Energy Market Size (2025-2030)
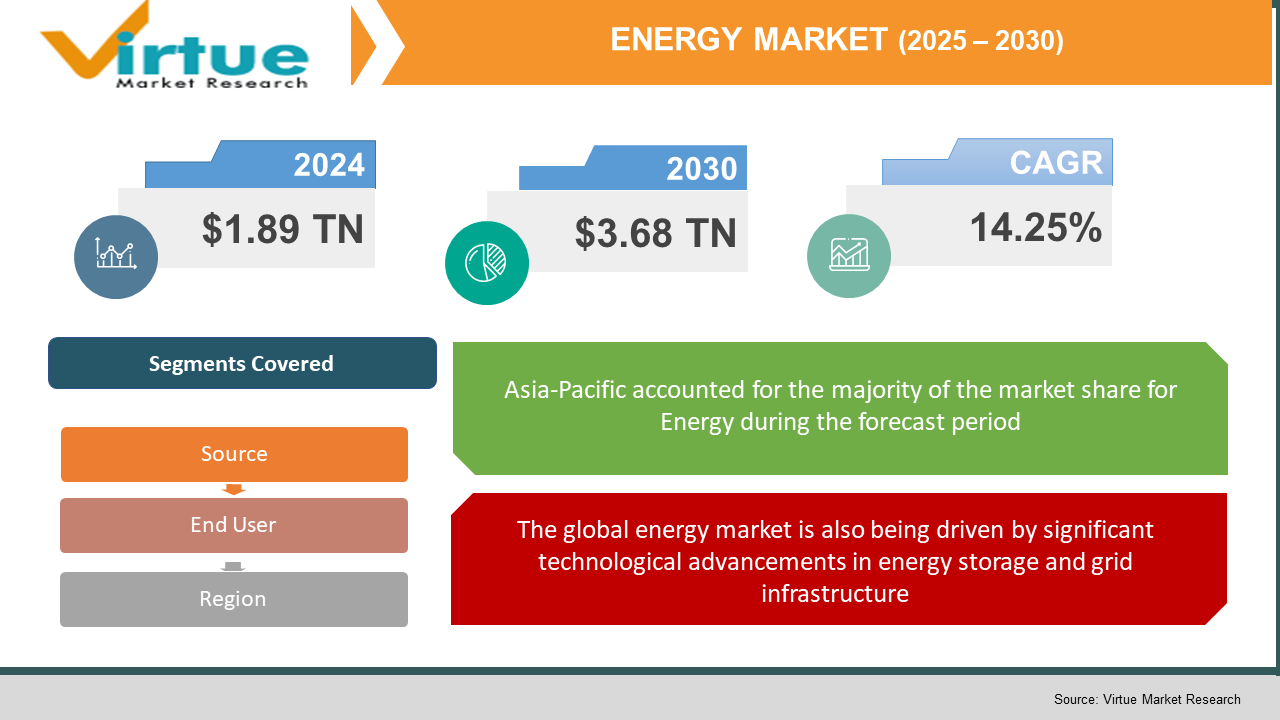
The Energy Market was valued at USD 1.89 trillion in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 3.68 trillion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.25%.
The global energy market is a very active, very mobile sector, yet is viewed in the form of production, dissemination, and consumption, all applicable to a variety of energy sources-intellectual or fossil fuels, nuclear, or renewable sources. Ever in the offing purely because of the rising global demand, meeting climate change commitments, and sustainable development, this dynamic industry is being transformed. Indeed, countries and corporations have turned their backs on conventional coal or oil energy systems into cleaner, more efficient alternatives such as solar, wind, hydropower, and hydrogen. In this respect, technological innovations in smart grids, energy storage, and digital monitoring are set to completely change the methodology of managing energy consumption. As new government regulations on emissions become stricter and further incentives are given to encourage investment in green energy, the energy market becomes a linchpin for future progress and can harness sustainability at its core.
Key Market Insights:
Electric vehicle (EV) sales reached over 14 million units in 2023, making up 18% of all car sales globally. This shift is drastically reducing dependency on gasoline and driving demand for clean electricity infrastructure.
More than 150 million homes now use rooftop solar systems globally, supported by declining panel costs and government subsidies. This decentralisation trend is reshaping traditional grid models and empowering individual consumers.
Energy Market Drivers:
One of the most significant drivers of the global energy market is the increasing demand for clean and renewable energy sources.
