Animal Vaccines Market Size (2024 – 2030)
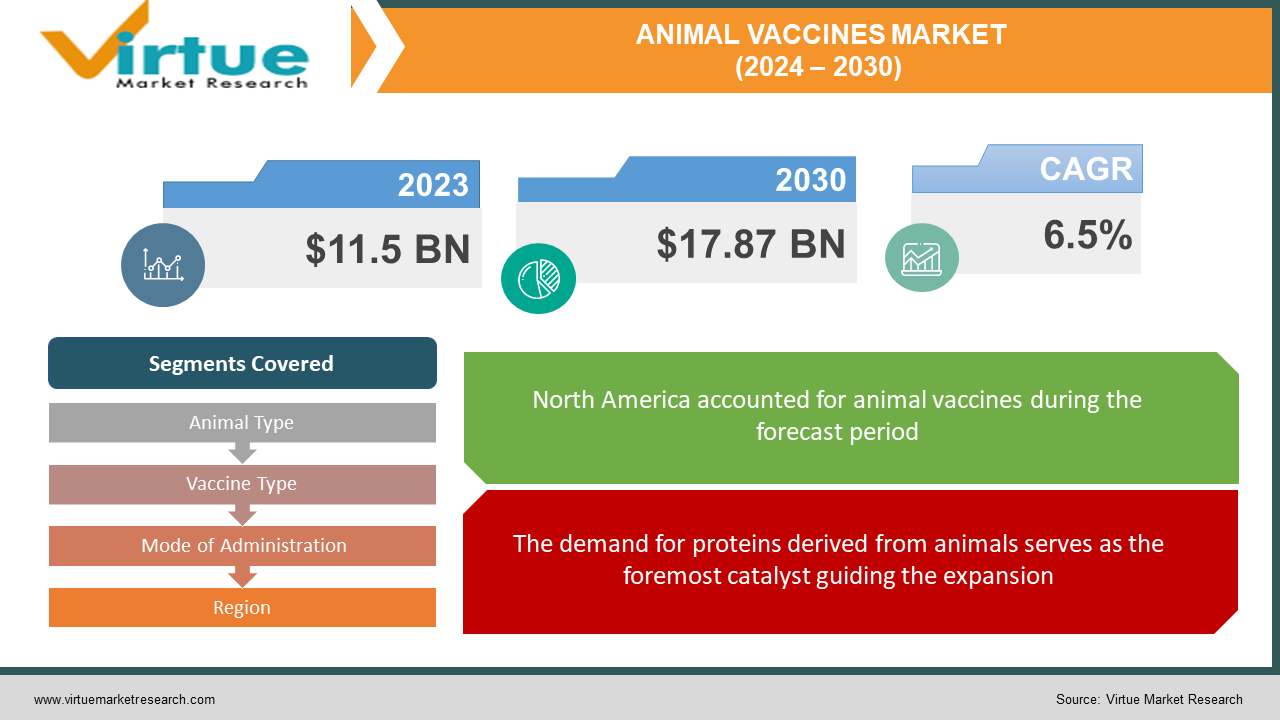
The animal vaccine market was valued at USD 11.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 17.87 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024–2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5%.
The field of animal vaccines has become a cornerstone of modern veterinary medicine and an indispensable tool for safeguarding both animal lives and human health. This dynamic market is shaped by a complex interplay of factors: a relentless need to curb zoonotic disease outbreaks, the demands of global food production, and the heartwarming trend of increased pet ownership. When we think of animal vaccines, it's easy to focus on the benefits for pets, livestock, or farmed fish. While these indeed represent central drivers of the market, the scope of impact extends far beyond animal wellbeing. Zoonotic diseases, transmissible from animals to humans, cause public health crises and economic disruption. Rabies, avian influenza, and the West Nile virus are just a few examples where animal vaccination forms a crucial barrier between harmful pathogens and human populations.
Key Market Insights:
China, India, and Japan are anticipated to exhibit a 7.2% CAGR through 2028 through surging meat production and rising pet adoption.
In the second quarter of 2023, animal healthcare business Zoetis saw a 12% rise in operational adjusted net income and a 9% increase in sales. Strong sales in the companion animal and livestock industries are the reason for this development.
