Low-Alkali Cement Market Size (2024-2030)
The global low-alkali cement market is projected to grow from an estimated USD 3.7 billion in 2023 to USD 5.45 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.7% over the forecast period of 2024-2030.
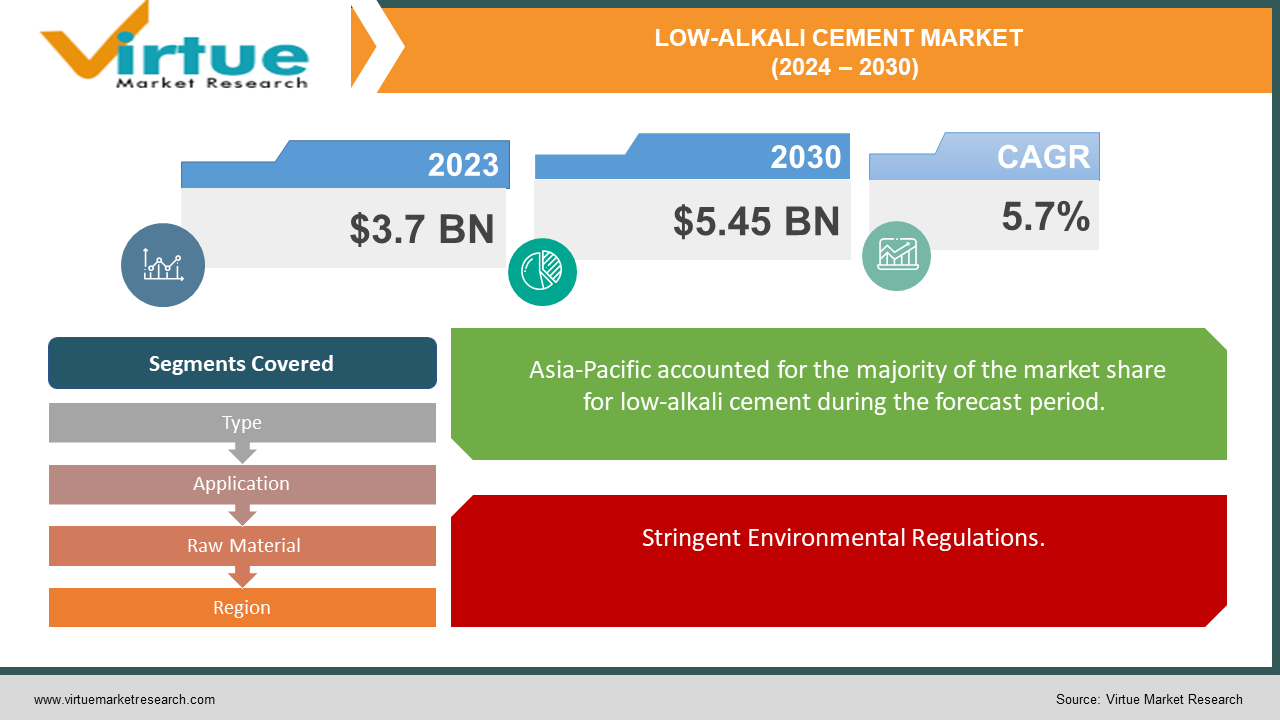
The low-alkali cement market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable construction materials and the need for high-durability cement in various infrastructure projects. In 2023, the market was valued at approximately USD 3.5 billion and is projected to reach around USD 5.2 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 5.7%. This growth is fueled by advancements in cement production technologies, stringent environmental regulations, and the rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific. Major players in the market, such as LafargeHolcim, HeidelbergCement, and Cemex, are continuously innovating and expanding their reach to capitalize on the increasing demand. The market's positive trajectory reflects a global shift towards eco-friendly construction practices and the adoption of materials that ensure long-term durability and resistance to chemical attacks.
Key Insights:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the consumption of low-alkali cement is expected to grow by 6.2% annually, fueled by rapid urbanization and extensive infrastructure development in countries like China and India.
Environmental regulations in Europe have led to a 15% increase in the adoption of low-alkali cement over the past five years, as construction companies strive to meet stricter sustainability standards.
Despite overall growth, the market in Latin America saw a decline of 2% in 2023 due to economic instability and reduced construction activity.
