Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Size (2024 – 2030)
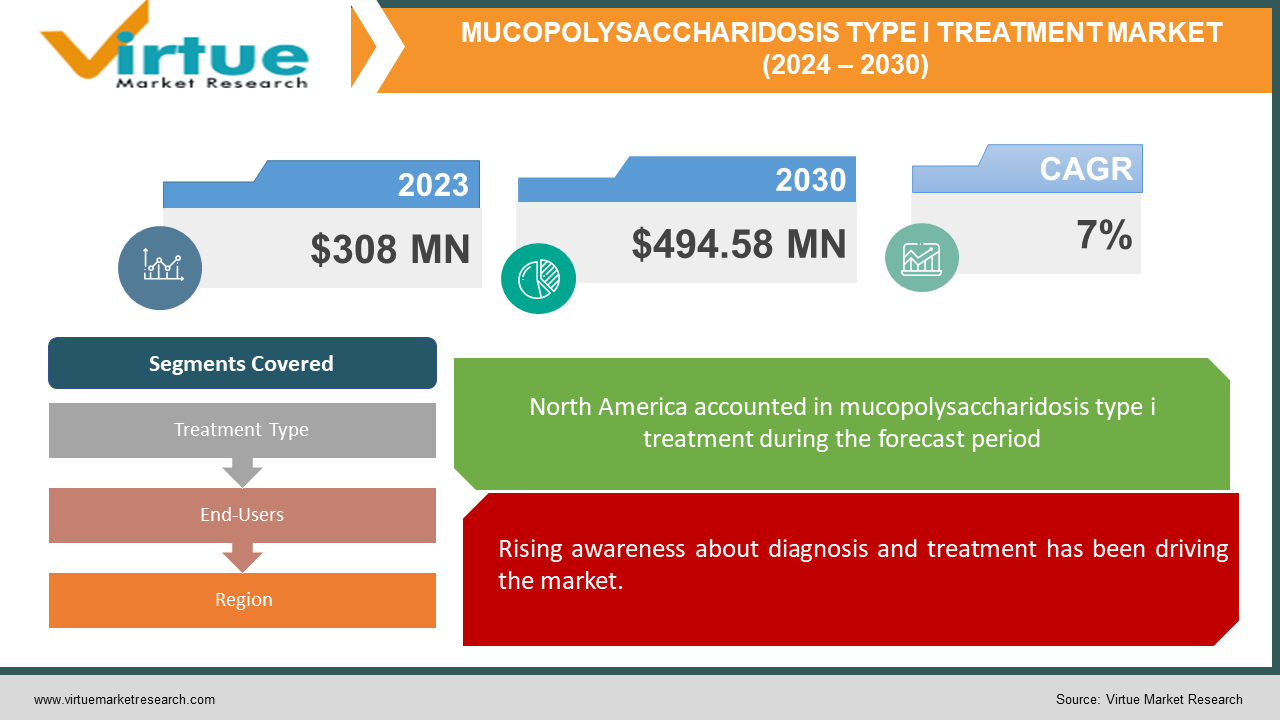
The global mucopolysaccharidosis type I treatment market was valued at USD 308 million in 2023 and will grow at a CAGR of 7% from 2024 to 2030. The market is expected to reach USD 494.58 million by 2030.
Treatment for mucopolysaccharidosis Type I (MPS I) includes a variety of therapeutic approaches intended to address the underlying causes and symptoms of this uncommon genetic condition. One of the mainstays of modern therapeutic strategies is enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), which slows the progression of the disease and relieves symptoms by putting the missing enzyme straight into circulation. Recent developments in gene therapy, however, give hope for treatment as they may be able to address the underlying genetic etiology of MPS I.
