LTE base stations Market Size (2024 – 2030)
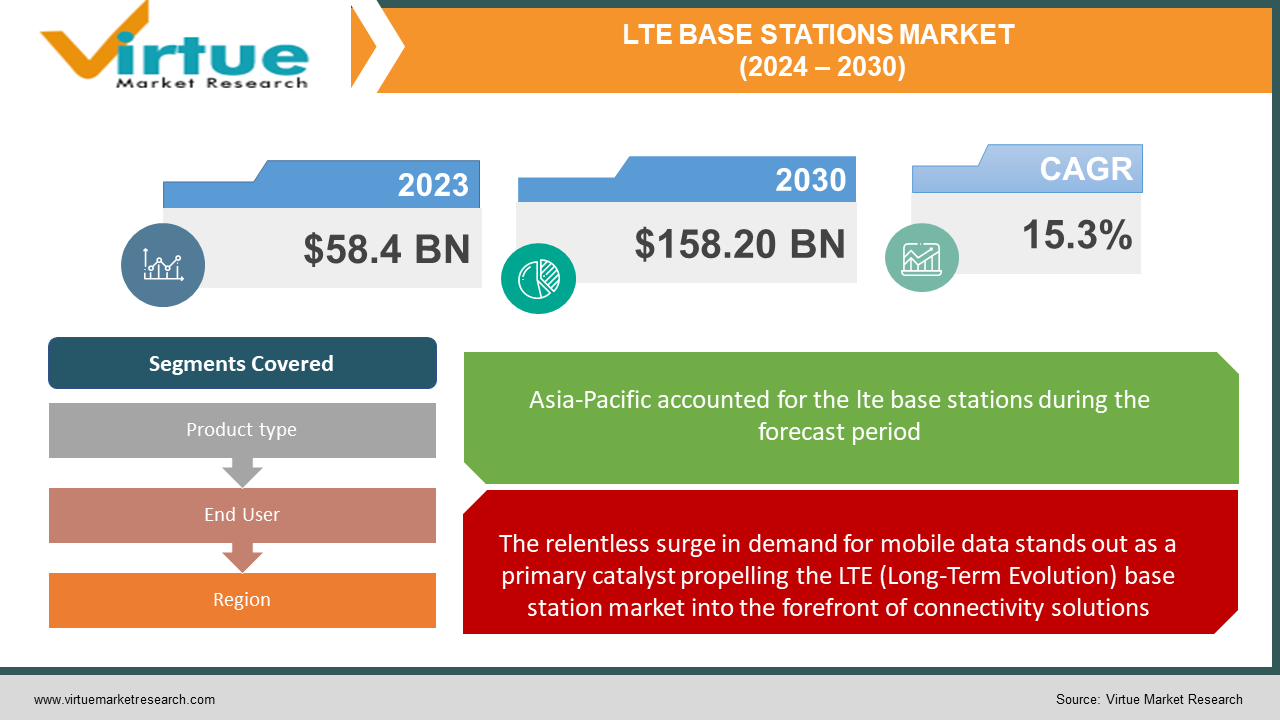
The LTE base station market was valued at USD 58.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 158.20 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024–2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.3%.
Globally, the market for LTE base stations has shown amazing growth. Driven by quick network rollouts and rising device usage, it soared from its humble beginnings in the late 2000s to a valuation of over $50 billion by 2022. However, the market is shifting as 5G becomes accessible. With a CAGR of 15.3 percent between 2022 and 2028, a slower rate of growth is still predicted. This shift has been brought about by operators' concentration on both 5G infrastructure and the optimization and upkeep of their current LTE networks. The established economies of North America and Europe are leading the way in the deployment of 5G, which is leading to a delay in LTE spending. However, growing regions like Asia-Pacific and Africa, where a huge portion of the population is under-connected, are still seeing significant LTE expansion. This gives suppliers of LTE solutions options that are both economical and energy-efficient. The very competitive LTE base station market is dominated by companies like ZTE, Nokia, Ericsson, Huawei, and others. These players offer a wide range of possibilities, from traditional macro-base stations to software-defined radios and microcells.
