Prescription Drugs Market Size (2025-2030)
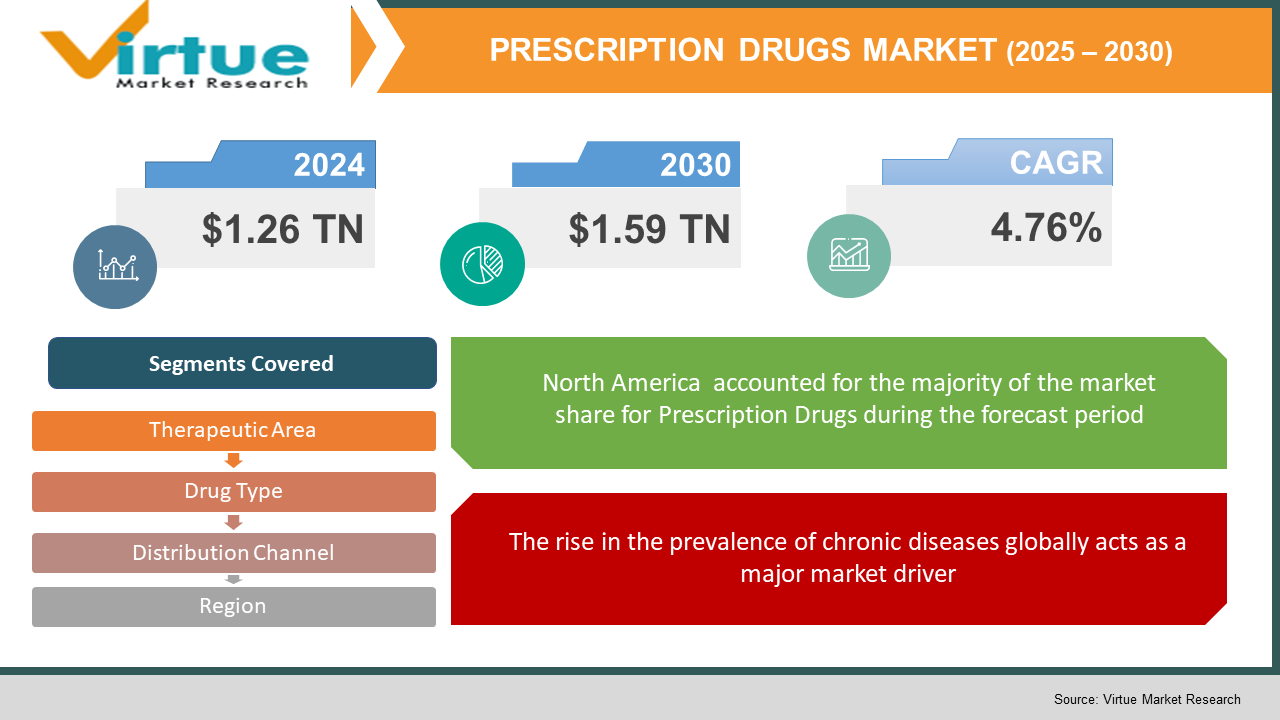
The Global Prescription Drugs Market was valued at USD 1.26 trillion and is projected to reach a market size of USD 1.59 trillion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.76%.
A projected strong development in the worldwide prescription drugs sector from 2025 to 2030 is to be experienced. Rising rates of chronic diseases, improvements in pharmaceutical research, and the growth of medical facilities help drive this growth. The market covers many different therapeutic fields, including neurology, cardiology, and oncology. The rise in the need for personalized medicine and the introduction of creative drug formulations also help to drive the market's expansion.
Key Market Insights:
- Particularly in the areas of obesity and chronic diseases, the prescription drug industry is seeing innovative treatments beginning to arise. For instance, Eli Lilly intends to meet the requirements of around 900 million people worldwide by launching Mounjaro, their diabetes and weight-loss medication, in several big developing markets. The increasing number of cyber pharmacies is changing the distribution environment and offering customers more easily available buying alternatives.
Prescription Drugs Market Drivers:
The rise in the prevalence of chronic diseases globally acts as a major market driver.
Roughly one in three people globally have multiple chronic conditions (MCCs), including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and cancer. Rising rates of chronic diseases lead to more expensive healthcare costs, much of which goes to prescription drugs.
