Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market Size (2024 – 2030)
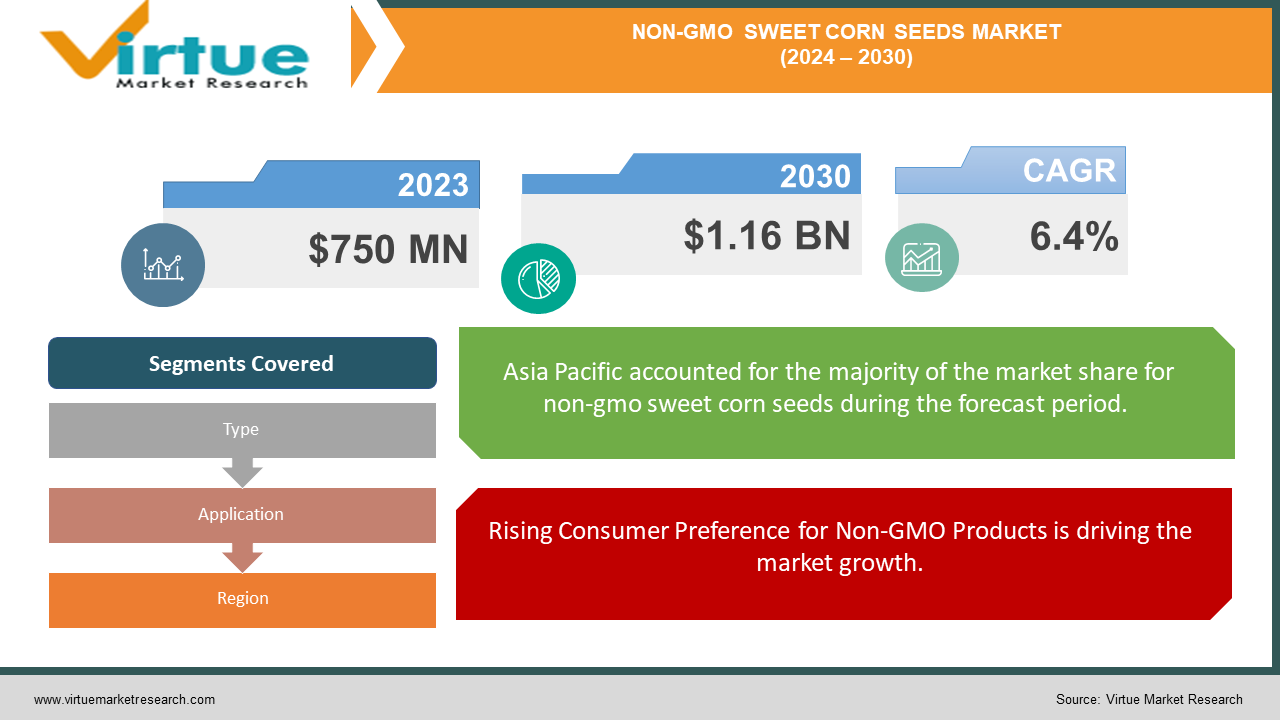
The Global Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market was valued at USD 750 Million in the year 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2024 to 2030. The market is projected to reach USD 1.16 billion by 2030.
Increasing consumer demand for non-GMO and organic products, combined with growing issues of health and environmental concern associated with GMOs, will keep on boosting the demand for non-GMO sweet corn seeds. Also, improved farming practices and seed technologies would play a major role in market growth.
Key Market Insights:
Fresh Consumption is the leading application segment due to the heavy demand for non-GMO sweet corn by the food industry.
Geographically, Asia Pacific remains the leading market. In 2023, Europe and North America held the second and third positions, respectively.
Growing consumer preference for non-GMO products is driving market growth, along with the development of seed technologies.
Global Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market Drivers:
Rising Consumer Preference for Non-GMO Products is driving the market growth.
One of the important factors driving the Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market is the consumer preference for non-GMO products. The segment, with a constant rise in consumer awareness of health concerns and knowledge about such products, experiences an increased demand for non-GMO and organic food products related to sweet corn. Non-GMO sweet corn is a healthier and safer variety cultured without using any GM seed and related chemicals. Increasingly available non-GMO certification and a labeling program further support the increase of the market by offering assurance to consumers about the origin and the appreciated production techniques of sweet corn seeds. As the demand for non-GMO products is rising at an exponential rate, the farmers and companies producing seeds are increasingly using non-GMO sweet corn seeds to make offers according to consumer tastes and tap the market opportunities that this burgeoning niche is offering.
Advancements in Agricultural Practices and Seed Technologies are driving market growth.
Modern agricultural innovations in this sphere, such as precision farming, integrated management of pests and diseases, and sustainable farming practices, have increased efficiency and improved quality in non-GMO sweet corn crops. These practices really focus on ensuring resource efficiencies, reduction in the use of synthetic inputs, soil health, and biodiversity. Advancements in seed technologies need to enhance the development of high-yielding and disease-resistant non-GMO sweet corn varieties to improve farming performance and profitability for non-GMO corn in general. When such good varieties, which have good nutritive value, alluring taste, and texture, become available, farmers are drawn to them and they facilitate the adoption process of non-GMO sweet corn seeds. Additionally, growing investments in research and development activities for conceptualizing seeds that are innovative and also sustainable are expected to fuel market growth.
