Enterprise Software Market Size (2024 – 2030)
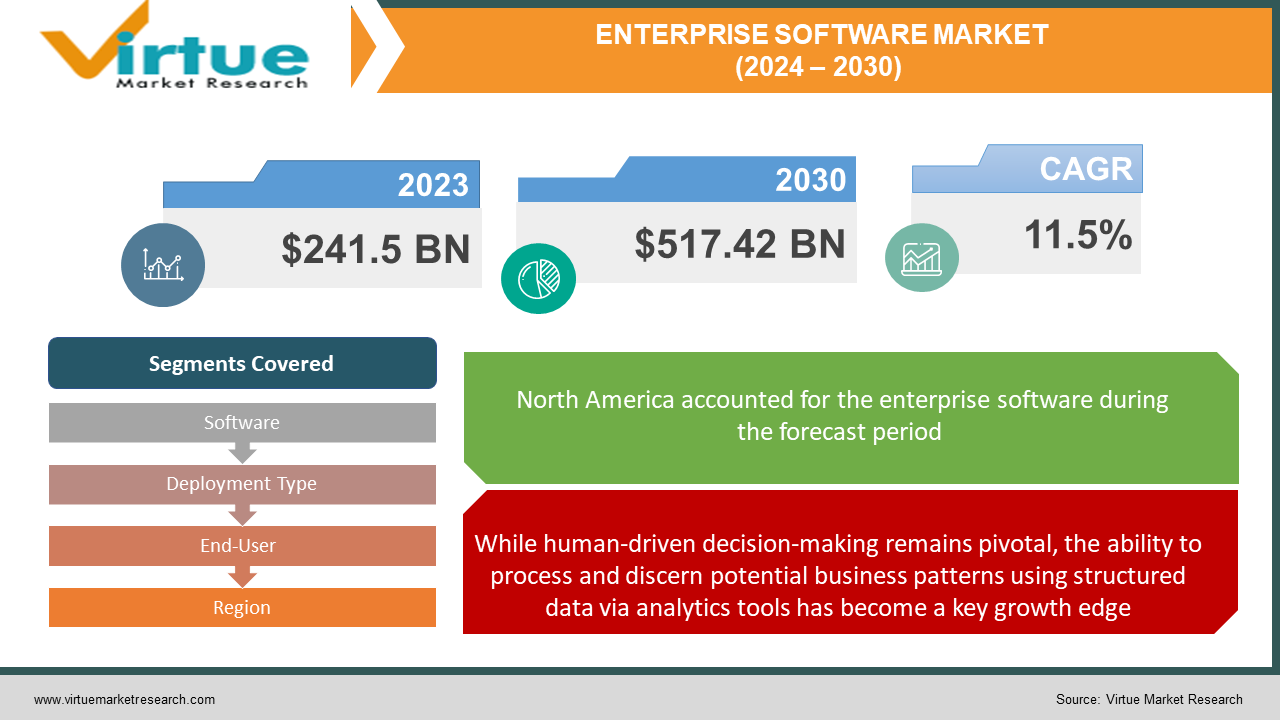
The enterprise software market was valued at USD 241.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 517.42 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024–2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5%.
The term enterprise software market describes on-premise and cloud-based software that facilitates collaboration, analysis, process automation, and fundamental business activities across expansive organizational settings. It includes domains such as supply chain management (SCM), analytics, human capital management (HCM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), productivity suites, databases, and infrastructure platforms. Due to the scattered labor requirements that come with globalization and the acceleration of digital transformation amid rapid technological breakthroughs, the industry has seen a tremendous boom in recent years. This demonstrates the critical role that business software programs play today as differentiators that set modern organizations apart from the competition and enable them to boost output, create new income streams, and cut expenses. Over the past ten years, there has been a noticeable trend in the market toward the use of integrated cloud-based business suites from top SaaS suppliers.
Key Market Insights:
A major shift witnessed involves organizations transitioning from licensed on-premise software suites to adopting flexible cloud-hosted solutions accessible over the internet. PwC expects around 70% of businesses to run operations predominantly via as-a-service cloud platforms by 2025, underscoring its dominant status as a preferred delivery medium due to advantages like reduced total cost of ownership, anytime-anywhere access, rapid scaling to accommodate spikes, and real-time upgrades. Currently, manufacturing, BFSI, and retail industry verticals together represent almost 38% of global enterprise software product adoption, according to Gartner. But over the next five years, telecom and professional services are expected to demonstrate higher growth rates owing to the digital transformation wave touching broader industry segments beyond conventional early adopters. Chief catalysts determining software spending budgets involve automating workflows, centralizing data lakes for advanced analytics, optimizing supply chain resiliency, boosting employee productivity, and ensuring regulatory compliance—mission-critical pillars benefiting from the latest tools.