By 2024, the size of the Chinese veterinary vaccine market is expected to reach 450 million yuan.
With a projected total sale of more than eight billion dollars in 2022, American pharmaceutical firm Zoetis is the biggest business in the animal health industry worldwide.
A study by Boston University carried out in 2023 showed that approximately 50% of dog owners are reluctant to vaccinate their animals. To tackle this, organizations have been focusing on educational campaigns to spread awareness. Besides, veterinary outreach has increased, especially in underdeveloped areas.
Animal Vaccine Market Drivers:
The demand for proteins derived from animals serves as the foremost catalyst guiding the expansion.
Of the various key factors propelling the steady expansion of the multi-billion-dollar animal vaccine industry, the most dominant underlying driver stems from the global demand for proteins derived from livestock and aquaculture sources. Per capita, meat consumption has progressively scaled new peaks over recent decades, with global citizens currently consuming over 43 kilograms per year. Several socio-economic undercurrents have guided this unrelenting growth trajectory in meat-eating habits. Rising incomes in heavily populated developing countries have made protein foods more affordable and desirable, with pork and poultry leading demand due to lower prices compared to red meats. The availability of processed and packaged meat products has also enhanced accessibility. At the same time, marketing campaigns by meat exporters and lax sustainability policies have boosted consumption volumes, despite health and ecological caveats. As the world's middle class expands by leaps and bounds, developing nations are particularly witnessing a dramatic shift toward more meat-heavy dietary patterns characteristic of Western lifestyles. The emerging appellation of meat as a status product, especially coveted during cultural celebrations, also continues to propel its soaring popularity within transitioning populations.
Next-generation versions leveraging viral vectors, nucleic acids, and other cutting-edge platforms are steering the industry toward higher-efficacy products.
While traditional modified live or inactivated vaccine platforms have continued to dominate animal vaccine volumes so far due to their known safety and efficacy, various limitations in this decades-old biological technology have left room for improvements in immunization potency. Hence, recent breakthroughs within cutting-edge vaccine engineering spheres are acting as a key driver accelerating the growth of the multi-billion-dollar animal vaccine industry worldwide. Both limitations in the consistency of protection levels as well as logistical bottlenecks have impacted the field efficacy of first-generation vaccine options. The necessity for 2-3 initial doses and annual booster shots with traditional products increases handling stress for livestock and compound production costs for manufacturers. Vaccination campaigns across large commercial flocks also leave immunity gaps due to the practical challenges of assuring administration to every single bird. Furthermore, the demanding cold storage requirements of delicate conventional platforms lead to excessive waste issues in many geographies. Novel vaccine engineering innovations are addressing such limitations to steer the industry toward higher-efficiency next-generation products. Recombinant vector vaccines utilizing viruses like fowl pox as a delivery mechanism to transport target antigens offer a rapid and longer-lasting shield triggered by just a single dose of inoculation. Nucleic acid platforms such as DNA and RNA vaccines can also enable precise stimulation of the immune system guided by specific genes without the need for whole infectious particles. As these can be synthesized chemically, high purity levels aid safety. Alongside enhancing effectiveness, cutting-edge platforms also enable DIVA capability for differentiating infected from vaccinated animals to precisely target control measures during outbreaks.
Animal Vaccine Market Restraints and Challenges:
Assuring smooth supply chains remains a barrier.
While production costs are dropping, non-metallic solutions remain more expensive to manufacture than metals in most cases. Multistep resin and fiber production, the intricacy of combining constituents, and high costs for pre- and post-processing contribute to inflated prices. The convoluted supply chain pathway serving the multi-billion-dollar animal vaccine industry has remained severely fraught with various structural and logistic challenges. From raw material procurement struggles impacting production schedules to gaps in cold chain integrity compromising vaccine viability through the last stretch of transportation, myriad complexities span across the ecosystem. At the manufacturing source, producers consistently grapple with meeting elevated demand for both conventional and next-generation vaccines as protein consumption amplifies livestock populations. Capacity expansion is throttled by bottlenecks in garnering reliable access to essential raw materials like cell culture media and adjuvants, as well as the availability of sterile vials, tanks, and other critical inputs. As nearly 70% of bio-manufacturing infrastructure dwells across the U.S. and Europe, developing regions with the largest farm animal populations face supply deficits. While outsourcing production to contract manufacturers offers temporary relief, quality assurances require oversight. The long, delicate journey traversed by vaccine post-production also suffers from links weakened by inadequate refrigeration and poor logistical coordination. A majority of first-generation inactivated or live-modified animal vaccines retain viability when stored between precise 2–8 °C temperature bands. However, breaching the threshold on either end rapidly degrades sensitive immunizing agents. Staff training gaps and record-keeping additionally complicate the verification of properly administered booster schedules.