Key Market Insights:
The global mucopolysaccharidosis type I treatment market is driven by growing public and medical professional acquaintance with MPS I, resulting in faster diagnosis. Accessibility constraints include high treatment prices, complicated payment processes, and a lack of available treatment options. Opportunities include lowering excessive treatment prices, expediting the reimbursement procedure, and creating cutting-edge treatments to fill gaps in the medical field. The industry is now dominated by North America, with Asia-Pacific developing at the fastest rate because of rising patient numbers and better healthcare facilities.
Global Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Drivers:
Rising awareness about diagnosis and treatment has been driving the market.
Historically, MPS I diagnoses were often delayed due to the rarity of the condition and the non-specific nature of early symptoms. However, growing public and healthcare professional awareness is significantly changing this landscape. Educational campaigns, patient advocacy groups, and media attention are raising awareness of MPS I's signs and symptoms. Doctors are becoming more familiar with the condition, leading to earlier screenings and diagnoses. This earlier identification is crucial. By catching MPS I before symptoms worsen, the disease's progression can be potentially slowed or even halted. This translates to a larger population needing treatment but being in a much better position to benefit from it. As a result, the market for MPS-I therapies is expanding. Pharmaceutical companies are incentivized to invest in research and development for this growing patient pool, leading to a wider range of treatment options and potentially driving down treatment costs in the long run.
Advancements in therapies are facilitating the expansion.
The emergence of novel therapies for MPS I, particularly enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and gene therapy, is revolutionizing treatment options and driving significant growth in the MPS I treatment market. Traditionally, management of MPS I focused primarily on symptom relief, leaving a significant gap in truly addressing the underlying cause of the disease. However, ERT offers a groundbreaking approach by introducing a replacement enzyme directly into the body. This enzyme helps break down the excess glycosaminoglycans that accumulate in MPS I patients, alleviating symptoms and potentially slowing disease progression. Gene therapy, while still under development, holds immense promise for a potential cure. By introducing a healthy copy of the defective gene responsible for MPS I, gene therapy could offer a permanent solution. These novel therapies not only improve patient outcomes but also incentivize investment in the MPS I treatment market. Pharmaceutical companies see a growing patient population with a genuine need for these new treatment options. This spurs investments in research and development, leading to further advancements and potentially reducing treatment costs in the long run. Additionally, the success of these therapies paves the way for streamlined regulatory processes and wider insurance coverage, ultimately driving patient access to these life-changing treatments. This influx of novel therapies and the resulting market growth create a more optimistic future for MPS I patients, offering hope for improved quality of life and potentially a future free from the burden of the disease.
Global Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Challenges and Restraints:
The high cost of treatment is a significant hurdle.
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is the current gold standard for MPS I treatment. While it offers a life-changing intervention, its staggering cost creates a significant barrier to access for many patients. The financial burden falls heavily on families, potentially draining resources and limiting their ability to provide for other necessities. This financial strain can also overwhelm healthcare systems, particularly in developing countries with limited budgets. The high cost of ERT can lead to the rationing of treatment or even the exclusion of some patients who could benefit. This not only creates ethical dilemmas but also hinders the potential benefits of early intervention. To ensure wider patient access and a more sustainable market, addressing the high cost of ERT is crucial. This might involve exploring alternative pricing models, negotiating with pharmaceutical companies, and advocating for government support programs. Ultimately, finding solutions to this cost conundrum is essential to ensuring that the promise of ERT reaches all MPS I patients who need it.
Reimbursement complexities create complexities.
The process of securing reimbursement for MPS I treatments throws another hurdle in the path of patients already struggling with a complex disease. Unlike picking up a typical prescription, obtaining coverage for enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) or future gene therapies can be a labyrinthine ordeal. Patients and their families often face a bureaucratic maze of paperwork, prior authorizations, and appeals with insurance companies. This can involve mountains of medical records, justification for treatment necessity, and battling with bureaucratic red tape. The delays caused by this complex process can be detrimental. MPS I is a progressive disease and timely access to treatment is crucial for slowing its course. The frustration and discouragement caused by navigating the reimbursement system can be immense, potentially leading some families to abandon the fight for coverage altogether. Streamlining the reimbursement process and advocating for clear guidelines are essential steps to ensure that patients don't have to fight the healthcare system on top of battling a debilitating disease.