Enterprise Software Market Drivers:
The potential that modern tools offer for process excellence through automation of complex business activities that traditionally relied on laborious, error-prone manual oversight and departmental coordination is one of the most important factors driving enterprise software adoption investments across functions and verticals.
One of the most prominent factors steering enterprise software adoption investments across functions and verticals involves the scope modern tools offer for process excellence through automation of complex business activities, which traditionally relied on tedious, error-prone manual oversight and coordination across departments. From supply chain execution and inventory management workflows spanning procurement, warehousing, dispatch, and reconciliations to delivering satisfactory service experiences by agents interacting with customers, even seemingly basic commercial operations encompass a myriad of interconnected sub-tasks often lost in siloed business units. This results in lapses impacting overall organizational efficiency directly tied to metrics like sales, attrition, and profitability when left unaddressed. Seeking a cure to such disconnects, integrated platforms like ERP, CRM, and analytics applications, through their modular approach, offer end-to-end visibility into convoluted operational sequences. Automating repetitive tasks via standardization into software systems minimizes deviation and enhances compliance across policy changes as updates propagate universally.
While human-driven decision-making remains pivotal, the ability to process and discern potential business patterns using structured data via analytics tools has become a key growth edge.
While experience-led human decision-making remains pivotal across management functions, the sheer volume and variety of structured data now available to enterprises enable the harnessing of analytical software to discern patterns and future scenario models to amplify planning prowess. As processes get increasingly digitized, critical business parameters across sales, customer interactions, inventory, logistics, compliance, etc. get perpetually logged into volumes spanning petabytes as data lakes. Though impossible to decipher intuitively at such microscopic granularity, analytics applications utilize the strengths of data science and machine learning to process, correlate, summarize, and highlight insights of value to different leadership roles. Such use of data-backed simulation capabilities, predictive analytics based on machine learning algorithms, interactive visualization dashboards that simplify complex interrelationships, and customizable reporting allows leaders to plan operations and growth strategically rather than relying solely on industry orthodoxies. In summary, deriving empirically validated models using trends harvested from their historical data using analytics software provides a competitive edge for leaders to course-correct strategies backed by tangible organizational insights rather than just market dynamics or third-party approximations. The ability to synthesize high-density quantitative evidence into directional signals hence remains a pivotal driver for the adoption of analytics capabilities within enterprise software environments as more entities realize beneficial use cases manifesting in growth and efficiency.
Enterprise Software Market Restraints and Challenges:The adoption of enterprise software, particularly cloud-based solutions, is significantly impacted by data security concerns. Companies are now extremely cautious about trusting sensitive data to cloud platforms and services provided by software suppliers due to high-profile data breaches.
Data security concerns greatly affect the adoption of enterprise software, especially cloud-based solutions. Because of the high-profile data breaches, businesses are now very wary about entrusting critical information to software suppliers' cloud platforms and services. Enterprise software platforms often centralize massive volumes of valuable data. Customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets are all tempting targets for cybercriminals. Nation-states actively develop hacking tools with increasing sophistication, sometimes directed at corporate targets for economic espionage or disruption of critical infrastructure. Ransomware attacks have exploded, and businesses heavily reliant on their operational software have become prime targets. Payment demands soar as days of lost operations rack up a financial toll beyond the ransom itself. Enterprise software vendors must adopt a 'security by design' philosophy. Data encryption, multi-factor authentication, strict access controls, proactive vulnerability scans, and swift patching are not features but fundamental tenets.
With cloud-based software, customers lack full visibility and control over how their data is being managed, secured, and accessed compared to on-premises solutions. They must fully trust vendors' security assurances. The loss of sensitive data sovereignty makes some prospects uncomfortable embracing the cloud.
With cloud-based enterprise software solutions, customers inherently cede some control compared to on-premises solutions, where they control the entire technology stack and infrastructure. This loss of control makes some enterprises uncomfortable about embracing the cloud. In the public cloud, customers lack full visibility into how their data is being managed, processed, and secured. They cannot inspect the underlying infrastructure or easily audit controls. Vendors only provide certain dashboards and reports giving snippet views of operations. Customers must trust vendors to properly secure their data. Customers become dependent on the vendor's ongoing commitment to security and system availability. If the vendor's platform has an outage or suffers a breach, customers have minimal control and recourse to immediately address the issue on their own. They must wait for the vendor to fix the problems. Public cloud services often implement standardized access controls that may not fully match an enterprise's specific security policies. Customers cannot customize role-based access tailored to their needs as precisely as with on-prem software.