Global Low-Alkali Cement Market Drivers:
Increasing Demand for Sustainable Construction Materials.
The construction industry is increasingly focused on sustainability, driving the demand for eco-friendly materials like low-alkali cement. This type of cement reduces the environmental impact by minimizing the alkali content, which helps in mitigating the adverse effects of alkali-silica reactions (ASR) in concrete structures. As a result, low-alkali cement is becoming a preferred choice for green building projects, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and promote sustainable development.
Stringent Environmental Regulations.
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter environmental regulations to control emissions and promote the use of sustainable materials. In regions such as Europe and North America, these regulations are pushing construction companies to adopt low-alkali cement to comply with environmental standards. The regulatory push is not only helping to reduce the environmental impact but also fostering innovation in the production and application of low-alkali cement, thereby driving market growth.
Rapid Urbanization and Infrastructure Development.
Emerging economies, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, are experiencing rapid urbanization and substantial infrastructure development. Countries like China and India are investing heavily in building new residential, commercial, and industrial projects, which necessitates the use of durable and sustainable construction materials. The superior performance of low-alkali cement in terms of durability and resistance to chemical attacks makes it an ideal choice for these large-scale infrastructure projects, thereby significantly boosting its demand in these rapidly developing markets.
Global Low-Alkali Cement Market Restraints and Challenges:
High Production Costs.
The production of low-alkali cement involves additional processing steps and the use of specialized raw materials, leading to higher manufacturing costs compared to traditional cement. These increased costs can be a significant barrier for many manufacturers, especially in price-sensitive markets. The higher price point of low-alkali cement can also deter its adoption among cost-conscious builders and developers, limiting market penetration and growth.
Limited Awareness and Technical Knowledge.
Despite the benefits of low-alkali cement, there is still a lack of widespread awareness and technical knowledge about its advantages and proper application techniques among construction professionals. This knowledge gap can lead to reluctance to adopt new materials and practices. Additionally, the limited availability of trained personnel who can effectively work with low-alkali cement can hinder its implementation in various projects, particularly in developing regions.
Economic Instability in Emerging Markets.
Economic instability and fluctuating construction activity in emerging markets, such as parts of Latin America and Africa, pose challenges to the growth of the low-alkali cement market. Political uncertainties, economic recessions, and lack of investment in infrastructure can lead to reduced demand for construction materials, including low-alkali cement. **Solution:** To mitigate this, governments and industry stakeholders should focus on stabilizing the economic environment and providing financial incentives for infrastructure development, which can, in turn, boost the demand for low-alkali cement.
Global Low-Alkali Cement Market Opportunities:
Growing Demand for Green Building Certifications.
With the increasing emphasis on sustainable construction practices, there is a rising demand for green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). Low-alkali cement, known for its environmental benefits and durability, plays a crucial role in achieving these certifications. As more construction projects aim to meet these green standards, the demand for low-alkali cement is expected to rise, creating significant market opportunities.
Technological Advancements in Cement Production.
Innovations in cement manufacturing technology present substantial opportunities for the low-alkali cement market. Advancements such as the development of more efficient kiln processes, alternative raw materials, and the incorporation of industrial by-products can reduce production costs and improve the performance of low-alkali cement. These technological improvements not only make the product more competitive but also expand its application in various construction sectors, thereby driving market growth.
Infrastructure Development in Emerging Economies.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa, are undergoing rapid urbanization and infrastructure expansion. Governments in these regions are investing heavily in the construction of new roads, bridges, railways, and residential buildings to support economic growth and urban population needs. The superior durability and chemical resistance of low-alkali cement makes it ideal for such large-scale infrastructure projects, presenting a lucrative opportunity for market expansion in these fast-developing regions.
LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
5.7% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, application, raw material, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Lafarge Holcim, HeidelbergCement, Anhui Conch Cement, Cemex, China National Building Material (CNBM), Taiwan Cement Corporation, UltraTech Cement, Votorantim Cimentos, Dangote Cement, CRH plc, Buzzi Unicem, Siam Cement Group (SCG) |
Market Segmentation of Global Low-Alkali Cement Market:
Low-Alkali Cement Market Segmentation: By Type:
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- Sulphate Resistant Cement
- Other
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is the most widely used type of low-alkali cement, making it a highly effective segment of the market. Its versatility and strength make it a preferred choice for a variety of construction applications, ranging from residential buildings to large-scale infrastructure projects. The low-alkali formulation of OPC minimizes the risk of alkali-silica reactions (ASR), which can cause significant structural damage over time. This enhanced durability is particularly valuable in environments exposed to moisture and chemical attacks. Moreover, the established production processes and widespread availability of OPC contribute to its cost-effectiveness and ease of adoption in the construction industry. As a result, OPC continues to drive significant demand in the global low-alkali cement market, underpinning the growth and expansion of sustainable construction practices.
