Power Generation Market Size (2024 – 2030)
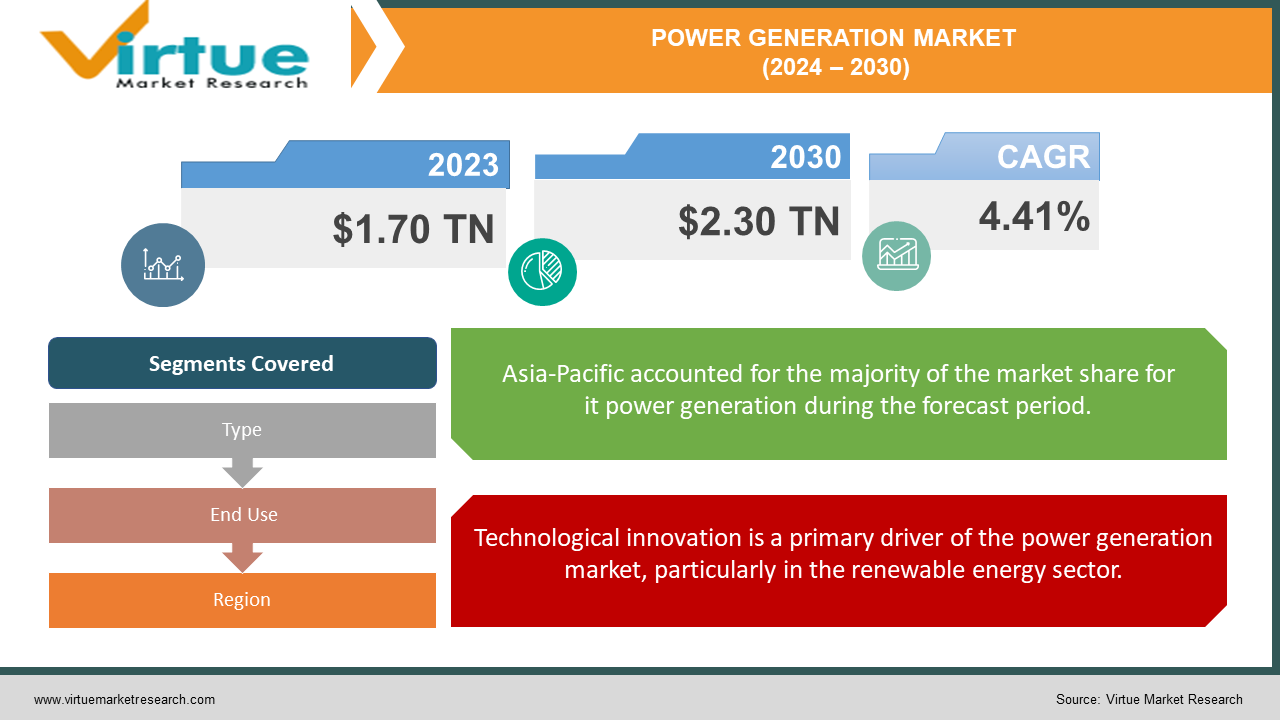
The Global Power Generation Market was valued at USD 1.70 Trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 2.30 Trillion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.41%.
The foundation of contemporary industrial and residential infrastructure is the worldwide market for electricity generation. It includes the generation of electrical energy from a variety of sources, such as nuclear power, renewable energy sources, and fossil fuels. Numerous elements, including economic situations, regulatory frameworks, technology breakthroughs, and environmental concerns, influence the dynamics of the industry. Power generation is an industry that is always innovating and adapting, from the massive coal plants to the clever wind turbines scattered along coasts. The journey of power generation dates back to the late 19th century with the advent of electricity generation and distribution. The invention of the electric dynamo and the establishment of the first power plants laid the groundwork for the rapid industrial growth of the 20th century. Initially dominated by coal and hydroelectric power, the sector diversified with the discovery and utilization of oil and natural gas. The mid-20th century saw the introduction of nuclear power, which promised a new era of energy security and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Key Market Insights:
Renewable energy sources—such as wind and solar power—are expanding quickly; by 2023, their total worldwide share will surpass 15%.
With an annual production of approximately 4,000 terawatt-hours (TWh), the United States ranks as the second-largest generator of energy in the world.
Although they still provide a sizable portion of the world's electricity, coal-fired power stations are becoming less common. By 2030, coal's share of the world's electrical production is predicted to drop below 30%.
Hydropower is still an important renewable energy source; in 2023, it will generate around 18% of the world's electricity.
Globally, solar energy is the renewable energy source that is expanding the quickest. By 2027, it's anticipated that the worldwide solar PV industry will have grown to USD 214.3 billion.
Another significant renewable energy source is wind power, which will have more than 830 gigawatts (GW) of installed capacity worldwide in 2023.
By 2027, the worldwide market for nuclear power is anticipated to grow to USD 74.2 billion. Nuclear energy does, however, confront difficulties with radioactive waste management and safety issues.
In order to incorporate additional renewable energy sources into the power system, battery storage technology is essential. By 2027, the energy storage industry is projected to grow to a value of USD 50.7 billion worldwide.