Key Market Insights:
The market for LTE base stations is driven by the rapid rise in mobile data usage. Strong LTE infrastructure is essential as more and more organizations and consumers rely on data-intensive applications, such as cloud services and video streaming. As the foundation of wireless networks, LTE base stations facilitate fast data transfer, satisfying users' unquenchable need for connectivity. The market for LTE base stations is significantly impacted by the impending switch to 5G networks. Although 5G is being deployed, LTE is still an essential part of the transformation. By acting as a bridge, LTE base stations facilitate a smooth transition to the era of extremely quick, low-latency 5G connectivity while also guaranteeing backward compatibility. Heterogeneous networks, or HetNet, in conjunction with small cells, constitute a significant development in the LTE base station industry. Femtocells and picocells are examples of small cells that work in conjunction with standard macro base stations to improve coverage and capacity in densely populated areas. The network infrastructure is made more flexible and agile by this integration. The market for LTE base stations is active, with major players propelling rivalry and innovation. Leading companies in LTE base station development include Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson AB, Nokia Corporation, and ZTE Corporation. Technology is driven forward by competition, resulting in base station systems that are more feature-rich and efficient.
LTE base stations Market Drivers:
The relentless surge in demand for mobile data stands out as a primary catalyst propelling the LTE (Long-Term Evolution) base station market into the forefront of connectivity solutions.
The ubiquitous presence of smartphones has become synonymous with modern living. As these devices evolve into indispensable companions, their role extends beyond mere communication tools to sophisticated platforms for streaming, gaming, and accessing a plethora of data-driven applications. The seamless integration of smartphones into daily life drives an exponential increase in mobile data consumption. The advent of data-intensive applications, ranging from high-definition video streaming to cloud-based services, has reshaped user expectations. Consumers now demand instant access to rich media content, real-time collaboration, and immersive experiences, driving the need for networks capable of handling the data deluge. LTE base stations emerge as linchpins, providing the infrastructure to support these bandwidth-intensive applications. The global shift towards remote work has further intensified the demand for mobile data. With professionals relying on mobile devices for work-related tasks, video conferencing, and collaborative projects, the seamless flow of data becomes paramount. LTE base stations play a pivotal role in ensuring connectivity that supports the efficiency and productivity of remote work environments. The proliferation of IoT devices further contributes to the surge in mobile data demand. As users look ahead to the capabilities of 5G, LTE base stations serve as crucial components in the current network infrastructure, ensuring a smooth transition towards the 5G era.
The imminent transition to 5G networks is a defining driver shaping the LTE base station market.
As we move toward 5G, one of the main functions of LTE base stations is to make sure that everything works together. LTE technologies serve as fundamental components that facilitate the seamless integration of 5G capabilities when 5G networks progressively become available. By offering backward compatibility and facilitating a smooth transfer of current infrastructure, LTE base stations act as bridges. By optimizing spectrum resources, LTE-Advanced and LTE-Advanced Pro technologies improve spectral efficiency. When network operators get ready for the switch to 5G, LTE base stations are essential to making the most of the available spectrum and guaranteeing higher data rates and overall performance. By optimizing spectrum resources, LTE-Advanced and LTE-Advanced Pro technologies improve spectral efficiency. When network operators get ready for the switch to 5G, LTE base stations are essential to making the most of the available spectrum and guaranteeing higher data rates and overall performance. A crucial component of 5G networks is network slicing, which makes it possible to build isolated, virtualized networks to meet certain use cases. To meet the dynamic and varied needs of 5G applications, LTE base stations help prepare the network for network slicing by laying the groundwork for resource segmentation and optimization.
LTE Base Station Market Restraints and Challenges:
Spectrum scarcity remains a persistent challenge in the LTE base station market.
The electromagnetic spectrum, the foundation of wireless communication, is a finite resource. As the demand for high-speed data transmission surges, the available spectrum becomes a scarce commodity. LTE base stations, reliant on specific frequency bands within this spectrum, face constraints in accommodating the ever-growing number of connected devices and data-intensive applications. Spectrum allocation involves a delicate balancing act among diverse industries, each vying for its slice of the spectrum pie. Telecommunications, broadcasting, aviation, and public safety, among others, compete for spectrum resources. The challenge lies in reconciling the needs of these sectors while ensuring the efficient utilization of spectrum for LTE networks. Spectrum allocation often involves auctions where telecommunication operators bid for specific frequency bands. Economic factors, including bidding strategies, financial capacities of operators, and government revenue considerations, influence the outcome of these auctions. Balancing market dynamics with the need for widespread connectivity requires a nuanced approach. The evolution of wireless communication standards introduces new complexities in spectrum management. As LTE transitions to 5G and beyond, the need for additional spectrum and the reallocation of existing bands become pressing issues. Ensuring smooth transitions while maintaining backward compatibility poses a challenge for regulators and industry players alike. Dynamic spectrum sharing and innovative sharing frameworks allow different services to coexist within the same frequency bands. Implementing and standardizing such approaches requires collaboration among industry stakeholders.