Low-Alkali Cement Market Segmentation: By Application:
- Residential Construction
- Commercial Construction
- Infrastructure Projects
- Industrial Construction
- Repair and Maintenance
Among the diverse applications driving the global low-alkali cement market, infrastructure projects stand out as particularly impactful. These projects encompass a broad spectrum, including bridges, highways, dams, and other essential public works. The demand for low-alkali cement in infrastructure arises from its ability to mitigate the risk of alkali-aggregate reaction (AAR), a chemical process that can cause significant structural damage over time. By utilizing low-alkali cement in infrastructure projects, stakeholders ensure longevity and durability, crucial for sustaining public safety and minimizing maintenance costs. This segment underscores the critical role of advanced cement formulations in enhancing the resilience and lifespan of vital infrastructure worldwide.
Low-Alkali Cement Market Segmentation: By Raw-Material:
- Natural Sources
- Industrial By-Products
- Others
Among the segmentation by raw materials in the cement industry, industrial by-products emerge as the most effective category. This includes materials like fly ash, slag from steel production, and silica fume, which are by-products of industrial processes. The utilization of these materials in cement production not only reduces the environmental footprint by reusing industrial waste but also enhances the performance characteristics of cement. Industrial by-products contribute to the development of sustainable cement solutions by improving strength, and durability, and reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional cement production methods. This segment reflects a growing trend towards environmentally responsible practices in construction materials, fostering innovation and resilience in the cement industry.
Low-Alkali Cement Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
The global cement industry is geographically diverse, with significant market shares distributed across various regions. Asia-Pacific leads with a dominant 35% share, driven by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and extensive infrastructure projects in countries like China and India. North America follows closely with a 30% share, supported by robust construction activity and infrastructure investments across the United States and Canada. Europe holds a 15% share, characterized by stringent environmental regulations that promote sustainable cement production practices. South America and the Middle East & Africa each account for 10% of the market share, fueled by growing construction sectors and increasing infrastructure development in regions like Brazil and the Gulf Cooperation Council countries, respectively. These regional dynamics underscore the global nature of the cement industry, shaped by local economic conditions, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure demands.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Low-Alkali Cement Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the global low-alkali cement market, introducing challenges and reshaping demand dynamics. Initially, the construction sector faced disruptions due to lockdowns, supply chain interruptions, and labor shortages, leading to project delays and cancellations worldwide. As economies gradually reopened, recovery in construction activities varied across regions, influencing the demand for low-alkali cement differently. Moreover, shifting consumer preferences towards sustainable and durable construction materials have bolstered interest in low-alkali cement, driven by its ability to mitigate alkali-aggregate reactions (AAR) and enhance structural longevity. The pandemic underscored the importance of resilient and sustainable building materials, stimulating innovation and adaptation in the global low-alkali cement market to meet evolving industry demands amidst ongoing recovery efforts.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
The global low-alkali cement market is currently characterized by a strong emphasis on sustainability, spurred by increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures. Innovations in materials science and production techniques are enhancing the performance and applicability of low-alkali cement, particularly in mitigating alkali-aggregate reactions (AAR) and improving structural durability. This trend towards eco-friendly construction materials is reshaping market dynamics, driving demand across residential, commercial, and infrastructure sectors as stakeholders prioritize sustainable building solutions to meet stringent environmental standards globally.
