Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market Size (2024 – 2030)
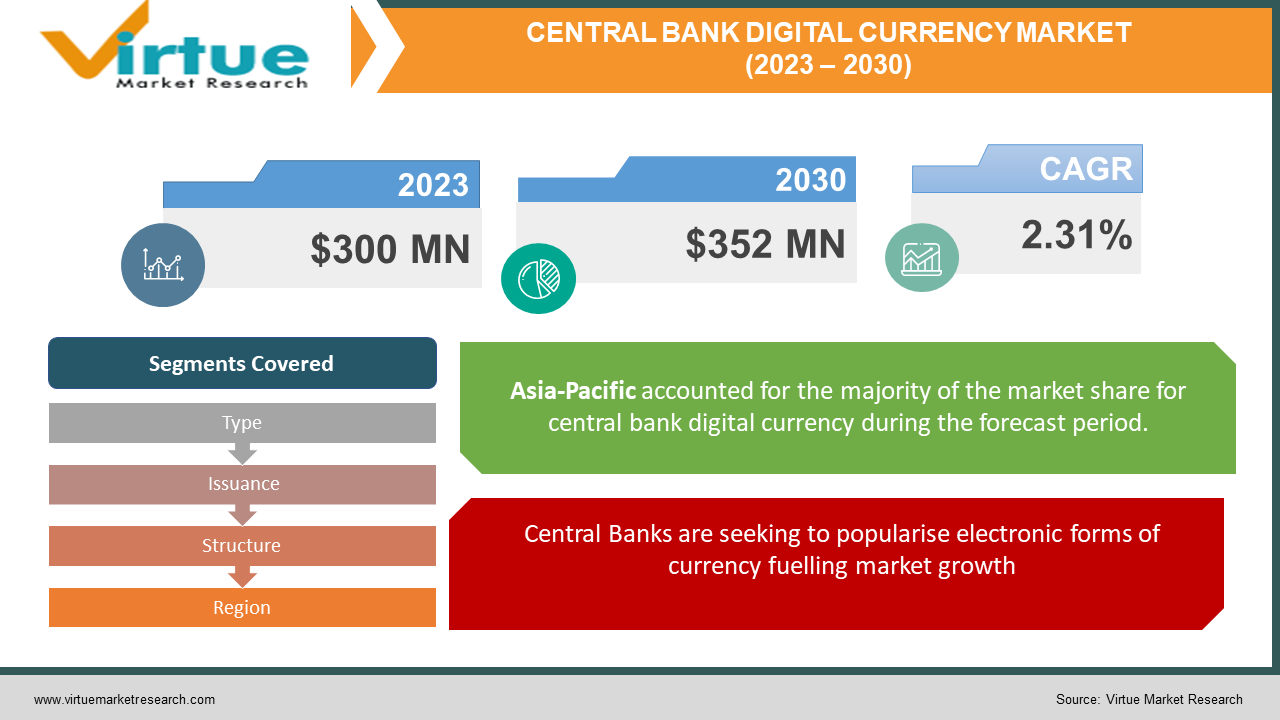
The Central Bank Digital Currency Market was valued at USD 300 Million in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 352 Million by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2.31%.
According to the definition given by the central bank, digital currencies are those that are issued by the bank and are connected to the country's currency. It is a digital equivalent of fiat money in the digital economy. The central bank, government-approved organizations, or both run the database that serves as its foundation. The database must be used in order to monitor CBDC flow. The main goals of CBDCs for businesses and customers alike are financial security, accessibility, privacy, transferability, and ease of use.
Key Market Insights
Nine out of ten central banks are investigating CBDCs, and more than half of them are actively creating or conducting actual trials with them, according to a survey report published by Banking International Settlements (BIS). More specifically, the process of establishing retail CBDCs has advanced. Moreover, a staggering 90% of the central banks included in the survey are working on CBDC initiatives. Overall, the research provides valuable insights into central banks' use of digital money and the path of monetary policy. Sixty-four countries make up the new high for the number of countries in the advanced phase of exploration (launch, pilot, or development).The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in India has been investigating and studying the possibilities of CBDCs for a considerable amount of time. On December 1, 2022, they also started the first pilot program for the Digital Rupee- Retail segment (e₹-R).