The deployment of LTE base stations involves substantial infrastructure costs.
The upfront costs associated with deploying LTE base stations constitute a significant portion of infrastructure expenses. This encompasses the purchase of hardware, antennas, transmission equipment, and site acquisition. The need for strategic site selection, especially in densely populated urban areas or challenging terrains, adds a layer of complexity to deployment costs. Securing suitable sites for LTE base stations involves not just financial considerations but also navigating regulatory and zoning landscapes. Obtaining permits, complying with environmental regulations, and addressing community concerns contribute to the overall cost. Site acquisition expenses are influenced by the complexity of regulatory processes and community engagement efforts. Ensuring a reliable power supply for LTE base stations is essential for uninterrupted operation. Infrastructure costs include the installation of power systems, backup generators, and energy-efficient solutions. Additionally, establishing connectivity infrastructure, such as backhaul connections, contributes to the overall capital intensity of LTE deployments. Deploying LTE base stations in varied terrains, from urban landscapes to rural expanses, requires tailored solutions. Environmental factors, such as extreme weather conditions, may necessitate additional investments in resilient infrastructure.
LTE Base Station Market Opportunities:
The imminent transition to 5G networks presents a golden opportunity for LTE base station deployment. While 5G unfolds its potential, LTE remains a linchpin, offering a bridge to the future of ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity. LTE base stations play a pivotal role in supporting this transition, ensuring seamless network evolution and compatibility. Bridging the digital divide in rural and underserved areas emerges as a compelling opportunity. Governments and telecommunication operators are embarking on initiatives to expand LTE coverage to remote regions. This presents a vast untapped market where LTE base stations can play a transformative role in delivering connectivity to previously underserved populations. The integration of small cells and HetNet's (heterogeneous networks) offers a strategic opportunity to enhance network coverage and capacity. Small cells, including femtocells and picocells, can complement traditional LTE macro base stations, enabling operators to deploy agile and adaptive networks that cater to diverse user needs, especially in urban areas. The relentless surge in mobile data consumption propels the demand for enhanced network capacity. LTE base stations, especially those leveraging LTE-Advanced and LTE-Advanced Pro technologies, stand at the forefront of this opportunity. By optimizing spectral efficiency, these solutions empower network operators to meet the growing demand for higher data rates. Upgrading existing LTE base stations to support new features, higher data rates, and improved efficiency allows for capitalizing on the market's appetite for cutting-edge solutions without the need for complete infrastructure overhauls.
LTE BASE STATIONS MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
15.3% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product type, End User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, NEC,Fujitsu Airspan, Cisco Systems, CommScope, Motorola Solutions |
LTE Base Station Market Segmentation: By Product Type
-
Macro Base Stations
-
Microbase Stations
-
Pico Base Stations
-
Small Cells
Macro base stations are high-power base stations with wide coverage areas, typically used in urban and suburban environments. They hold the largest market share (around 60%) due to their widespread deployment for ensuring basic cellular connectivity. Microbase stations are the fastest-growing segment. They are lower-power base stations with smaller coverage areas, often used in urban areas to fill coverage gaps or provide high data capacity in specific locations. They account for approximately 25% of the market share. Small cells are even smaller, low-power base stations with very limited coverage areas, primarily used indoors or in dense urban environments to provide high data rates and improve capacity. Their market share is around 10% but is expected to grow rapidly. Pico base stations are the smallest and lowest-power base stations, typically used indoors for in-building coverage or in homes. They currently hold a small market share of around 5% but have potential for future growth in specific applications.
LTE Base Station Market Segmentation: by End User
-
Telecommunication Service Providers (TSPs)
-
Enterprises
-
Government Agencies
Telecommunication Service Providers (TSPs) are the largest and fastest-growing in this market, with a share of around 80%. TSPs like Verizon, AT&T, and China Mobile are the primary drivers of base station deployment to build and expand their mobile networks. Their needs focus on wide coverage, capacity, and cost-effectiveness. Enterprises account for roughly 15% of the market share. Enterprises like airports, factories, and corporate campuses deploy base stations for private LTE networks to ensure secure and reliable connectivity for their operations. Their needs prioritize security, customization, and dedicated bandwidth. The government agencies segment holds a smaller share of around 5% but is expected to grow. Governments deploy base stations for public safety networks, critical infrastructure communication, and rural connectivity initiatives. Their needs focus on reliability, emergency response capabilities, and wide-area coverage in remote areas.