Key Players:
- Lafarge Holcim
- HeidelbergCement
- Anhui Conch Cement
- Cemex
- China National Building Material (CNBM)
- Taiwan Cement Corporation
- UltraTech Cement
- Votorantim Cimentos
- Dangote Cement
- CRH plc
- Buzzi Unicem
- Siam Cement Group (SCG)
Chapter 1. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET– SCOPE & METHODOLOGY
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Sources
1.5. Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET– COMPETITION SCENARIO
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET - ENTRY SCENARIO
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET- LANDSCAPE
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET– BY Raw-Material
6.1. Introduction/Key Findings
6.2. Natural Sources
6.3. Industrial By-Products
6.4. Others
6.5. Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Raw-Material
6.6. Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Raw-Material , 2024-2030
Chapter 7. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET– BY APPLICATION
7.1. Introduction/Key Findings
7.2. Residential Construction
7.3. Commercial Construction
7.4. Infrastructure Projects
7.5. Industrial Construction
7.6. Repair and Maintenance
7.7. Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By APPLICATION
7.8. Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By APPLICATION , 2024-2030
Chapter 8. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET– BY Type
8.1. Introduction/Key Findings
8.2. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
8.3. Sulphate Resistant Cement
8.4. Other
8.5. Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis Type
8.6. Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis Type , 2024-2030
Chapter 9. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET, BY GEOGRAPHY – MARKET SIZE, FORECAST, TRENDS & INSIGHTS
9.1. North America
9.1.1. By Country
9.1.1.1. U.S.A.
9.1.1.2. Canada
9.1.1.3. Mexico
9.1.2. By APPLICATION
9.1.3. By Type
9.1.4. By Raw-Material
9.1.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.2. Europe
9.2.1. By Country
9.2.1.1. U.K.
9.2.1.2. Germany
9.2.1.3. France
9.2.1.4. Italy
9.2.1.5. Spain
9.2.1.6. Rest of Europe
9.2.2. By APPLICATION
9.2.3. By Type
9.2.4. By Raw-Material
9.2.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.3. Asia Pacific
9.3.1. By Country
9.3.1.1. China
9.3.1.2. Japan
9.3.1.3. South Korea
9.3.1.4. India
9.3.1.5. Australia & New Zealand
9.3.1.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.3.2. By APPLICATION
9.3.3. By Type
9.3.4. By Raw-Material
9.3.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.4. South America
9.4.1. By Country
9.4.1.1. Brazil
9.4.1.2. Argentina
9.4.1.3. Colombia
9.4.1.4. Chile
9.4.1.5. Rest of South America
9.4.2. By APPLICATION
9.4.3. By Type
9.4.4. By Raw-Material
9.4.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.5. Middle East & Africa
9.5.1. By Country
9.5.1.1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
9.5.1.2. Saudi Arabia
9.5.1.3. Qatar
9.5.1.4. Israel
9.5.1.5. South Africa
9.5.1.6. Nigeria
9.5.1.7. Kenya
9.5.1.8. Egypt
9.5.1.9. Rest of MEA
9.5.2. By APPLICATION
9.5.3. By Type
9.5.4. By Raw-Material
9.5.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 10. GLOBAL LOW-ALKALI CEMENT MARKET– COMPANY PROFILES – (OVERVIEW, PRODUCT PORTFOLIO, FINANCIALS, STRATEGIES & DEVELOPMENTS)
10.1 Lafarge Holcim
10.2. HeidelbergCement
10.3. Anhui Conch Cement
10.4. Cemex
10.5. China National Building Material (CNBM)
10.6. Taiwan Cement Corporation
10.7. UltraTech Cement
10.8. Votorantim Cimentos
10.9. Dangote Cement
10.10. CRH plc
10.11. Buzzi Unicem
10.12. Siam Cement Group (SCG)
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The global low-alkali cement market is projected to grow from an estimated USD 3.7 billion in 2023 to USD 5.45 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.7% over the forecast period of 2024-2030.
The primary driver of the global low-alkali cement market is increasing awareness and regulations focused on reducing alkali-aggregate reactions (AAR) in concrete structures.
The key challenge facing the global low-alkali cement market is the need for widespread acceptance and adoption due to higher initial costs and limited awareness of its benefits.
In 2023, Asia-Pacific held the largest share of the global low-alkali cement market.
. LafargeHolcim, Heidelberg Cement, Anhui Conch Cement, Cemex, China National Building Material (CNBM), Taiwan Cement Corporation, UltraTech Cement, Votorantim Cimento, Dangote Cement, CRH plc, Buzzi Unicem, Siam Cement Group (SCG) are the main players.