Limited treatment options create barriers.
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) has been a revolutionary step forward in MPS I treatment, but it's not a perfect solution. While it offers a crucial tool for managing the disease, it falls short of being a complete cure. ERT works by replacing the missing enzyme, but it doesn't address the underlying genetic defect. Additionally, ERT's effectiveness can vary depending on the severity of the MPS I case. For patients with milder phenotypes, ERT can significantly improve symptoms and slow disease progression. However, in severe cases, ERT may not be as effective, particularly for addressing neurological complications. This lack of a wider treatment arsenal tailored to different disease severity levels creates a gap in care for some MPS I patients. The limitations of ERT highlight the urgent need for a more diverse range of treatment options. Ideally, these options would target the specific needs of varying MPS I presentations. This could involve advancements in ERT technology, exploring alternative therapeutic approaches, and the continued development of gene therapy as a potential cure. By expanding the treatment toolbox, doctors can create more personalized treatment plans, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for all MPS I patients.
Global Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Opportunities:
The MPS I treatment market presents exciting opportunities fueled by growing awareness, advancements in therapies, and a large unmet medical need. Increased public and healthcare professional awareness is leading to earlier diagnoses, resulting in a larger patient population requiring treatment. This fuels market growth for existing therapies like enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and incentivizes investment in research and development of novel options. The limitations of ERT, however, create significant opportunities. The high cost of treatment creates an access barrier for many patients, particularly in developing countries. Streamlining the reimbursement process and exploring alternative pricing models can open doors for wider patient access. Additionally, ERT's limitations in addressing all disease severity levels highlight the need for a broader treatment arsenal. Gene therapy, though still under development, holds immense promise as a potential cure. Further research into gene therapy and exploring alternative therapeutic approaches presents significant market opportunities. Addressing these challenges through innovation, collaboration between stakeholders, and advocating for better access will be crucial for unlocking the full potential of the MPS I treatment market. Ultimately, this will lead to a future where more effective and accessible treatments are available to all MPS I patients, offering them a brighter outlook and an improved quality of life.
MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
7% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Treatment Type, End-Users, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
BioMarin Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Sanofi S.A., Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc., JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., Regenxbio Inc., Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc., Abeona Therapeutics Inc., Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc., Orchard Therapeutics Plc |
Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Segmentation: By Treatment Type
-
Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT)
-
Gene Therapy
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
-
Others
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is the largest and fastest-growing treatment type. It offers a vital tool for managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, making it the mainstay treatment for MPS I patients. However, ERT's high cost and limitations in addressing all disease severities create a push for a more permanent solution. This is where gene therapy emerges as a challenger. While still under development, gene therapy holds immense promise as a potential cure by introducing a healthy copy of the defective gene that causes MPS I. As gene therapy trials progress and regulatory hurdles are cleared, it has the potential to become a more prominent player in the MPS I treatment market in the future.
Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Segmentation: By End-Users
-
Hospitals
-
Specialty Clinics
-
Others
Hospitals currently dominate the market. Due to the complexity of administering enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), the mainstay treatment for MPS I, and the need for close monitoring, hospitals provide the most controlled and secure environment. Trained medical professionals can ensure proper administration, manage potential side effects, and closely track patient progress. However, specialty clinics are emerging as the fastest-growing end-user. As treatment protocols become more established and patient education improves, specialty clinics could offer a more convenient and potentially less expensive alternative to hospital-based treatment for stable patients.
Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Europe
-
Asia-Pacific
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America currently holds the dominant position in the Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market. This dominance is driven by factors like advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare spending, and strong awareness of MPS I among medical professionals. This translates to earlier diagnoses, established reimbursement processes for expensive therapies like ERT, and a focus on research and development of novel therapies like gene therapy. Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market. With nations like China, Japan, India, and South Korea, the MPS I therapy industry has a lot of room to grow in the Asia-Pacific area. The region's appeal is influenced by factors such as a growing patient population, rising healthcare costs, improving healthcare infrastructure, and raising awareness. Furthermore, legislative changes and partnerships with multinational pharmaceutical corporations are propelling improvements in MPS I treatment alternatives.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Treatment Market
The COVID-19 pandemic's impact on the MPS I treatment market was a mixed bag. While the initial focus shifted towards critical care, leading to potential disruptions in MPS I treatment routines and clinical trial delays, the long-term effects might be positive. Increased awareness of rare diseases due to COVID-19's spotlight on vulnerable populations could lead to a greater focus on MPS I. Telemedicine advancements implemented during the pandemic might improve patient access to consultations and potentially even remote monitoring for stable MPS I patients on ERT. However, the potential long-term economic effects of COVID-19 could strain healthcare budgets, impacting reimbursement for expensive MPS I therapies. Overall, the long-term impact of COVID-19 on the MPS I treatment market remains to be seen. It hinges on factors like the global economic recovery, the continued development of telehealth practices, and ensuring sustained government support for rare disease treatment programs.
Latest trends/Developments
The MPS I treatment market is experiencing a wave of exciting developments fueled by a growing focus on unmet medical needs. Advancements in gene therapy are leading the charge, with several companies conducting clinical trials for potential curative options. These gene therapy approaches aim to deliver a functional copy of the missing enzyme directly into a patient's cells, potentially halting disease progression and improving long-term outcomes. However, ERT, the current mainstay treatment, is also undergoing improvements. Research is exploring ways to enhance its efficacy, potentially leading to extended dosing intervals or improved delivery methods for better patient compliance. The high cost of ERT remains a major hurdle, prompting efforts to develop more affordable biosimilar versions. Streamlining reimbursement processes and advocating for wider insurance coverage are also crucial steps toward ensuring treatment accessibility. Overall, the MPS I treatment market is experiencing a surge in innovation, with a focus on gene therapy, improved ERT, and exploring combination therapies. These advancements offer a promising future for MPS I patients, with the potential for more effective, accessible, and potentially curative treatment options on the horizon.
Key Players:
-
BioMarin Pharmaceuticals
-
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
-
Sanofi S.A.
-
Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc.
-
JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.
-
Regenxbio Inc.
-
Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.
-
Abeona Therapeutics Inc.
-
Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc.
-
Orchard Therapeutics Plc
Chapter 1. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – By Treatment Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT)
6.3 Gene Therapy
6.4 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
6.5 Others
6.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Treatment Type
6.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Treatment Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – By End-Users
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Hospitals
7.3 Specialty Clinics
7.4 Others
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End-Users
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End-Users, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Treatment Type
8.1.3 By End-Users
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Treatment Type
8.2.3 By End-Users
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Treatment Type
8.3.3 By End-Users
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Treatment Type
8.4.3 By End-Users
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Treatment Type
8.5.3 By End-Users
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE I TREATMENT MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 BioMarin Pharmaceuticals
9.2 Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
9.3 Sanofi S.A.
9.4 Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc.
9.5 JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.
9.6 Regenxbio Inc.
9.7 Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.
9.8 Abeona Therapeutics Inc.
9.9 Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc.
9.10 Orchard Therapeutics Plc
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The global mucopolysaccharidosis type I treatment market was valued at USD 308 million in 2023 and will grow at a CAGR of 7% from 2024 to 2030. The market is expected to reach USD 494.58 million by 2030.
Rising awareness and advancements in therapies are the reasons that are driving the global mucopolysaccharidosis type I treatment market.
Based on end-users, the market is divided into hospitals, specialty clinics, and others.
North America is the most dominant region for the global mucopolysaccharidosis type I treatment market.
BioMarin Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Sanofi S.A., Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc., and JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. are the major players in the global mucopolysaccharidosis type I treatment market.