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Drivers:
Central Banks are seeking to popularise electronic forms of currency fuelling market growth.
Payment and settlement systems have made it possible for the common individual to access a vast array of digital opportunities, demonstrating how the globe is embracing the digital revolution. In order to complete a transaction, clients have a wide range of options to choose from these days. They select a payment method depending on the value they believe it has in a certain situation because each payment mechanism has a specific role and purpose. The shift from cash to electronic payments leads to an increased reliance on electronic payment systems, which impacts the payment environment's resilience and diversity. With the use of paper smoney decreasing, central banks hope to encourage a more widely recognized electronic form of payment. Using a lot of real currency, jurisdictions want to improve the effectiveness of their issuance procedures.
Among the countries that were inspired to adopt CBDC were the Bahamas and the Caribbean, which are made up of a huge number of tiny and large islands. The growing use of private virtual currencies indicates the public's desire for digital currencies, which central banks seek to balance while sidestepping the more problematic aspects of such currencies.
The dangers of utilizing cryptocurrencies, or digital currency, as they exist now would be diminished by CBDCs.
The risks associated with using cryptocurrencies and digital currencies in their current form would be reduced with the introduction of CBDCs. The value of cryptocurrencies is constantly fluctuating and quite unpredictable. This volatility may have a negative effect on the overall stability of an economy and severely strain the finances of many households. Thanks to CBDCs, which are supported by the government and governed by a central bank, individuals, businesses, and houses would all have a safe way to exchange digital cash.
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Restraints:
CBDCs might be subjected to cyber hacks which might lead to server blockages unforced timeouts or service declines.
Cyberattacks that target CBDCs may cause unexpected timeouts, server outages, or a decline in service quality. CBDC may also be susceptible to other cyberthreats, the principal ones being distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks that disrupt services, supply-side attacks directed at infrastructure, and side-channel attacks on user devices and payment apps. DLT-based CBDC systems are vulnerable to DDoS assaults since each transaction in these systems necessitates communication with every other node on the network. The goal of a denial-of-service (DDoS) assault is to overload a server or network with too much traffic in too short a period of time, causing it to crash. If the government does not address these cyberattacks, the public's trust in the ecosystem will be weakened and the integrity of the CBDC system endangered.
inclusive tool by utilising innovation to remove the barriers, just like with offline payments.
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Opportunities:
The sudden spike in interest in CBDC can be attributed to central banks' perception of its importance in advancing public policy objectives, maintaining economic stability, and providing individuals with a convenient, secure, and reliable payment medium.
Every country has a different approach to implementing CBDC. Others are conducting research and testing iterations to gradually develop their CBDC, while some countries are speeding towards implementation. To determine when and how CBDC can be implemented, discussions and activities are now underway in India. Consequently, this will give all players in the ecosystem far more chances to create services that streamline and ease digital payment processing and citizen transactions for a variety of use cases and requirements.
Financial inclusion is described as a desired outcome of retail CBDC projects, which appear increasingly developed in emerging economies. In more developed nations with sophisticated financial markets and interbank networks, the bulk of wholesale activities occur.
CENTRAL BANK DIGITAL CURRENCY MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
2.31% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Issuance, Structure, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Company 1, Company 2, Company 3 Company 4, Company 5, Company 6 |
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Segmentation: By Type
-
Wholesale CBDC
-
Retail CBDC
A 2021 survey conducted by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) found that 14% of central banks globally were putting trial programmes into place, 60% were testing the technology, and 86% of central banks globally were actively looking into the feasibility of utilising CBDCs. Financial inclusion is described as a desired outcome of retail CBDC projects, which appear increasingly developed in emerging economies. In more developed nations with sophisticated financial markets and interbank networks, the bulk of wholesale activities occur.
