Heavy Fuel Oil Market Size (2024 – 2030)
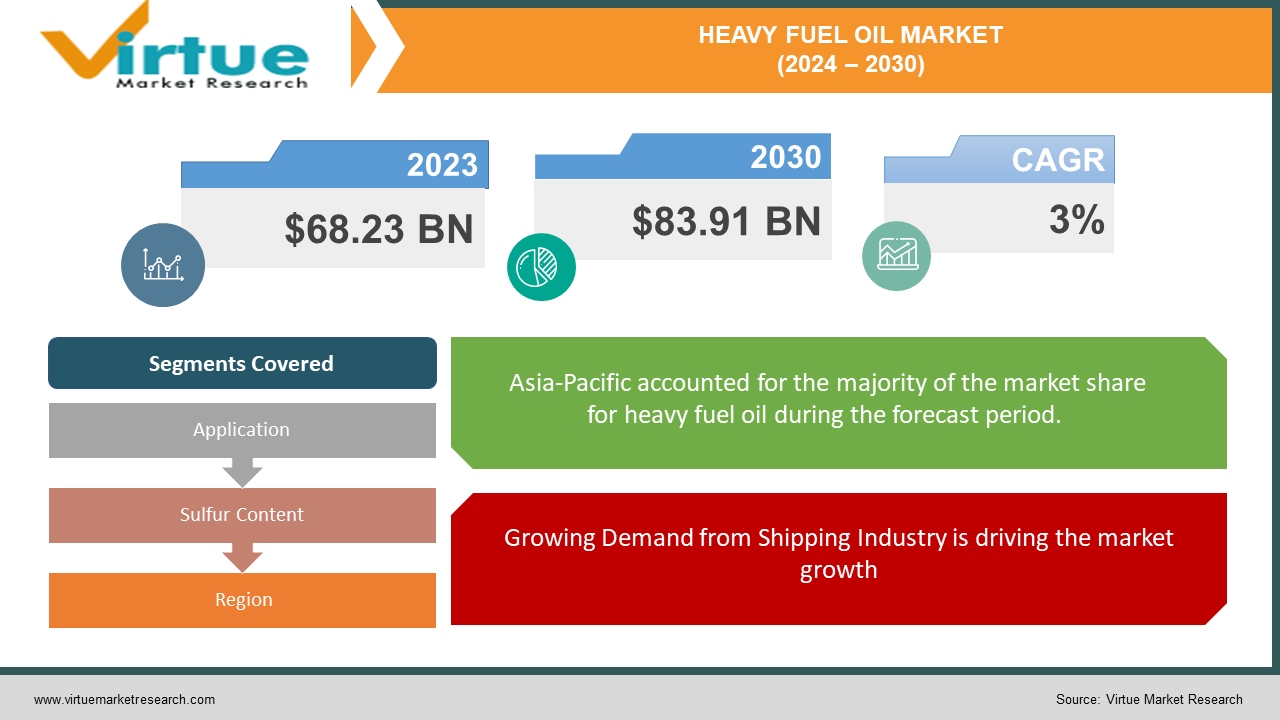
The Global Heavy Fuel Oil Market was valued at USD 68.23 billion in 2023 and will grow at a CAGR of 3% from 2024 to 2030. The market is expected to reach USD 83.91 billion by 2030.
The global heavy fuel oil market, valued in the tens of billions of dollars, is a vital cog in global trade and industry. Powering ships, especially large cargo vessels, remains its dominant application. While its established infrastructure and lower upfront costs make it attractive for developing economies in both maritime and industrial sectors, stricter environmental regulations and a push for cleaner alternatives are challenging its long-term dominance.
Key Market Insights:
Asia-Pacific currently leads the market with market share 31.6%, but its growth is projected to slow, while other regions like North America and South America might play a more prominent role in the future.The market exhibits regional differences due to factors like economic development, energy policies, and infrastructure.Increased global trade activity is a major driver, as heavy fuel oil remains the primary fuel for many maritime vessels. The market is expected to cross 90 billion by next 10 years.Heavy fuel oil is used in various industries like power generation, refineries, and building materials production.A major challenge of the market is the high sulfur content of heavy fuel oil, leading to stricter regulations and a push for cleaner alternatives. However, compliance solutions like scrubbers may create temporary growth opportunities.
Global Heavy Fuel Oil Market Drivers:
Growing Demand from Shipping Industry is driving the market growth
Heavy fuel oil (HFO) maintains a strong grip on the shipping industry, particularly for powering larger vessels. This dominance stems from several factors. First, HFO boasts a well-established infrastructure for bunkering (refuelling) ships at ports worldwide, making it readily available on most maritime trade routes. Additionally, the sheer size and power requirements of large cargo ships make HFO an attractive choice. While cleaner burning options like LNG are emerging, the technology for efficiently storing and using them on these massive vessels is still under development. Finally, the economics play a role. HFO remains a relatively low-cost fuel source, especially compared to cleaner alternatives. While stricter environmental regulations might lead to a gradual shift towards cleaner fuels, HFO's dominance in powering global maritime trade is likely to continue in the near to mid-term.