Stringent and lengthy regulatory pathways can be challenging to tackle.
Stringent approval frameworks, often spanning years, tend to disadvantage smaller industry players lacking the financial muscle to navigate convoluted review channels. Startups endure high risks of research pipeline derailment if mandated trial protocols overwhelm resources. Researchers highlight glaring gaps in the proportion of vaccine candidates able to progress beyond early development phases compared to the number of candidates attaining eventual commercial launch consent across veterinary medicine. Numerous novel vaccine methodologies targeting improved immunization potency languish in technology incubators and university labs, as the majority of vaccine approvals center on variations of existing platforms rather than novel alternatives. Permitting testing of early vaccine prototypes on limited sample populations under real-life conditions can guide iterative refinement before submitting for comprehensive efficacy and safety reviews essential for full launch consents. Additionally, enhancing structural aspects to bolster regulatory efficiency remains vital to counter the review timeframe lag. Expanding the pool of evaluators can accelerate the assessment of submitted trial data packages for innovator vaccines already subjected to stringent study protocols. Prioritizing applications for technologies targeting protection against economically devastating transboundary diseases also merits consideration to incentivize R&D in impactful but neglected areas like food and mouth disease, or PRRS.
Manufacturers of animal vaccines must strike a careful balance between affordability, profitability, and innovation, coupled with shifting disease outbreaks and market demands.
Animal vaccine manufacturers operate under continuous tension, struggling to align the product affordability interests of high-volume commercial farms and pet owners against profitability pressures from within that allow continued investments in advancing immunization technology. As recurring expenditure necessities rather than one-time treatments within animal health management ecosystems, vaccine doses witness substantial demand elasticity linked to end pricing, especially in developing markets. Statutory price control mechanisms in several countries also restrain the ability to periodically account for fluctuating input costs about raw materials, labor, and transportation that influence delivered pricing. This leaves limited buffer room along margins for manufacturers to channel revenues into R&D for novel platforms as well as expanding manufacturing capacities. Additionally, recurrent waves of animal disease outbreaks like African swine fever or avian influenza trigger spikes in emergency vaccination response efforts financed by state funding, which temporarily deflate market pricing due to a sudden vaccine surplus.
Animal Vaccine Market Opportunities:
The towering growth predictions for the global animal vaccine industry stem largely from optimistic projections around lucrative opportunities dwelling across developing markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and even Africa. Home to nearly 70% of the world's farm animal inventory, these regions exemplify the fastest-expanding protein demand, reflecting rising incomes and urbanization. Development initiatives geared toward upgrading veterinary access down to the farm gate via trained para vets equipped with refrigerator vans that permit directly administered inoculation campaigns rather than dependence on middlemen could hugely uplift rural penetration. Locally active health workers also ensure reliable follow-up booster compliance, which is critical for vaccine effectiveness. Customizing innovation pipelines to serve developing market needs also offers unfulfilled potential.
ANIMAL VACCINES MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
6.5% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Animal Type, Vaccine Type, Mode of Administration, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Zoetis, Merck Animal Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ceva Santé Animale, Elanco Animal Health, Virbac, Hester Biosciences, Biogénesis Bagó, Phibro Animal Health Corporation |
Animal Vaccines Market Segmentation: By Animal Type
-
Livestock
-
Poultry (Chickens, Turkeys, etc.)
-
Cattle (Cows, Buffalo, etc.)
-
Swine (Pigs).