Enterprise Software Market Opportunities:
Migrating enterprise systems and workloads to the cloud and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models present massive opportunities as organizations seek the flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency of cloud-based software. Vendors can enable smooth cloud transitions. Incorporating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation capabilities into enterprise software to drive efficiency, insights, and productivity is a big opportunity. Intelligent features will enhance value propositions. Software solutions that enable businesses to extract value from data through analytics, visualization, and useful business intelligence are in great demand. Offering data-driven insights and predictive analytics will give you a competitive edge. Specializing in tailored enterprise solutions for specific verticals like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing rather than generic horizontal solutions opens up opportunities to dominate niche markets. Industry-specific features improve relevance. Offering value-added security, access controls, and compliance management services on top of software solutions resonates with customers concerned about cyber threats and regulations. This provides differentiation. Supporting cutting-edge emerging technologies like IoT, edge computing, blockchain, AR/VR, and conversational interfaces in enterprise software will appeal to forward-looking customers. Staying ahead of the tech curve wins market share.
ENTERPRISE SOFTWARE MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
11.5% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Software, Deployment Type, End-User and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Salesforce, IBM, Workday ServiceNow, Infor, Epic Systems |
Enterprise Software Market Segmentation: By Software
-
Customer Relationship Management Software
-
Content Management Software
-
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
-
Supply Chain Management Software
-
Business Intelligence Software
-
Others
Customer relationship management software is the largest segment. Software for customer relationship management (CRM) enables companies to manage, track, and act upon client data. Additionally, it may assist companies in understanding their clientele, projecting their needs, and building a more efficient, successful business. Enterprise resource planning software is the fastest-growing category. Software for enterprise resource planning (ERP) assists companies in running their daily operations. For the sake of their particular requirements, cross-functional teams may use it as a centralized database. The ability of ERP software to help end-user organizations reduce their inventory and raw material costs and enable effective cross-functional information flow is the reason for the rise in demand for this software.
Enterprise Software Market Segmentation: By Deployment Type
-
On-Premises
-
Cloud-Based
-
Hybrid
The on-premises segment has the largest market. The category is growing because of the on-premise software's capacity to offer reliable services and improved data security without requiring an internet connection. Additionally, several users can use the system at different times without causing data transfer to lag, due to on-premise software. The cloud-based category is the fastest-growing. The benefits of cloud-based corporate software include reduced subscription and maintenance costs, continuous system accessibility, improved collaboration, and infinite storage space. These factors contribute to the program's increased popularity. To increase the value of their brands, corporate software suppliers are turning their focus back to cloud-based solutions.
Enterprise Software Market Segmentation: By End-User
-
Manufacturing
-
BFSI
-
Healthcare
-
Retail & E-commerce
-
Government and Public Sector
-
Others
BFSI has the largest market share in 2023. Banking, investment, and insurance rely on CRM, risk management, compliance software, and solutions tailored to handle complex financial transactions and regulations. Banks require ERP in large part because the banking sector is expanding and providing a greater range of services and operations. The volume of data and transactions processed daily increases with the number of services, which raises the possibility of human mistakes and necessitates longer processing times. Furthermore, cutting-edge technologies like AI and ML are being aggressively adopted by the banking industry, which is transforming how customers engage with banks. The healthcare sector is the fastest-growing. Electronic Health Records (EHR), clinical decision support systems, billing and payment processing, and telemedicine solutions drive this growing segment. The industry is predicted to develop as a result of advances in I.T. infrastructure and the increasing usage of cloud computing services in the healthcare sector. Moreover, a growing number of medical research institutes have employed information technology infrastructure.
Enterprise Software Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
Europe
-
North America
-
Asia Pacific
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America holds the largest market share, boasting roughly 35% in 2023. This dominance is driven by several factors, such as the early adoption of technology in business, well-established IT infrastructure, the presence of numerous major enterprise software vendors, a strong investment climate that favors innovation, and the adoption of new software solutions. Europe comes in as a strong second, holding a market share of roughly 30%. Maturity in European markets combined with strong data privacy regulations drive demand for robust enterprise solutions. Asia Pacific (APAC) is the fastest-growing market, with a share of roughly 25% and steadily increasing. Key factors for growth are rapidly expanding technology hubs, increased government initiatives to support digitalization, and a growing focus on operational efficiency and automation within businesses. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa (MEA) regions hold a smaller but gradually growing market share in the enterprise software realm.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Enterprise Software Market.