An increase in demand for clean and renewable energy sources has emerged as a key factor determining the trend of global energy markets. Amidst climate change, governments and the private sector are going in for an aggressive push to find alternatives to fossil fuels. When it comes to renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro, they are now being harnessed since they are less harmful to the environment and cheaper in the long run. The Paris Agreement and national net-zero targets are providing further impetus to the decarbonization of energy systems. Rapid urbanisation and industrialisation in developing economies have taken energy consumption levels to soaring heights, with a thrust for sustainable solutions. Increasing public awareness of environmental issues and health risks posed by fossil fuels is also feeding into energy policies. On the other hand, declining prices for solar panels and wind turbines are helping improve the economic viability of renewable projects. The global companies, in search of sustainability, are increasingly looking at green power purchase agreements (PPAs). This cumulative momentum is displacing the energy market from the core dynamics toward sustainability.
The global energy market is also being driven by significant technological advancements in energy storage and grid infrastructure.
The world's energy landscape is in change owing to technological advancements in energy storage and grid infrastructure. Being intermittent energy sources, solar and wind generate a great need for storing energy efficiently. Battery technologies, especially lithium-ion, solid-state, and flow batteries, are innovating towards the enhanced retention of energy and provision of stability to the grid. These technologies are improving the reliability of the grid with predictive maintenance to forecast outages based on patterns of usage to optimise power delivery. Demand response programs and decentralised energy systems allow consumers to be active participants in energy management. Quite often, the government also supports modernisation projects through funding and policy incentives. Some of these innovations will not just help create resilience in the energy systems but also improve the efficiency of integrating large-scale renewable energy, thus providing a sustained growth impetus in the market.
Energy Market Restraints and Challenges:
One of the major restraints in the global energy market is the high initial capital investment required for setting up renewable energy projects and modernising existing infrastructure.
The high initial capital outlays to set up renewable energy projects and develop the existing infrastructure remain one of the prime restraints of global energy markets. Although operational expenses for solar and wind energy are lower than those for fossil fuels over the long run, the front-end cost barriers arising from technology installation, land acquisition, transmission lines, and energy storage challenge even developing countries. So many areas do not have an enabling grid infrastructure to accommodate staggered inputs from renewable sources, causing inefficiencies and massive underutilization. Further, thus far, rural and remote areas grapple with problems like limited grid connectivity and high transmission losses, further discouraging renewable adoption. At the same time, attracting investments in areas politically unstable or economically weak poses further impediments to energy transition. The multiplicity of these infrastructure and funding-related challenges constitutes a sizable barrier to the large-scale development of clean and reliable energy systems, thereby rendering policy support and innovative financing critical to surmounting this particular limitation.
Energy Market Opportunities:
The global energy market is full of opportunity, especially with the world shifting toward a low-carbon future. One of the bright spots in this future is the area of renewable energy infrastructure, especially for solar and wind, and even green hydrogen, where vast opportunities are seen to accrue from a plethora of clean energy generation. Developments in electric vehicles (EVs) and the enabling infrastructures for them, such as their charging networks, present new opportunities for energy providers and technology innovators. Other horizons for inventive market opportunities include energy storage and smart grid technologies, creating new markets for advanced battery systems, AI-enabled power management, and decentralised energy models. Developing countries are perhaps the most promising opportunity, as increasing energy demand meets a rising need for sustainable development, encouraging investments in off-grid and microgrid systems. Also, public-private collaboration has been buoyed by policy initiatives, carbon pricing, and green financing mechanisms. However, probably the most significant growth markets for scalable, clean, and innovative energy solutions are expected to open up as global industries ramp up net-zero goals.
ENERGY MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
14.25% |
|
Segments Covered |
By SOURCE, END USER, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch Shell, BP, TotalEnergies, Chevron, NextEra Energy, Iberdrola, Enel, General Electric, Siemens Energy, Ørsted, Vestas, Tesla, Schneider Electric, and First Solar |
Energy Market Segmentation:
Energy Market Segmentation: By Source
- Fossil Fuels
- Renewable Energy
- Nuclear Energy
The global energy market is classified by source, including fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear energy. Fossil fuels are still the largest sources of energy worldwide, particularly used in developing countries due to the prerequisite of established infrastructure and high energy density. However, fossil fuels are coming under increased regulatory and environmental scrutiny due to greenhouse gas emissions. Solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy renewables are rapidly developing, spurred on by declining technology costs, government support, and demand for sustainable power. Solar and wind power, in that order, are undergoing rapid adoption, particularly in developed nations as well as emerging markets. Nuclear remains an ever-stable moderator to power an energy base and a carbon-free one, especially where countries have solid nuclear infrastructures, such as the U.S., France, and China. Advanced nuclear reactors and small modular reactors (SMR) investment show the potential for future growth. As countries aim for net-zero targets, a greater degree of the energy mix is expected to tilt toward renewables and nuclear, while phasing out coal and oil.