Economic Development in Emerging Economies is driving the market growth
As developing nations experience booming economies and ramp up industrialization, their energy needs soar. Heavy fuel oil (HFO) steps in as a compelling solution in the short term, thanks to two key advantages. Firstly, HFO benefits from a well-established infrastructure. From storage facilities to readily available bunkering options, the system is already in place, making it easy for these developing economies to access and utilize HFO. Secondly, HFO boasts a significant cost advantage, particularly when compared to some cleaner burning alternatives. The upfront investment required for cleaner technologies can be a major hurdle for developing economies. While this reliance on HFO might not be ideal for the environment, its affordability and readily available infrastructure make it a pragmatic choice for these countries as they focus on establishing a strong industrial base. However, it's crucial to remember that this is likely a short-term solution. As environmental regulations become stricter and cleaner technologies become more affordable, developing economies will need to transition towards more sustainable energy sources.
Industrial Applications is driving the market growth
Heavy fuel oil (HFO) isn't just for powering ships. It plays a vital role in various industrial processes across the globe, particularly in regions lacking readily available or cost-effective cleaner alternatives. Industries like cement production, steel manufacturing, and power generation rely heavily on HFO to generate the intense heat and power required for their operations. These industries often operate in locations with limited access to cleaner burning options like natural gas, or where the infrastructure for such options might be underdeveloped. Additionally, the upfront costs associated with implementing cleaner technologies can be a significant barrier for these industries. HFO, with its established infrastructure and lower initial investment, becomes a pragmatic choice. However, this reliance on HFO comes with environmental drawbacks, as its combustion releases pollutants. As regulations tighten and clean technology costs become more competitive, these industries will be under pressure to find sustainable alternatives. In the meantime, HFO remains a crucial industrial workhorse, especially in developing regions.
Global Heavy Fuel Oil Market challenges and restraints:
Shift Towards Cleaner Alternatives is restricting the market growth
Heavy fuel oil's reign as king of dirty energy might be nearing its end. Environmental concerns are fueling a fiery competition for cleaner alternatives. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is emerging as a major threat, posing a significant challenge to the heavy fuel oil market. Unlike its heavy counterpart, LNG burns much cleaner, emitting less sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and harmful particulates. This translates to cleaner air and a healthier planet. Moreover, LNG is increasingly seen as a more sustainable option for powering maritime vessels and industrial operations. As environmental regulations tighten and the push for cleaner energy intensifies, heavy fuel oil is likely to face increasing pressure to clean up its act or risk being left behind in the dust (or should we say, fumes) of progress.
High Upfront Costs of Transition is restricting the market growth
Switching gears from heavy fuel oil to cleaner options isn't as simple as flipping a switch. The biggest hurdle? The hefty price tag. Adopting cleaner technologies like LNG-powered engines or installing scrubber systems to reduce emissions on existing ships requires significant upfront investments. These costs can be a major barrier for many industries, particularly those with tight margins. Imagine a small shipping company struggling to afford a new LNG-powered vessel. The transition becomes a slow climb instead of a swift leap, potentially delaying the widespread adoption of cleaner alternatives and hindering the overall shift away from heavy fuel oil.
Market Opportunities:
The heavy fuel oil market isn't all doom and gloom. Opportunities exist for those who can navigate the challenges. Firstly, stricter environmental regulations create a demand for compliance solutions. Companies that develop and manufacture efficient scrubber systems, which can clean emissions from existing ships burning heavy fuel oil, might experience a temporary boom. Secondly, the vast existing infrastructure for heavy fuel oil, especially in developing economies, suggests a continued role for this fuel in the short to medium term. Companies that can provide high-quality, low-sulfur heavy fuel oil that meets stricter regulations can cater to this ongoing demand. Thirdly, innovation in cleaner burning heavy fuel oils is a possibility. Research into technologies that reduce emissions or improve combustion efficiency could offer a lifeline to the industry. Finally, the heavy fuel oil market's future might lie in specialized applications. In situations where alternative fuels are impractical or too expensive, improved efficiency and emission reduction technologies could allow heavy fuel oil to remain a viable option in specific sectors. While the long-term trend is towards cleaner energy sources, companies that embrace innovation, compliance solutions, and cater to specialized needs can carve out opportunities in the evolving heavy fuel oil market.
HEAVY FUEL OIL MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
3% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Application, Sulfur Content, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch Shell, BP, Chevron Corporation, Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco), China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), Rosneft, TotalEnergies , Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) Marathon Petroleum Corporation |
Heavy Fuel Oil Market Segmentation - by Application
-
Maritime Transportation
-
Industrial Applications
The most dominant application for heavy fuel oil is in Maritime Transportation. It's the lifeblood of a large portion of the global shipping fleet, powering massive cargo ships that carry goods across oceans. While industrial applications like power generation and manufacturing also rely on heavy fuel oil, their consumption pales in comparison to the vast quantities used by the global shipping industry.