Recent advancements in drug development are seen as an important market driver.
The integration of genomics, pharmacogenomics, and biomarker discovery allows the development of targeted treatments that improve treatment effectiveness and reduce side effects. Accelerating drug discovery and delivery, optimizing treatment regimens, and improving patient outcomes are artificial intelligence methods such as machine learning and deep learning. The goals of precision medicine are being supported by advanced computational techniques that are enabling the development of customized treatments.
The rise in the aging population is also a key market driver leading to increased demand in the market.
Chronic illnesses, which seniors are more vulnerable to, cause more need for prescription medicines. Because of the frequency of polypharmacy among senior citizens, careful control is needed to guarantee treatment compliance and lower adverse drug interactions.
The development of healthcare infrastructure is a key market driver, helping it to expand.
Improved healthcare infrastructure and services, especially in developing countries, provide easier access to prescription medicines, therefore driving market expansion. Government measures directed at broadening health coverage and lowering drug prices are raising prescription medication availability.
Prescription Drugs Market Restraints and Challenges:
The high levels of costs related to drug development are a major challenge faced by the market.
Estimates show that creating a new prescription medicine is an expensive process with an average cost that has notably increased throughout the last two decades. For smaller pharmaceutical businesses, these considerable financial needs present major obstacles that might stymie creativity and restrict their capacity to introduce new treatments to the market.
Strict rules and regulations act as a great challenge for the market, affecting its growth.
Pharmaceutical firms have to negotiate complex and different legal standards in many countries, which might slow down drug approvals and market entry, therefore impeding timely access to new treatments. Strict rules have to be followed to guarantee drug safety and performance, but doing so calls for significant time and great financial support.
The pressure of affordable pricing affects the potential growth of the market.
Government programs and public demand for inexpensive healthcare are driving price controls that affect pharmaceutical firms' profit margins. For instance, the European Union has declared plans to lower dependence on Asia for antibiotics and other vital medicines to fix weaknesses in the supply chain and maybe affect drug pricing dynamics.
The competition in the generic drug segment affects the market by affecting its sales.
Market competition is increased by the proliferation of generic medicines after patent expiries, hence impacting the sales of brand-name medicines. Rising competition from generic drugs could cause major price cuts in medicine, therefore helping customers but straining the income streams of original drug developers.
Prescription Drugs Market Opportunities:
The developing nations present a great opportunity for this market to expand and grow its presence.
Pharmaceutical businesses have great growth chances in emerging markets, which include developing nations with better medical infrastructure. Though these areas constitute almost 85% of the world population, they get fewer than 10% of healthcare facilities, therefore showing a considerable unmet medical need. Growing economies and better healthcare infrastructure provide ideal conditions for drug manufacturers to grow their coverage and cater to fresh consumer groups. To meet the increasing need for health services and medicines, pharmaceutical companies are actively investing in these areas.
The emergence of telemedicine is leading to improved healthcare accessibility.
Especially in increasing healthcare availability, telemedicine has become a transforming power in the delivery of healthcare. It provides creative ideas to increase access to health services and better include underrepresented groups, including those in far-off locations. Integrating telemedicine helps healthcare professionals overcome geographical, financial, sociocultural, and infrastructural obstacles, improving prescription drug availability and fostering market expansion. Regulatory agencies are starting to see how telemedicine could enhance the delivery of healthcare.
The development of orphan drugs is helping the market to expand its operations globally.
Emphasizing rare diseases with unsatisfied medical needs gives pharmaceutical firms chances for product differentiation. Developing orphan medications not only fulfills these unmet demands but also lets businesses distinguish themselves in a less competitive environment. This emphasis may result in the creation of creative therapies that enhance patient outcomes for rare conditions. To help orphan medications gain development, regulatory authorities frequently offer credits. For pharmaceutical businesses, orphan drug development can be an appealing opportunity, including market exclusivity periods, grant subsidies, and tax credit incentives.
The collaboration among various companies offers an opportunity for the market to increase the drug development process.