Energy Market Segmentation: By End User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Transportation
- Power Utilities
End-user segmentation offers different outlooks with respect to demand patterns and innovation needs. The residential sector continues to consume substantial electricity for lighting, appliances, and heating and cooling. The increasing adoption of rooftop solar and smart meters is also present. Commercial users, office spaces, hospitals, and retail demand power that is reliable and uninterrupted. Hence, investment in energy-efficient buildings and backup systems is growing. The industrial sector remains the largest consumer of energy, supported by manufacturing, mining, chemicals, and heavy industry, which have also become prime candidates for energy-efficient interventions and clean energy transformations. Transportation is transforming: the shift from fossil-fueled vehicles to EVs comes with grid integration and charging infrastructure, thus creating synergies between the transportation and electricity markets. Power utilities, the backbone of energy distribution, are now integrating more renewable sources, battery storage, and digital platforms such as smart grids. Each segment, therefore, presents unique opportunities and unique challenges, all focusing on reliability, efficiency, and sustainability during our forecast period.
Energy Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
The global energy market is showing a strong distinction of the regions across the requirements and landscape of energy use; the most predominant of these regions is Asia-Pacific, which seems to be characterised by a rapidly increasing population, aggressive industrialisation, and overwhelming urban energy needs. Countries like China and India are ensuring that expansion is subject to a growing demand for fossil fuels and capacity for renewables. North America is still playing a role, being driven by shale gas advances, strong renewable integration, and revamping energy infrastructure. Europe is the world leader in new energy policies and carbon-neutral goals; however, it is making gigantic contributions in wind, solar, and hydrogen energy investment. South America is exploiting its natural renewables, mostly in the area of hydro and solar power. In the Middle East and Africa, these continue to be tied to fossil fuels, but they are gradually going solar and forming energy partnerships to promote energy security and diversification. Their respective contributions to the global reality about energy markets are dependent on their resource bases, policy landscapes, and economic priorities.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Energy Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic had a very definite, multi-dimensional effect on the global energy market. Unprecedented drops in energy demand (especially for oil and gas), triggered by lockdowns, travel restrictions, and industrial closures in 2020, collided with price collapses and large financial losses in the fossil fuel sectors. Oil demand worldwide dropped by close to 9%, the steepest annual decline in history, hitting oil-exporting countries and companies hard. The crisis also accelerated the change in energy consumption patterns, and renewables have demonstrated resilience amid the disruption. Both solar and wind power continued growing thanks to government stimulus packages focusing on green recovery and climate commitments. Aside from these, the pandemic underscored the need for energy security, digital grid infrastructure, and decentralised solutions, spurring greater investments into smart grids, battery storage systems, and home energy management systems. In attempts to recover from the economic strain resulting from the pandemic, many countries have intensified their efforts in promoting clean energy production for economic survival. It is a watershed moment in the history of energy perspectives toward the future: toward a more sustainable energy future with resilience against the shocks.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
One of the most significant transitions in the global energy market is which encompasses rapid innovation, sustainability targets, and changes in consumption patterns. Rapid growth of renewable energy, in terms of installed capacity, investments, and the volume of projects, most notably solar, wind, and green hydrogen, dominated global energy trends during the past decade. Strategic alliances like that between RWE and Amazon now enable smarter energy forecasting and trading and AI-based optimisation of power usage. Smart grids and decentralised applications, including virtual power plants, storage, and microgrids, are on their way to integration with flexible and resilient energy systems. In parallel, the booming data centre segment is increasingly demanding hybrid power solutions, expressed in combinations of renewables, natural gas, and carbon capture technologies designed to ensure an uninterrupted and sustainable supply of energy. It doesn't stop here: hydrogen infrastructure breakthroughs, such as Australia's first hydrogen refuelling stations, so far firmly propel development toward clean fuels. Importantly, these are trends manifesting in global energy transition primarily revolving around digitalisation, decarbonization, and decentralisation, fundamentally shaping the new future of power generation and consumption.