Organizations looked to cloud-based software's scalability and flexibility to accommodate remote work and evolving requirements, which led to an acceleration of cloud adoption and migration during the epidemic. Interest in SaaS and other cloud-based enterprise software has increased. Priorities shifted away from large transformational projects towards solutions supporting urgent remote work, collaboration, customer engagement, and cost optimization needs. Vendors had to adapt strategies. With employees displaced outside the office and priorities focused on crisis response, new software procurement faced delays. Complex contract negotiations and CIO approvals were stalled. Many enterprises faced budget cuts due to economic uncertainty, reducing technology expenditures. Certain new software initiatives and upgrades were postponed. Vendors had to realign pricing. As employees accessed enterprise systems remotely, security, access controls, and compliance became urgent priorities. Vendors responded with secure connectivity solutions. For healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and biomedical sectors directly involved in the COVID-19 response, demand rose for specialized software like telemedicine, drug development, lab, and logistics solutions.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
The shift from on-premises enterprise software to SaaS and cloud-based solutions is rapidly accelerating as organizations seek greater scalability, agility, and cost efficiencies. Cloud migration and hybrid cloud deployments are dominating strategic IT initiatives. Vendors like Adobe, Microsoft, and Salesforce have popularized subscription-based pricing and software/platform-as-a-service delivery models. This provides greater flexibility for enterprises to scale software usage up or down. SaaS is becoming mainstream. Advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning features are being added to enterprise software more and more to help find data insights, forecast results, suggest actions, and enable automation. Making decisions based on data is essential. Software solutions to optimize omni-channel customer experiences, journeys, and touchpoints are in high demand as user expectations rise. Customer data platforms are emerging to centralize CX data. While horizontal business software still dominates, demand is growing for solutions tailored to specific verticals like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing. Niche specialization allows for targeting underserved needs. APIs, microservice architectures, and containerization are enabling easier integration of disparate enterprise software components. Vendors are also partnering for enhanced interoperability. Enterprise security to protect increasingly distributed IT resources and workforces is a top investment priority.
Key Players:
-
SAP
-
Oracle
-
Microsoft
-
Salesforce
-
IBM
-
Workday
-
ServiceNow
-
Infor
-
Epic Systems
Chapter 1. Enterprise Software Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Enterprise Software Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Enterprise Software Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Enterprise Software Market Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Enterprise Software Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Enterprise Software Market – By Software
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Customer Relationship Management Software
6.3 Content Management Software
6.4 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
6.5 Supply Chain Management Software
6.6 Business Intelligence Software
6.7 Others
6.8 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Software
6.9 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Software, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Enterprise Software Market – By Deployment Type
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 On-Premises
7.3 Cloud-Based
7.4 Hybrid
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Deployment Type
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Deployment Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Enterprise Software Market – By End-user
8.1 Introduction/Key Findings
8.2 Manufacturing
8.3 BFSI
8.4 Healthcare
8.5 Retail & E-commerce
8.6 Government and Public Sector
8.7 Others
8.8 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End-user
8.9 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End-user, 2024-2030
Chapter 9. Enterprise Software Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
9.1 North America
9.1.1 By Country
9.1.1.1 U.S.A.
9.1.1.2 Canada
9.1.1.3 Mexico
9.1.2 By Software
9.1.3 By Deployment Type
9.1.4 By By End-user
9.1.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.2 Europe
9.2.1 By Country
9.2.1.1 U.K
9.2.1.2 Germany
9.2.1.3 France
9.2.1.4 Italy
9.2.1.5 Spain
9.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
9.2.2 By Software
9.2.3 By Deployment Type
9.2.4 By End-user
9.2.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.3 Asia Pacific
9.3.1 By Country
9.3.1.1 China
9.3.1.2 Japan
9.3.1.3 South Korea
9.3.1.4 India
9.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
9.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.3.2 By Software
9.3.3 By Deployment Type
9.3.4 By End-user
9.3.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.4 South America
9.4.1 By Country
9.4.1.1 Brazil
9.4.1.2 Argentina
9.4.1.3 Colombia
9.4.1.4 Chile
9.4.1.5 Rest of South America
9.4.2 By Software
9.4.3 By Deployment Type
9.4.4 By End-user
9.4.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.5 Middle East & Africa
9.5.1 By Country
9.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
9.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
9.5.1.3 Qatar
9.5.1.4 Israel
9.5.1.5 South Africa
9.5.1.6 Nigeria
9.5.1.7 Kenya
9.5.1.8 Egypt
9.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
9.5.2 By Software
9.5.3 By Deployment Type
9.5.4 By End-user
9.5.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 10. Enterprise Software Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
10.1 SAP
10.2 Oracle
10.3 Microsoft
10.4 Salesforce
10.5 IBM
10.6 Workday
10.7 ServiceNow
10.8 Infor
10.9 Epic Systems
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
Organizational efficiency and strategic decision-making are the main drivers in this market.
Data security and sensitive data sovereignty are the main concerns in the market.
SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Salesforce, IBM, Workday, ServiceNow, and Infor are the key players.
North America currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 35%.
Asia-Pacific exhibits the fastest growth, driven by its increasing population and expanding economy.