Power Generation Market Drivers:
Technological innovation is a primary driver of the power generation market, particularly in the renewable energy sector.
Renewable energy sources are becoming more economical and efficient due to developments in battery storage, solar, and wind technology. The capacity and efficiency of renewable energy installations are rising due to advancements in solar cells and the creation of larger, more efficient wind turbines. Considerable technical progress has been made in the wind energy industry, especially in the areas of materials and turbine design. Compared to earlier models, contemporary wind turbines are more powerful, bigger, and more efficient. These developments are especially beneficial to offshore wind farms, as they enable the placement of bigger turbines in locations with stronger and more constant wind speeds. Advancements in floating turbine technology are broadening the range of possible sites for wind farms, encompassing deep-water regions that were previously deemed unsuitable.
Government policies and incentives are powerful drivers of the power generation market, particularly in the renewable energy sector.
A variety of policies are being implemented by national and local governments to promote the use of renewable energy technology and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Subsidies, tax breaks, requirements for renewable energy sources, and carbon pricing schemes are some of these measures. Subsidies and tax credits are examples of financial incentives that are essential to the viability of renewable energy projects. In many nations, the development of solar and wind power has been aided by feed-in tariffs (FiTs), which guarantee a set price for electricity produced from renewable sources. Production tax credits (PTCs) and investment tax credits (ITCs) give renewable energy projects extra funding, lowering their initial costs and increasing the return on investment for developers.
Power Generation Market Restraints and Challenges:
The high initial capital expenditure associated with the development and implementation of new technologies represents one of the main obstacles facing the power production business, especially in the renewable energy sector. Building wind farms requires large capital outlays, particularly for offshore wind farms. High initial capital expenditures are another drawback of energy storage alternatives like battery systems and pumped hydro storage. Even though their cost is coming down, lithium-ion batteries are still rather expensive for large-scale storage applications. Among the energy projects requiring the greatest capital are nuclear power facilities. Large sums of money are needed for engineering, construction, and safety measures while building new nuclear reactors. Another major obstacle facing the electricity generating business is the unpredictability of regulations and policies.
Power Generation Market Opportunities:
Significant prospects for the increase of renewable energy capacity are presented by the worldwide transition towards low-carbon and sustainable energy sources. Clean energy solutions are becoming more and more important to businesses, consumers, and governments as a way to combat climate change, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance energy security. The wind energy industry presents significant development prospects, especially in the offshore wind sector. The potential for offshore wind farms in deep-water regions is growing because of developments in turbine technology and the creation of floating wind turbines. Advanced energy storage systems are becoming more and more necessary as renewable energy sources increase. Among the many potential applications of battery storage are grid stabilization and intermittent renewable energy management. The trend towards decentralized power generation and the development of microgrids present significant opportunities for the power generation market. Decentralized energy systems, which involve the generation of electricity close to the point of consumption, offer numerous benefits, including increased energy security, reduced transmission losses, and enhanced grid resilience.
POWER GENERATION MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
4.41% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, End Use, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
|
Power Generation Market Segmentation: By Types
-
Coal
-
Natural Gas
-
Oil
-
Nuclear Power
-
Wind Power
-
Solar Power
-
Hydropower
-
Other Renewables
Because it may act as a bridge fuel throughout the transition to renewable energy sources, natural gas continues to be the most often used kind in the power production sector. Natural gas is a preferred option for power generation due to its abundance, especially in areas with substantial shale gas deposits, and its comparatively lower emissions when compared to coal and oil. In order to supplement sporadic renewable energy sources, natural gas power plants provide baseload and peaking electricity while maintaining flexibility and dependability.
The market for power generation with the quickest rate of growth is solar energy. Solar power is becoming more and more competitive with conventional energy sources due to the quick drop in the cost of solar panels brought about by technological improvements and economies of scale. The reason behind the growing acceptance of solar power is its scalability, which can be applied to both small rooftop installations and huge utility-scale projects. Additionally, solar resources are abundant in many places. Solar electricity is becoming more efficient and economical because of advancements in photovoltaic technology, such as bifacial panels and perovskite cells.
Power Generation Market Segmentation: By End Use
-
Utilities
-
Industrial
-
Commercial
-
Residential sectors
In charge of overseeing the production, transmission, and distribution of power, utilities are the main purchasers and sellers of energy. Utility-scale power generating projects meet the demands of utilities and include big wind farms, solar power plants, and fossil fuel power plants. The development of smart grid technology and the incorporation of renewable energy sources into the utility system are the two main developments in this market.
In the market for electricity generation, the residential sector is the one that is expanding the quickest. The quick adoption of domestic solar power is being fueled by the falling costs of house batteries and rooftop solar panels, as well as legislative incentives and rising consumer awareness. In an effort to lower energy expenses, improve energy independence, and protect the environment, homeowners are investing more and more in solar panels and energy storage systems.