Retail CBDC is the term for the digital form of fiat money that is meant for average consumers and used by everyday people for daily financial activities. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) functions like a privately controlled blockchain network under government supervision, permitting transaction tracking while safeguarding identities. Furthermore, it diminishes the power of private entities, discouraging deception and other unlawful activities.
Wholesale CBDC can be very helpful in the development of wholesale payments, which central banks are trying to modernise. Wholesale CBDC will permit net-basis interbank settlements. It will also make the conditionality of payment easier, which is the process of paying off a debt subject to the performance of a duty or the delivery of an asset or security. The use of wholesale CBDC can help financial markets, interbank payments, and cross-border remittances making it the fastest-growing segment during the forecasted years.
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Segmentation: By Issuance
-
Direct CBDC
-
Indirect CBDC
-
Hybrid CBDC
The two models utilised for the issue and management of CBDCs are the Direct Model (Single Tier model) and the Indirect Model (Two-Tier model). Under an indirect approach, a central bank and other intermediaries, like banks and other service providers, each have their own unique role. In this structure, the central bank does not directly issue CBDC to customers through intermediaries; rather, it just oversees wholesale payments to intermediaries. It is anticipated to be both the largest and the fastest growing segment during the outlook period due to this.
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Segmentation: By Structure
-
Account-based
-
Token-based
A token-based CBDC is regarded as a bearer instrument, much like banknotes, and is thought to belong to the person holding the tokens at any given time. However, an account-based system would have to maintain track of all CBDC holders' balances, transactions, and ownership of the funds. Moreover, in a token-based CBDC, the recipient of the token must attest that he actually is the token's owner; in an account-based CBDC, an intermediary verifies the identity of an account holder. Although both types of CBDCs have advantages, token-based CBDCs are seen to be a superior choice for CBDC-R due to their resemblance to real cash; nevertheless, account-based CBDCs may also be a viable option for CBDC-W. Because account-based and token-based languages do not create categories that are mutually exclusive, they present challenges when used for digital payments. If a taxonomic hierarchy of digital payment systems were to be defined, members of the higher taxonomic rank would not be separated by these terms.
Central Bank Digital Currency Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
A total of 130 countries, accounting for 98% of global GDP, are examining CBDCs. By May 2020, there were only 35 countries considering creating a CBDC. 64 countries are involved in advanced exploration, which include development, piloting, or launch, breaking previous records. Currently, CBDC development is at an advanced stage in 19 of the G20 countries. Nine of those are currently part of pilot projects. Nearly all of the G20 countries have made substantial progress on these projects and contributed new financing in the last six months. Eleven countries have fully implemented digital currency. More than 200 scenarios are being investigated for China's pilot programme, which currently covers 260 million people, including public transport, stimulus payments, and e-commerce. The European Central Bank plans to launch a digital euro pilot programme shortly. More than 20 more countries will start getting ready to pilot their CBDCs in 2023. Thailand, Australia, and Russia intend to do additional pilot testing. India and Brazil want to make their debuts in 2024. In the US, retail CBDC development has come to an end. Conversely, other G7 banks, like the Bank of England and the Bank of Japan, are developing CBDC prototypes and offering advice to the public and private sectors regarding financial stability and privacy. However, the US is moving forward with a wholesale CBDC (bank-to-bank). Wholesale CBDC innovations have accelerated after the G7 sanctions response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Currently, twelve efforts for cross-border wholesale CBDC are active.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Central Bank Digital Currency Market:
The Bank for International Settlements believes that the COVID-19 crisis' effects on retail payments will help central banks build digital currencies. First, the study draws attention to the sharp decline in cash payments brought on by shop and customer concerns about virus propagation. The "precautionary holdings" of cash resulting from economic uncertainty have led to a decline in daily cash transactions. In tandem with this, national government regulations like eliminating physical stores have resulted in an increase in e-commerce payments. Due to decreased mobility, there has been a significant decline in both the volume of cross-border visa transactions and migrant remittances. All of these changes, in BIS's opinion, emphasise the advantages and drawbacks of the current payment methods. On the one hand, digital payments have enabled the continuation of numerous economic operations, although causing major disruptions to daily living. However, the crisis has made already-existing socioeconomic divides more pronounced, in part because of unequal financial inclusion, which may make it more difficult for some people to qualify for government assistance: Demands for future payment services that are more affordable and inclusive as well as for vulnerable communities to have more access to digital payments have increased as a result of the crisis.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
Japan plans to host a CBDC forum and extend an invitation to private enterprises engaged in retail payments or related technologies to participate in the discourse. Based on the data, the bank will decide by 2026 whether to launch a digital currency.