LTE Base Station Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
Asia-Pacific holds the largest market share of around 33%. This region is driven by rapid economic growth, rising mobile data consumption, and government initiatives promoting infrastructure development. China and India are major contributors. The North American region accounts for roughly 30% of the market share, with established telecom infrastructure and high technology adoption. This is the fastest-growing region. Europe represents around 25% of the market share. Europe focuses on network modernization and targeted deployments in underserved areas. Stringent regulations and infrastructure challenges influence market dynamics. The South American region holds a smaller share of around 7% but exhibits promising growth potential due to increasing internet penetration and government investments in digital infrastructure.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global LTE Base Station Market.
The LTE Base Station market faced the brunt of semiconductor shortages, a consequence of disrupted supply chains. The scarcity of critical components, including microprocessors and memory chips, led to delays in manufacturing and deployment. Manufacturers grappled with challenges in sourcing essential components, hindering the production of LTE base stations. The semiconductor industry's interdependence exacerbated the impact, creating a ripple effect across the telecommunications ecosystem. Manufacturers faced logistical hurdles in maintaining operational continuity. Production delays not only impacted delivery timelines but also posed challenges in meeting the escalating demand for enhanced connectivity. The pandemic accelerated digital transformation initiatives across industries. Remote work, online education, and increased reliance on digital platforms led to a surge in demand for robust and reliable LTE connectivity. The heightened demand for LTE connectivity in both urban and remote areas presented opportunities for the LTE base station market. Operators sought to bolster network infrastructure to meet the evolving connectivity needs of a digitally transformed world. The economic fallout introduced challenges in funding large-scale LTE projects. Operators navigated budget constraints, affecting the pace of LTE base station deployment in certain regions. Supply chain diversification efforts present opportunities for strengthening the resilience of the LTE base station market, ensuring more robust responses to future disruptions.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
LTE base stations are no longer just signal transmitters. They're morphing into mini-data centers at the network edge, processing and storing data locally. This edge computing capability reduces latency, improves responsiveness for applications like AR and VR, and paves the way for the Internet of Things (IoT) explosion. Energy efficiency is a top priority. Manufacturers are developing eco-friendly base stations with features like sleep modes and power-saving technologies. Additionally, renewable energy sources like solar power are being integrated to reduce carbon footprints and operational expenses. Artificial intelligence is infiltrating base stations, optimizing performance and resource allocation in real time. Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) disrupts the traditional vendor-locked model, allowing operators to mix and match components from different suppliers. This fosters innovation, reduces costs, and promotes faster technology adoption. Bridging the digital divide is a key focus. Initiatives like small cell deployments and low-power base stations are bringing connectivity to remote areas previously considered uneconomical. Rural communities can access the benefits of online education, telehealth, and e-commerce, due to these targeted solutions. While 5G takes center stage, LTE isn't fading away. 5G-capable base stations are being designed to seamlessly integrate with existing LTE infrastructure, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing existing investments.
Key Players:
-
Huawei
-
Ericsson
-
Nokia
-
ZTE
-
Samsung
-
NEC
-
Fujitsu
-
Airspan
-
Cisco Systems
-
CommScope
-
Motorola Solutions
Chapter 1. LTE base stations Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. LTE base stations Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. LTE base stations Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. LTE base stations Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. LTE base stations Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. LTE base stations Market – By Product Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Macro Base Stations
6.3 Microbase Stations
6.4 Pico Base Stations
6.5 Small Cells
6.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Product Type
6.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Product Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. LTE base stations Market – By End User
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Telecommunication Service Providers (TSPs)
7.3 Enterprises
7.4 Government Agencies
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End User
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End User, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. LTE base stations Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By By Product Type
8.1.3 By End User
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By By Product Type
8.2.3 By End User
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By By Product Type
8.3.3 By End User
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By By Product Type
8.4.3 By End User
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Type
8.5.3 By End User
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. LTE base stations Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Huawei
9.2 Ericsson
9.3 Nokia
9.4 ZTE
9.5 Samsung
9.6 NEC
9.7 Fujitsu
9.8 Airspan
9.9 Cisco Systems
9.10 CommScope
9.11 Motorola Solutions
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
Rising mobile data consumption, evolution towards 5G, advancements in base station technology, edge computing capabilities, government initiatives for digital inclusion, and increasing demand for reliable and secure connectivity are the main key factors.
High deployment costs, energy consumption, spectrum availability, cybersecurity threats, an economic slowdown, and competition from alternative technologies are the main concerns.
Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, NEC, Fujitsu, Airspan, Cisco Systems, CommScope, Motorola Solutions
The Asia-Pacific currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 33%.
North America exhibits the fastest growth, driven by its massive population, expanding economies, and government programs aimed at bridging the digital divide and fostering technological innovation.