Power Generation Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
Asia-Pacific
-
North America
-
Europe
-
Middle East & Africa
-
South America
With a dominating 42% of the worldwide power generating industry, the Asia-Pacific region easily stands out as the main player. Many elements that have influenced the energy landscape of the area over the last few decades can be credited for this leading position. Asia-Pacific's tremendous economic expansion and industrialization are major factors contributing to its supremacy. Global economic growth in nations like China and India has resulted in an increase in energy demand in a number of industries, including industry, transportation, and home use.
The Middle East and Africa region is growing at the fastest rate and is predicted to experience significant expansion in the years to come, although making up only 9% of the world's power generating industry currently. A number of factors have contributed to its rapid development trajectory, which elevates it to a more prominent position in the world energy market. The growing need for energy brought on by population expansion, urbanization, and economic development is one of the main factors driving growth in the Middle East and Africa area.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Power Generation Market:
The global adoption of lockdowns and social distancing techniques resulted in a sharp decline in economic activity. Transportation networks slowed down, industries idled, and businesses closed. As a result, the demand for power significantly decreased. 2020 saw the biggest-ever drop in worldwide power consumption, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), of 7%. The impact on renewable energy sources, such solar and wind, was less severe even if global demand declined. These sources are usually less sensitive to changes in fuel prices and have lower operational expenses. In certain areas, when lockdowns have decreased air pollution, solar energy output has even marginally increased. The recovery for fossil fuel sources has been mixed. Coal-fired power plants continued to face challenges due to environmental regulations and lower electricity prices. Natural gas, however, saw a resurgence due to its relatively cleaner burning profile compared to coal and its ability to ramp power generation up or down quickly to meet fluctuating demand.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
Fossil fuels have long dominated the power generation mix. However, concerns about climate change and air pollution are driving a significant shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology is experiencing a remarkable boom. The cost of solar panels has plummeted, making them a cost-competitive option in many regions. Additionally, advances in solar cell efficiency and energy storage solutions are further propelling solar power adoption. Wind energy remains a major player in the renewable energy landscape. Technological innovations such as larger, more efficient wind turbines are enabling the harnessing of wind energy even in low-wind areas. Offshore wind farms are also gaining traction, offering vast potential for electricity generation. The growing popularity of rooftop solar panels in homes and businesses is a prime example of DG. These installations allow consumers to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on the central grid and potentially feeding excess power back into the system. Microgrids, consisting of a cluster of DG units such as solar panels or small wind turbines, can provide localized power solutions for communities or campuses.
Key Players:
-
-
ExxonMobil (US)
-
Chevron (US)
-
Royal Dutch Shell (Netherlands)
-
BP (UK)
-
Siemens AG (Germany)
-
General Electric (US)
-
Enel SpA (Italy)
-
EDF (France)
-
State Grid Corporation of China (China)
-
Goldwind (China)
-
Longi Solar (China)
-
Vestas Wind Systems A/S (Denmark)
-
NextEra Energy (US)
-
Duke Energy (US)
-
Chapter 1. Power Generation Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Power Generation Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Power Generation Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Power Generation Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Power Generation Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Power Generation Market – By Types
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Coal
6.3 Natural Gas
6.4 Oil
6.5 Nuclear Power
6.6 Wind Power
6.7 Solar Power
6.8 Hydropower
6.9 Other Renewables
6.10 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Types
6.11 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Types, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Power Generation Market – By End Use
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Utilities
7.3 Industrial
7.4 Commercial
7.5 Residential sectors
7.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End Use
7.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End Use, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Power Generation Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Types
8.1.3 By End Use
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Types
8.2.3 By End Use
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Types
8.3.3 By End Use
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Types
8.4.3 By End Use
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Types
8.5.3 By End Use
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Power Generation Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 ExxonMobil (US)
9.2 Chevron (US)
9.3 Royal Dutch Shell (Netherlands)
9.4 BP (UK)
9.5 Siemens AG (Germany)
9.6 General Electric (US)
9.7 Enel SpA (Italy)
9.8 EDF (France)
9.9 State Grid Corporation of China (China)
9.10 Goldwind (China)
9.11 Longi Solar (China)
9.12 Vestas Wind Systems A/S (Denmark)
9.13 NextEra Energy (US)
9.14 Duke Energy (US)
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The global population is projected to continue growing, leading to an increasing demand for electricity for residential and commercial use. Urbanization trends further intensify this demand, as cities require more power for infrastructure, transportation, and industrial activities.
The global population is projected to continue growing, leading to an increasing demand for electricity for residential and commercial use. Urbanization trends further intensify this demand, as cities require more power for infrastructure, transportation, and industrial activities.
ExxonMobil (US), Chevron (US), Royal Dutch Shell (Netherlands), BP (UK), Siemens AG (Germany), General Electric (US), Enel SpA (Italy), EDF (France), State Grid Corporation of China (China), Goldwind (China), Longi Solar (China), Vestas Wind Systems A/S (Denmark), NextEra Energy (US), Duke Energy (US).
The market is dominated by Asia Pacific, which commands a market share of around 45%.
With a market share of about 5%, the Middle East is expanding the quickest.