Heavy Fuel Oil Market Segmentation - By Sulfur Content
-
High Sulfur Fuel Oil (HSFO)
-
Low Sulfur Fuel Oil (LSFO)
The dominance of High Sulfur Fuel Oil (HSFO) is under threat. Traditionally, HSFO has been the king of the heavy fuel oil market due to its lower cost. However, stricter environmental regulations to curb air pollution from ships are rapidly changing the game. Low Sulfur Fuel Oil (LSFO), a cleaner alternative with a lower sulfur content, is becoming increasingly dominant as it complies with these regulations. This shift is likely to continue as environmental concerns and regulations tighten, pushing the heavy fuel oil market towards cleaner options.
Heavy Fuel Oil Market Segmentation - Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
Asia-Pacific has reigned supreme, fueled by rapid industrial growth and a burgeoning maritime trade sector in countries like China and India. However, stricter environmental regulations and a push for cleaner fuels are starting to dampen demand in this region. North America remains a significant consumer, but its market is relatively mature. Europe leans towards cleaner alternatives, while South America and Middle East and Africa show potential for growth due to developing economies, though their overall market size is still smaller. The future landscape might see a more balanced market with Asia-Pacific's dominance waning and other regions playing a more prominent role.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Heavy Fuel Oil Market
The COVID-19 pandemic delivered a heavy blow to the global heavy fuel oil market. Strict lockdowns and travel restrictions caused a significant drop in global trade and maritime transportation, leading to a plummet in demand for heavy fuel oil, the lifeblood of the shipping industry. This resulted in a surplus of fuel and a sharp decline in prices. Refineries faced reduced demand for heavy fuel oil, impacting their operations and forcing some to cut production. However, the impact might be temporary. As global trade recovers and economic activity rebounds, demand for heavy fuel oil is expected to rise again. The long-term outlook remains uncertain. The pandemic might have accelerated the adoption of cleaner alternatives in some sectors, but heavy fuel oil is likely to retain a role in the energy mix for the foreseeable future, particularly in developing economies with established infrastructure. Stringent environmental regulations and a push for cleaner options will likely continue to pressure the market, but opportunities might exist for companies that can provide compliant fuels, develop cleaner burning technologies, or cater to specialized applications where heavy fuel oil remains the most viable option.
Latest trends/Developments
The tides are turning in the heavy fuel oil market, driven by a fierce battle for cleaner energy. Environmental regulations are tightening, pushing the industry towards adopting cleaner alternatives like LNG, which boasts significantly lower emissions. This has heavy fuel oil scrambling to clean up its act. While scrubber systems offer a temporary solution for existing ships, innovation in cleaner burning heavy fuel oils and improved efficiency technologies are being explored to extend its lifespan. However, the high upfront costs of switching to LNG or implementing scrubber systems pose a major hurdle, especially for developing economies with established heavy fuel oil infrastructure. This creates a potential short-term opportunity for companies providing compliant low-sulfur heavy fuel oil and efficient scrubber systems. The long-term trend is undeniable: the heavy fuel oil market needs to adapt or risk being overshadowed by cleaner options. The future might see a specialization of heavy fuel oil, remaining a viable choice for specific applications where alternatives are impractical, alongside continued use in developing regions. Ultimately, innovation and a focus on compliance will be key for companies navigating this evolving landscape.
Key Players:
-
ExxonMobil
-
Royal Dutch Shell
-
BP
-
Chevron Corporation
-
Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco)
-
China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC)
-
Rosneft
-
TotalEnergies
-
Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC)
-
Marathon Petroleum Corporation
Chapter 1. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Heavy Fuel Oil Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – By Application
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Maritime Transportation
6.3 Industrial Applications
6.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Application
6.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Application, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – By Sulfur Content
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 High Sulfur Fuel Oil (HSFO)
7.3 Low Sulfur Fuel Oil (LSFO)
7.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Sulfur Content
7.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Sulfur Content, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Heavy Fuel Oil Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By Application
8.1.3 By Sulfur Content
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By Application
8.2.3 By Sulfur Content
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By Application
8.3.3 By Sulfur Content
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By Application
8.4.3 By Sulfur Content
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Application
8.5.3 By Sulfur Content
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. Heavy Fuel Oil Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 ExxonMobil
9.2 Royal Dutch Shell
9.3 BP
9.4 Chevron Corporation
9.5 Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco)
9.6 China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC)
9.7 Rosneft
9.8 TotalEnergies
9.9 Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC)
9.10 Marathon Petroleum Corporation
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Heavy Fuel Oil Market was valued at USD 68.23 billion in 2023 and will grow at a CAGR of 3% from 2024 to 2030. The market is expected to reach USD 83.91 billion by 2030.
Growing Demand from Shipping Industry, Economic Development in Emerging Economies these are the reasons which is driving the market.
Based on sulphur content it is divided into two segments – High Sulfur Fuel Oil (HSFO), Low Sulfur Fuel Oil (LSFO)
Asia Pacific is the most dominant region for the Heavy Fuel Oil Market.
ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch Shell, BP, Chevron Corporation