rapid industrialization, urban growth, and enormous investments in renewables, particularly in China and India. The region is aggressively adding capacity in solar, wind, and hydro installations to address increasing demand for electricity. Following behind North America offers considerable momentum in areas such as modernizing the grid, energy transitions, and infrastructure for electric vehicles. The European markets lead the way in decarbonization efforts, focusing on offshore wind farm development, smart grid deployment, and green hydrogen initiatives. There is an increased interest in solar power in MEA-Middle East and Africa, with large-scale investments in solar farms by countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, and several African countries trying to scale up energy access through microgrids and renewables. South America, particularly Brazil, is still building up its hydroelectric resources, while countries like Chile and Argentina are ramping up solar capacity to diversify the energy mix and enhance sustainability.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Power Market:
A mixed bag and transformative impact were dealt by COVID-19 to the global power market. During the beginning stages of lockdown, electricity demand in commercial and industrial sectors plummeted due to reduced operations, more significantly in sectors like manufacturing, construction, and transportation. This caused temporary oversupply, revenue losses for utilities, disruption in ongoing projects of power infrastructure, yet there was a significant increase in electricity demand from the residential sector due to the work-from-home practices and digital activities. Even global supply chains for solar panels, wind turbines, and grid components were severely affected due to which delayed clean energy projects. In the short term, therefore, the pandemic did its job of rapid progress toward renewables and digitalization. That included green recovery initiatives in their stimulus packages. Investments in solar, wind, and smart grid technologies have quickly rebounded after 2020, as clean energy has proved to be more resilient and cost-effective. Vulnerable centralized grids and fossil fuels have been exposed through COVID, wherein renewed focus would be on decentralization, microgrids, and energy resilience. Overall, although the short run was in some measures slowing down activity in power markets, it has also accelerated change in the structures that will now build a much more sustainable and digitized energy future.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
Technological advancements and policy reform have all combined with even the changing face of consumer choice to transform the power market in the world today. Notable is the growing trend in renewable energy, particularly wind and solar, which accounted for a staggering share of new power capacity put in place in 2024. With the rapid pace towards smart grids, digital energy management systems realize new opportunities to continuously monitor and optimize energy flow across networks. Energy storage technologies, mainly lithium-ion and flow batteries, prove their growing relevance for grid reliability and renewable integration. Data Centers and AI Infrastructure resourcing are giving rise to new power demand clusters that include: the U.S., India, and Europe. Bringing green hydrogen to the production scene is picking up as a long-term energy storage and decarbonization solution. Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) systems and decentralized energy systems are redefining power generation systems and even consumption patterns for power technologies. Developed countries took advantage of the private investments made in modernized microgrids or off-grid solutions for access expansion. In the end, however, the market moves towards smaller, cleaner, smarter, and more resilient systems to achieve energy security and sustainability objectives.
Key Players:
- General Electric
- Siemens Energy
- EDF Group
- Enel S.p.A.
- Duke Energy Corporation
- NextEra Energy, Inc.
- Iberdrola S.A.
- Électricité de France
- Tata Power Company Limited
- China Yangtze Power Co.
Chapter 1. Power Market – SCOPE & METHODOLOGY
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Technology
1.5. Secondary Technology
Chapter 2. POWER MARKET – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2025 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. POWER MARKET – COMPETITION SCENARIO
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. POWER MARKET - ENTRY SCENARIO
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes Players
4.5.6. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. POWER MARKET - LANDSCAPE
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. POWER MARKET – By Power Source
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Renewables
6.3 Non-renewables
6.4 Nuclear
6.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Power Source
6.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Power Source , 2025-2030
Chapter 7. POWER MARKET – By Technology
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Smart Grids
7.3 Traditional Grids
7.4 Energy Management Systems
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Technology
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Technology, 2025-2030
Chapter 8. POWER MARKET - By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1. North America
8.1.1. By Country
8.1.1.1. U.S.A.
8.1.1.2. Canada
8.1.1.3. Mexico
8.1.2. By Technology
8.1.3. By Power Source
8.1.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2. Europe
8.2.1. By Country
8.2.1.1. U.K.
8.2.1.2. Germany
8.2.1.3. France
8.2.1.4. Italy
8.2.1.5. Spain
8.2.1.6. Rest of Europe
8.2.2. By Power Source
8.2.3. By Technology
8.2.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3. Asia Pacific
8.3.1. By Country
8.3.1.1. China
8.3.1.2. Japan
8.3.1.3. South Korea
8.3.1.4. India
8.3.1.5. Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2. By Power Source
8.3.3. By Technology
8.3.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4. South America
8.4.1. By Country
8.4.1.1. Brazil
8.4.1.2. Argentina
8.4.1.3. Colombia
8.4.1.4. Chile
8.4.1.5. Rest of South America
8.4.2. By Power Source
8.4.3. By Technology
8.4.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5. Middle East & Africa
8.5.1. By Country
8.5.1.1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2. Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3. Qatar
8.5.1.4. Israel
8.5.1.5. South Africa
8.5.1.6. Nigeria
8.5.1.7. Kenya
8.5.1.8. Egypt
8.5.1.8. Rest of MEA
8.5.2. By Power Source
8.5.3. By Technology
8.5.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. POWER MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Power Source Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 General Electric
9.2 Siemens Energy
9.3 EDF Group
9.4 Enel S.p.A.
9.5 Duke Energy Corporation
9.6 NextEra Energy, Inc.
9.7 Iberdrola S.A.
9.8 Électricité de France
9.9 Tata Power Company Limited
9.10 China Yangtze Power Co.
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Power Market was valued at USD 465.95 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 2,159.91 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 35.90%.
The power market is driven by rising global electricity demand and the rapid shift toward renewable energy sources. Government policies, climate goals, and advancements in smart grid and storage technologies also accelerate market growth.
Based on Service Provider, the Power Market is segmented into material manufacturers, Raw Material Suppliers, Lab information management systems, Distributors & Wholesalers, End-to-End Solution Providers.
Asia-Pacific is the most dominant region for the Power Market.
General Electric, Siemens Energy, EDF Group, Enel S.p.A., Duke Energy Corporation, NextEra Energy, Iberdrola, Vestas Wind Systems, First Solar, and Canadian Solar are the key players in the Power Market