-
Sheep and Goats
-
Companion Animals
-
Aquaculture
With 60–70% of the market shares overall, the livestock segment—which includes a variety of livestock animals—consistently makes up the largest portion of the animal vaccine market. Due to the vast size of livestock husbandry required to supply the demand for meat, milk, and eggs worldwide, there is a large animal population that needs to be protected and disease-free. Intensive and concentrated farming methods increase the danger of disease transmission, necessitating routine vaccination to prevent significant financial losses. Vaccinating livestock against illnesses like anthrax or brucellosis has a wider effect than only protecting animal populations; it also saves people from contracting zoonotic infections. Companion animals account for 25–35 percent of the market for animal vaccines, making it the sector with the fastest rate of growth. Due to shifting lifestyles and urbanization, people around the world are becoming more and more pet owners as their need for companionship grows. Pets stop being merely animals and start to become part of the family. Pet owners want the greatest possible medical care for their animals, including complete immunizations against serious diseases like canine parvovirus, feline leukemia, and distemper.
Animal Vaccines Market Segmentation: By Vaccine Type
-
Attenuated Live Vaccines
-
Inactivated Vaccines
-
Subunit Vaccines
-
Recombinant Vaccines
Attenuated live vaccines account for the largest share, around 40% in 2023. It involves the use of live microbes that are weakened to not cause disease but still trigger protective immunity. They offer long-lasting immunity with a single dose and are commonly used for diseases like rabies, rotavirus, cattle plague, etc. Recombinant vaccines are expected to exhibit the fastest growth. It utilizes vector viruses or molecules to deliver target antigens. These vaccines enable rapid and sustained immune responses using the latest biotech approaches. It is gaining traction for pigs, poultry, and companion animals.
Animal Vaccines Market Segmentation: By Mode of Administration
-
Subcutaneous
-
Intramuscular
-
Intranasal
Most animals have subcutaneous injection sites in their necks and behind their shoulder blades. The ability of medications to be injected subcutaneously and absorbed gradually by the body is anticipated to propel market expansion. For animals, the subcutaneous approach also causes less discomfort. Moreover, subcutaneous injection training for veterinary professionals is less complicated. The intranasal segment is the fastest-expanding mode, growing by over 7% annually. It is administered via nasal drops or aerosol sprays that trigger mucosal immunity, preventing pathogen entry through nasal passages, which is important for diseases like kennel cough.
Animal Vaccines Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America has the largest market share. Factors like large populations of livestock and companion animals, strong government support for animal health, and a sophisticated veterinary infrastructure contribute to this dominance. Asia-Pacific is currently considered the fastest-growing region in the animal vaccine market. The expansion of livestock production to meet demands from a growing population in countries like China and India plays a major role. Increased pet ownership and government-sponsored vaccination programs are further pushing the APAC market forward. Europe is another established market. Stringent animal welfare regulations, advanced healthcare systems, and a focus on disease prevention fuel the market in Europe. South America is seeing steady growth. Burgeoning poultry and cattle industries, particularly in Brazil, fuel the demand for animal vaccines. Improving economies and an upsurge in companion animal care add to this market segment. The potential for growth in the Middle East and Africa remains significant. Government focus on food security, the need to curb livestock disease outbreaks, and a gradual increase in companion animal ownership contribute to this positive growth outlook.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Animal Vaccine Market.