In 2023, Reliance Retail, the largest retail chain in India, will start accepting digital rupee payments at its test locations. In March, India began testing an offline function for its CBDC.
Key Players:
- Bank Of England
- People's Bank of China (PBOC)
- European Central Bank (ECB)
- Federal Reserve (United States)
- Swiss National Bank (SNB)
- Bank of Japan (BOJ)
- Bank of Canada
- Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
- National Bank of Poland
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Several nations intend to introduce Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), however, none of them have formally adopted it as of yet. To determine whether CBDC programs are credible, they have all started the first test program and research studies. One of the earliest nations to put forth this notion was England. Not long after, China joined. Russia is about to produce a "crypto Rubel" of its own.
Chapter 1. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – By Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Wholesale CBDC
6.3 Retail CBDC
6.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Type
6.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – By Issuance
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Direct CBDC
7.3 Indirect CBDC
7.4 Hybrid CBDC
7.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Issuance
7.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Issuance, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – By Structure
8.1 Introduction/Key Findings
8.2 Account-based
8.3 Token-based
8.4 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Structure
8.5 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Structure, 2024-2030
Chapter 9. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
9.1 North America
9.1.1 By Country
9.1.1.1 U.S.A.
9.1.1.2 Canada
9.1.1.3 Mexico
9.1.2 By Issuance
9.1.3 By Structure
9.1.4 By Type
9.1.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.2 Europe
9.2.1 By Country
9.2.1.1 U.K
9.2.1.2 Germany
9.2.1.3 France
9.2.1.4 Italy
9.2.1.5 Spain
9.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
9.2.2 By Issuance
9.2.3 By Structure
9.2.4 By Type
9.2.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.3 Asia Pacific
9.3.1 By Country
9.3.1.1 China
9.3.1.2 Japan
9.3.1.3 South Korea
9.3.1.4 India
9.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
9.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.3.2 By Issuance
9.3.3 By Structure
9.3.4 By Type
9.3.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.4 South America
9.4.1 By Country
9.4.1.1 Brazil
9.4.1.2 Argentina
9.4.1.3 Colombia
9.4.1.4 Chile
9.4.1.5 Rest of South America
9.4.2 By Issuance
9.4.3 By Structure
9.4.4 By Type
9.4.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.5 Middle East & Africa
9.5.1 By Country
9.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
9.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
9.5.1.3 Qatar
9.5.1.4 Israel
9.5.1.5 South Africa
9.5.1.6 Nigeria
9.5.1.7 Kenya
9.5.1.8 Egypt
9.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
9.5.2 By Issuance
9.5.3 By Structure
9.5.4 By Type
9.5.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 10. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
10.1 Bank Of England
10.2 People's Bank of China (PBOC)
10.3 European Central Bank (ECB)
10.4 Federal Reserve (United States)
10.5 Swiss National Bank (SNB)
10.6 Bank of Japan (BOJ)
10.7 Bank of Canada
10.8 Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)
10.9 National Bank of Poland
10.10 Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
Over the forecast period of 2024-2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2.31%.
A record-breaking 64 nations are engaged in advanced exploration, which includes development, piloting, or launch.
CBDCs might be subjected to cyber hacks which might lead to server blockages unforced timeouts or service declines.
The top 5 regions in the Central Bank Digital Currency market are England, Russia, Japan, China, and the US.
The Central Bank Digital Currency market is segmented into account-based CDBC and token-based CDBC.