Collaborations between research institutions and drug companies can greatly speed up the drug development timeline. Sharing knowledge, technology, and resources, these partnerships can enable more effective discovery and realization of new treatments. Working projects sometimes produce creative treatments. These collaborations could result in breakthroughs impossible by themselves by melding the technical knowledge of research institutions with the real-world experience of pharmaceutical firms.
PRESCRIPTION DRUGS MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
4.76% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Therapeutic area, drug type, distribution channel, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson, Merck and Co., Inc., GlaxoSmithKlien plc, Sanofi S.A., AstraZeneca plc, AbbVie Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Roche Holding AG |
Prescription Drugs Market Segmentation:
Prescription Drugs Market Segmentation: By Therapeutic Area
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Diabetes
- Neurology
- Respiratory Diseases
- Others
The increasing worldwide frequency of cancer has caused a surge in demand for oncology drugs. Oncology's supremacy in the prescription medications sector has been further confirmed by continuous developments in cancer treatments including targeted drugs and immunizations. Driven by aspects including inactive lifestyles and dietary habits, the worldwide incidence of diabetes is rising. Ongoing pharmaceutical treatments are needed in response to this spike, so driving the fast-expanding market of diabetes medications.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system: medications dealing with issues of the heart and blood vessels. Neurology includes medicinal remedies for diseases of the nervous system. Respiratory diseases include medicines for lung and breathing problems. Others segment include medicines for several other problems.
Prescription Drugs Market Segmentation: By Drug Type
- Brand-Name Drugs
- Generic Drugs
- Biologics
- Biosimilars
Established effectiveness and substantial market presence keep brand-name medications front runners. New treatments and ideas keep their preeminence alive. Accelerating development in this field results from biosimilars providing inexpensive replacements as patents for major biologics expire.
Biologics are often prescribed for long-term illnesses, complex drugs sourced from living organisms. Generic drugs are equivalent versions of branded medicines usually much less expensive.
Prescription Drugs Market Segmentation: By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
Retail pharmacies are the dominant segment. Offering access and custom services to a wide patient base, retail pharmacies continue to be the main source of prescription medicines. The ease of online shopping and advancements in digital health technology have led to a boom in the use of online pharmacies.
Prescription Drugs Market Segmentation: By Region
- North America
- Asia-Pacific
- Europe
- South America
- Middle East and Africa
North America is the leader of the market and Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market. Dominance in the prescription drugs sector for North America arises from its great healthcare spending, sophisticated medical infrastructure, and strong presence of major pharmaceutical companies. Significant market expansion in the Asia-Pacific prescription drugs sector is driven by fast economic development, improved healthcare infrastructure, and a large patient count. South America and the MEA regions are the emerging markets.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global Prescription Drugs Market:
The pharmaceutical sector has been dramatically impacted by the coronavirus epidemic, causing short-term changes as well as more permanent ones. Particularly among people trying to guarantee their treatments in uncertainty, there was a large accumulation of drugs, most notably respiratory system ones, at the start of the epidemic. Reduced manufacturing capabilities as a result of worldwide lockdowns and restrictions led to deficits in vital medicines. Prescription drug spending in the United States was greatly affected by the epidemic, and remarkable changes in outlay patterns were observed. The need for remote healthcare services during the epidemic hastened the acceptance of telemedicine, which changed prescription patterns and raised the popularity of the Internet pharmacy sector. Accelerated approval systems for COVID-19 treatments and vaccines show regulatory agencies' ability to react quickly to public health crises. Though the prescription medicines industry faced major hurdles during the COVID-19 epidemic, it also served as a driver for creativity, technological adoption, and regulatory change that would reshape the terrain for the next years.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) helps Medicare negotiate drug prices, which should lower consumer expenses. Still, some worry that regulating prices too much could stifle drug development and restrict access to new medicines.
Essential medicines for women's health are receiving more and more government subsidies. For example, the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) of Australia has dramatically lessened expenses for women and expanded access to essential healthcare by including medicines for contraception, endometriosis, and IVF treatment.
The growing incidence of obesity globally has raised the need for impactful weight control treatments, driving substantial capital in this field.
Key Players:
- Pfizer Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck and Co., Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKlien plc
- Sanofi S.A.