Key Players:
- ExxonMobil Corporation
- Royal Dutch Shell plc
- BP plc
- TotalEnergies SE
- Chevron Corporation
- NextEra Energy, Inc.
- Iberdrola S.A.
- Enel S.p.A.
- General Electric (GE) Power
- Siemens Energy AG
Chapter 1. Energy Market – SCOPE & METHODOLOGY
1.1. Market Segmentation
1.2. Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3. Research Methodology
1.4. Primary End User
1.5. Secondary End User
Chapter 2. ENERGY MARKET – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2.1. Market Size & Forecast – (2025 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2. Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1. Demand Side
2.2.2. Supply Side
2.3. Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. ENERGY MARKET – COMPETITION SCENARIO
3.1. Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2. Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3. Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4. Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. ENERGY MARKET - ENTRY SCENARIO
4.1. Regulatory Scenario
4.2. Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3. Customer Analysis
4.4. PESTLE Analysis
4.5. Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2. Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3. Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4. Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5. Threat of Substitutes Players
4.5.6. Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. ENERGY MARKET - LANDSCAPE
5.1. Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2. Market Drivers
5.3. Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4. Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. ENERGY MARKET – By Source
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Fossil Fuels
6.3 Renewable Energy
6.4 Nuclear Energy
6.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Source
6.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Source , 2025-2030
Chapter 7. ENERGY MARKET – By End User
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Residential
7.3 Commercial
7.4 Industrial
7.5 Transportation
7.6 Power Utilities
7.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End User
7.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End User , 2025-2030
Chapter 8. ENERGY MARKET - By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1. North America
8.1.1. By Country
8.1.1.1. U.S.A.
8.1.1.2. Canada
8.1.1.3. Mexico
8.1.2. By End User
8.1.3. By Source
8.1.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2. Europe
8.2.1. By Country
8.2.1.1. U.K.
8.2.1.2. Germany
8.2.1.3. France
8.2.1.4. Italy
8.2.1.5. Spain
8.2.1.6. Rest of Europe
8.2.2. By Source
8.2.3. By End User
8.2.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3. Asia Pacific
8.3.1. By Country
8.3.1.1. China
8.3.1.2. Japan
8.3.1.3. South Korea
8.3.1.4. India
8.3.1.5. Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6. Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2. By Source
8.3.3. By End User
8.3.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4. South America
8.4.1. By Country
8.4.1.1. Brazil
8.4.1.2. Argentina
8.4.1.3. Colombia
8.4.1.4. Chile
8.4.1.5. Rest of South America
8.4.2. By Source
8.4.3. By End User
8.4.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5. Middle East & Africa
8.5.1. By Country
8.5.1.1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2. Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3. Qatar
8.5.1.4. Israel
8.5.1.5. South Africa
8.5.1.6. Nigeria
8.5.1.7. Kenya
8.5.1.8. Egypt
8.5.1.8. Rest of MEA
8.5.2. By Source
8.5.3. By End User
8.5.4. Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. ENERGY MARKET – Company Profiles – (Overview, Source Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 ExxonMobil Corporation
9.2 Royal Dutch Shell plc
9.3 BP plc
9.4 TotalEnergies SE
9.5 Chevron Corporation
9.6 NextEra Energy, Inc.
9.7 Iberdrola S.A.
9.8 Enel S.p.A.
9.9 General Electric (GE) Power
9.10 Siemens Energy AG
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The Energy Market was valued at USD 1.89 trillion in 2024 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 3.68 trillion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2025-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.25%.
The energy market is driven by the global push for decarbonization and the rising demand for reliable, sustainable power. Advancements in renewable technologies and supportive government policies are accelerating this transition.
Based on the Service Provider, the Energy Market is segmented into material manufacturers, Raw Material Suppliers, Lab information management systems, Distributors & Wholesalers, and End-to-End Solution Providers
Asia-Pacific is the most dominant region for the Energy Market.
ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch Shell, BP, TotalEnergies, Chevron, NextEra Energy, Iberdrola, Enel, General Electric, Siemens Energy, Ørsted, Vestas, Tesla, Schneider Electric, and First Solar are the key players in the Energy Market.