Increasing Health and Environmental Awareness Problems are driving the market growth.
The increasing awareness regarding health and environmental issues linked with GMOs drives the demand for non-GMO sweet corn seeds. The most noteworthy reasons for these trends in moving away from GMOs are consumers' worries about the long-term health impacts related to GMO intake, such as allergies, antibiotic resistance, and gut health effects. Another reason for concern about the environment that adds to the movement toward a GMO-free form of agriculture is the loss of biodiversity, pesticide resistance, and the contamination of non-GMO crops with GMOs. The non-GMO sweet corn is considered more viable and sustainable environmentally because of the pro-biodiversity effects, the less application of chemicals, and the preservation of the integrity of the varieties that a crop is supposed to have. NGOs, advocacy groups, and regulatory organizations increasingly convey more awareness and education, which again raises the level of consciousness among consumers and advances the cause. Resulting of this, the demand for non-GMO sweet corn seeds is expected to take a high pace over the following years.
Global Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market Challenges and Restraints:
High Production Costs and Scarcity are restricting the market growth.
Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market poses a major challenge of high production cost along with the scarcity of its very own Non-GMO sweet corn seeds, which results in limited availability. The development of non-GMO sweet corn seeds includes rigid, documented testing and certification procedures for genetic modification, segregated to prove that it does not exist. All these processes are time-consuming and can be expensive; thus, producing the seeds will be more expensive than conventional GMO seeds. Another challenge brought about by the limited supply of non-GMO sweet corn seeds in the market relates to farmers and seed producers. However, the demand for non-GMO seeds is growing, but the supply chain infrastructures and the distribution channels for non-GMO seeds are still in a formative period. A key bottleneck to further adoption and increases in non-GMO sweet corn production might remain for some time, reflected by the limited availability of non-GMO sweet corn seed in regions with large areas under cultivation of GMOs. Seed distribution involves the planned production, distribution, and marketing of seeds without failing to consider the investment needed to create a consistently reliable supply of non-GMO sweet corn seeds.
Regulatory and Certification Complexities are restricting the market growth.
Another challenge faced by the Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market is issues associated with regulatory and certification complexities. Notice is done for non-GMO seeds to their production and commercialization, where the regulatory requirements and certification standards are so severe that the lack of genetic manipulation and integrity of crops are assured to be non-GMO. Regulation and certification under such can be very involving, time-consuming, and costly to seed producers. Additionally, the heterogeneity in the regulatory framework and certification standards executed by the different countries makes the operation of market players very challenging across borders. This has resulted in inconsistencies and delays in the approval and certification processes that are occasioned by the shortcomings in harmonization and clarity in the regulatory guidelines. Moreover, the costs for small-scale farmers would be increased by seeking and maintaining non-GMO certification. Streamlining the regulatory process and setting clear, harmonized certification standards could reduce such bottlenecks.
Market Opportunities
Opportunities to address growth and innovation come in the global non-GMO sweet corn seeds market with some: the market is ripe with exponentially growing consumer demands for organic and non-GMO foodstuffs. Increasing health consciousness and a preference for natural and sustainable food options act to propel the demand for non-GMO sweet corn and similar organic crops. The current growing trend in non-GMO certification and labeling will continue to give consumers increasing confidence and clarity over the origin and methodology of the production of sweet corn seeds. This is likely to create opportunities for seed producers and farmers to take advantage of this growing demand for non-GMO sweet corn. Besides, prospects for enhanced non-GMO sweet corn farm productivity and profitability are provided by using farms with sustainable practices and developing non-GMO sweet corn hybrids with a high yield that is disease resistant. Market growth is also anticipated in the investment in activities of research and development for creating innovative, sustainable seed solutions. In general, the market harbors significant growth stretching from the rising consumer demand for organic and non-GMO food products to the embracement of sustainable farming practices and advancements in seed technologies.
NON-GMO SWEET CORN SEEDS MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
6.4% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Monsanto Company, Syngenta AG, Bayer CropScience AG, DuPont Pioneer, Groupe Limagrain Holding SA, Sakata Seed Corporation, Takii & Co., Ltd., Advanta Seeds, Rijk Zwaan Holdings BV, Mahyco Seeds Ltd. |
Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market Segmentation - by Type
-
Yellow Sweet Corn Seeds
-
White Sweet Corn Seeds
-
Bicolor Sweet Corn Seeds
The yellow sweet corn seeds segment dominates the Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market. It is majorly used and preferred by consumers due to its preferred characteristics for sweet taste, tenderness in texture, and brightened color of the corn. The food industries' demand, particularly in fresh and processing categories, is propelling this wide consumption, further fueling market leadership in this segment.
Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market Segmentation - by Application
-
Fresh Consumption
-
Food Processing
-
Animal Feed
-
Industrial Use
The fresh consumption segment is the most dominant application segment in the Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market. Fresh sweet corn is in great demand, both for its taste and high nutritional content and is put to some really diversely different applications as a culinary food product. Growing consumer preference towards the consumption of fresh and natural food products, coupled with mounting trends for the consumption of non-GMO vegetables, are some of the reasons why the segment retains dominance in the fresh consumption segment of the market.
Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market Segmentation - by Region
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
Asia Pacific dominates the Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market. The well-established agriculture infrastructure, high consumer awareness, and demand in huge numbers for non-GMO and organic food products are the various driving factors for the market. The presence of major seed companies and most of the R&D activities adds to the dominance of this market in the Asia Pacific.
COVID–19 Impact Analysis on Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market
The COVID-19 pandemic affected the Global Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market in mixed and varying ways. At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, industries in the Global Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market were affected by disruptions in the supply chains, production, and distribution lines, including lockdowns and restrictions in various countries. All this uncertainty and challenges through the economies have had a negative impact on the demand for non-GMO sweet corn seeds. As the pandemic grew longer and more pronounced, so did the sensitivity to food security and the push towards healthy and sustainable food products. The demand for non-GMO sweet corn seed probably increased because of the growing focus on home gardening and local food production during the pandemic. The reasons for prominent purchases in this sector are driven by increasing consumer awareness of such foodstuffs, imperatives to avoid genetically modified organisms and the considerable benefits of non-GMO and organic foodstuffs in maintaining good health. Post-pandemic phase: The post-pandemic phase is expected to increase the demand for non-GMO sweet corn seeds due to the growing awareness about health, sustainability, and food security among consumers.
Latest Trends/Developments:
A few remarkable trends and developments are observed in the Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market. One of the prominent trends realized in the market includes the adoption of methodologies of sustainable farming practices. Farmers are increasingly adopting practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced chemical applications to enhance the health of soils, biodiversity, and general sustainability. The other major trend among many companies is investments in seed technologies. Companies dealing with seeds are actually engaging in several non-genetically modified sweet corn research and development to come up with high-yielding, disease-resistant, and drought-tolerant varieties. These advancements aim to increase crop performance by minimizing the environmental impact and maximizing the gain for farmers in the non-GMO sweet corn. Nowadays, there is an increasing demand in the market for organic non-GMO sweet corn seeds. This means that the type of farming where there is no application of synthetic inputs and natural and healthy methodologies are gaining more popularity among consumers. Major drivers in the demand for organic non-GMO sweet corn seeds include increasing consumer preference for organic food products and the rising availability of organic certification programs. Other important market trends include a high shift towards direct-to-consumer sales channels. Farmers and seed manufacturers have started using e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces to connect directly with consumers to sell non-GMO sweet corn seeds. This trend provides more convenience, transparency, and accessibility for consumers while providing farmers with the ability to retain higher margins and develop direct relationships with their customers.
Key Players:
-
Monsanto Company
-
Syngenta AG
-
Bayer CropScience AG
-
DuPont Pioneer
-
Groupe Limagrain Holding SA
-
Sakata Seed Corporation
-
Takii & Co., Ltd.
-
Advanta Seeds
-
Rijk Zwaan Holdings BV
-
Mahyco Seeds Ltd.
Chapter 1. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Yellow Sweet Corn Seeds
6.3 White Sweet Corn Seeds
6.4 Bicolor Sweet Corn Seeds
6.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – By Application
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Fresh Consumption
7.3 Food Processing
7.4 Animal Feed
7.5 Industrial Use
7.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Application
7.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Application, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Type
8.1.3 By Application
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Type
8.2.3 By Application
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Type
8.3.3 By Application
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Type
8.4.3 By Application
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Type
8.5.3 By Application
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Monsanto Company
9.2 Syngenta AG
9.3 Bayer CropScience AG
9.4 DuPont Pioneer
9.5 Groupe Limagrain Holding SA
9.6 Sakata Seed Corporation
9.7 Takii & Co., Ltd.
9.8 Advanta Seeds
9.9 Rijk Zwaan Holdings BV
9.10 Mahyco Seeds Ltd.
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Non-GMO Sweet Corn Seeds Market was valued at USD 750 Million in 2023 and is expected to grow at a healthy compound annual growth rate of 6.4% to USD 1.16 billion by 2030.
The market is driven by the rise in consumer preference for non-GMO products, developments in agriculture practices and seed technologies, and growing awareness of health and environmental concerns because of GMOs.
The market is categorized based on type into yellow sweet corn seeds, white sweet corn seeds, and bicolor sweet corn seeds; by application into fresh consumption, food processing, animal feed, and industrial use.
Asia Pacific is the most dominant region, as the region already has well-established agricultural infrastructure, along with consumer awareness, supported by surging demand for organic and non-GMO food products.
Some of the major market players in the seed sub-segment are Monsanto Company, Syngenta AG, Bayer CropScience AG, DuPont Pioneer, Groupe Limagrain Holding SA, Sakata Seed Corporation, Takii & Co., Ltd., Advanta Seeds, Rijk Zwaan Holdings BV, and Mahyco Seeds Ltd.