- AstraZeneca plc
- AbbVie Inc.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Roche Holding AG
Chapter 1. Prescription Drugs Market – SCOPE & METHODOLOGY
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary Distribution Channel s
1.5. Secondary Distribution Channel s
Chapter 2. Prescription Drugs Market – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2025 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Prescription Drugs Market – COMPETITION SCENARIO
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Distribution Channel Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Prescription Drugs Market - ENTRY SCENARIO
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes Players
4.5.6. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Prescription Drugs Market - LANDSCAPE
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Prescription Drugs Market – By Therapeutic Area
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Oncology
6.3 Cardiovascular Diseases
6.4 Diabetes
6.5 Neurology
6.6 Respiratory Diseases
6.7 Others
6.8 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Therapeutic Area :
6.9 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Therapeutic Area :, 2025-2030
Chapter 7. Prescription Drugs Market – By Distribution Channel
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Hospital Pharmacies
7.3 Retail Pharmacies
7.4 Online Pharmacies
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Distribution Channel
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Distribution Channel , 2025-2030
Chapter 8. Prescription Drugs Market – By Drug Type
8.1 Introduction/Key Findings
8.2 Brand-Name Drugs
8.3 Generic Drugs
8.4 Biologics
8.5 Biosimilars
8.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis Drug Type
8.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis Drug Type , 2025-2030
Chapter 9. Prescription Drugs Market, BY GEOGRAPHY – MARKET SIZE, FORECAST, TRENDS & INSIGHTS
9.1. North America
9.1.1. By Country
9.1.1.1. U.S.A.
9.1.1.2. Canada
9.1.1.3. Mexico
9.1.2. By Distribution Channel
9.1.3. By Drug Type
9.1.4. By Therapeutic Area
9.1.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.2. Europe
9.2.1. By Country
9.2.1.1. U.K.
9.2.1.2. Germany
9.2.1.3. France
9.2.1.4. Italy
9.2.1.5. Spain
9.2.1.6. Rest of Europe
9.2.2. By Distribution Channel
9.2.3. By Drug Type
9.2.4. By Therapeutic Area
9.2.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.3. Asia Pacific
9.3.1. By Country
9.3.1.1. China
9.3.1.2. Japan
9.3.1.3. South Korea
9.3.1.4. India
9.3.1.5. Australia & New Zealand
9.3.1.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.3.2. By Distribution Channel
9.3.3. By Drug Type
9.3.4. By Therapeutic Area
9.3.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.4. South America
9.4.1. By Country
9.4.1.1. Brazil
9.4.1.2. Argentina
9.4.1.3. Colombia
9.4.1.4. Chile
9.4.1.5. Rest of South America
9.4.2. By DRUG TYPE
9.4.3. By Distribution Channel
9.4.4. By Therapeutic Area
9.4.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.5. Middle East & Africa
9.5.1. By Country
9.5.1.1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
9.5.1.2. Saudi Arabia
9.5.1.3. Qatar
9.5.1.4. Israel
9.5.1.5. South Africa
9.5.1.6. Nigeria
9.5.1.7. Kenya
9.5.1.8. Egypt
9.5.1.9. Rest of MEA
9.5.2. By DRUG TYPE
9.5.3. By Distribution Channel
9.5.4. By Therapeutic Area
9.5.5. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 10. Prescription Drugs Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Packaging Automation Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
10.1 Pfizer Inc.
10.2 Novartis AG
10.3 Johnson & Johnson
10.4 Merck and Co., Inc.
10.5 GlaxoSmithKlien plc
10.6 Sanofi S.A.
10.7 AstraZeneca plc
10.8 AbbVie Inc.
10.9 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
10.10 Roche Holding AG
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Prescription Drugs Market was valued at USD 1.26 trillion and is projected to reach a market size of USD 1.59 trillion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.76%.
Before being given to a patient, a prescription drug calls for permission from a licensed medical expert. It is a medication that requires approval before being dispensed.
Research and development costs, production costs, market competition, and pricing approaches of pharmaceutical companies all affect prescription drug prices.
Manufacturing problems, supply chain interruptions, regulatory difficulties, or an unanticipated rise in demand can all cause drug shortages.
Before prescription medicines hit the market, the FDA manages their approval, production, and marketing to guarantee their quality, safety, and performance.