The global market for animal vaccinations has been significantly impacted by the COVID-19 outbreak. The supply chain and the manufacture of animal vaccines have been disrupted by lockdowns and travel restrictions. A primary consequence has been the postponement of planned veterinary appointments and animal immunization campaigns. Social distancing standards prevented many pet owners from making unnecessary trips to the vet. There was a decrease in elective operations such as pet vaccines. Regular livestock vaccinations were also impacted, particularly in underdeveloped nations with inadequate access to veterinary care. Due to the gaps in herd immunity caused by this, animal populations are now more susceptible to disease outbreaks. Lockdown-related labor shortages also had an impact on the production of vaccines. A lot of facilities ran into a staffing shortage, which caused production schedules to slow down. Getting consumables and raw materials was also difficult. Delays in shipping compounded the issues. As a result, there was a shortage of some essential vaccinations for companion and production animals. Early in the pandemic, slower animal sales and poorer livestock production also significantly affected the demand for immunizations. But during the latter half of the pandemic, demand began to increase as lockdowns became less frequent. Governments' increasing animal immunization programs and the rise in pet ownership contributed to the market's recovery. Accelerating efforts to create mRNA vaccines for animals that resemble human COVID vaccinations is one of the longer-term effects. Additionally, businesses are concentrating on enhancing vaccination distribution systems and lowering reliance on cold chain logistics. Infrastructure for vaccine production has seen a rise in investment to strengthen supply chain resilience. Growth will be fueled by higher pet healthcare expenditures and a greater emphasis on zoonotic disease prevention. It is anticipated that market revenues will exceed pre-COVID levels due to increased demand and use of next-generation vaccination technology. However, if there are more waves of the pandemic, the consequences of postponing routine animal vaccination regimens and the advent of vaccine shortages in some areas may present difficulties.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
The global animal vaccine market has been experiencing significant growth, fueled by rising pet ownership, increasing consumption of animal proteins, and a greater focus on preventing zoonotic diseases. Novel vaccine platforms: Conventional vaccine production methods are steadily being replaced by innovative technologies like mRNA, DNA, viral vectors, and subunit vaccines. These platforms allow for faster design and development of highly efficacious vaccines compared to traditional approaches. Several animal health majors like Zoetis, Elanco, and Ceva are investing heavily in these platforms to produce vaccines for various bacterial and viral pathogens affecting livestock and companion animals. Needleless vaccine delivery through mucosal routes like nasal, oral, and transdermal is gaining immense traction. Nasal sprays and oral baits eliminate the stress of injection and allow easy administration of booster doses. Transdermal patches are also becoming more popular with pets. Other innovations include microneedle patches and jet injectors that penetrate the skin without traditional hypodermic needles. Companies like ImmuCell and Color Health are bringing novel animal vaccine delivery solutions to market. The use of robotics, interconnected sensors, and advanced analytics allows consistent, high-quality vaccines to be manufactured at scale. Companies like Boehringer-Ingelheim are implementing automation to meet growing demand.
Key Players:
-
Zoetis
-
Merck Animal Health
-
Boehringer Ingelheim
-
Ceva Santé Animale
-
Elanco Animal Health
-
Virbac
-
Hester Biosciences
-
Biogénesis Bagó
-
Phibro Animal Health Corporation
Chapter 1. Animal Vaccines Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. Animal Vaccines Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. Animal Vaccines Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. Animal Vaccines Market Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. Animal Vaccines Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. Animal Vaccines Market – By Animal Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Livestock
6.3 Poultry (Chickens, Turkeys, etc.)
6.4 Cattle (Cows, Buffalo, etc.)
6.5 Swine (Pigs).
6.6 Sheep and Goats
6.7 Companion Animals
6.8 Aquaculture
6.9 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Animal Type
6.10 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Animal Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. Animal Vaccines Market – By Vaccine Type
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Attenuated Live Vaccines
7.3 Inactivated Vaccines
7.4 Subunit Vaccines
7.5 Recombinant Vaccines
7.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Vaccine Type
7.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Vaccine Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. Animal Vaccines Market – By Mode of Administration
8.1 Introduction/Key Findings
8.2 Subcutaneous
8.3 Intramuscular
8.4 Intranasal
8.5 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Mode of Administration
8.6 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Product Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 9. Animal Vaccines Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
9.1 North America
9.1.1 By Country
9.1.1.1 U.S.A.
9.1.1.2 Canada
9.1.1.3 Mexico
9.1.2 By Animal Type
9.1.3 By Vaccine Type
9.1.4 By Mode of Administration
9.1.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.2 Europe
9.2.1 By Country
9.2.1.1 U.K
9.2.1.2 Germany
9.2.1.3 France
9.2.1.4 Italy
9.2.1.5 Spain
9.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
9.2.2 By Animal Type
9.2.3 By Vaccine Type
9.2.4 By Mode of Administration
9.2.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.3 Asia Pacific
9.3.1 By Country
9.3.1.1 China
9.3.1.2 Japan
9.3.1.3 South Korea
9.3.1.4 India
9.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
9.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
9.3.2 By Animal Type
9.3.3 By Vaccine Type
9.3.4 By Mode of Administration
9.3.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.4 South America
9.4.1 By Country
9.4.1.1 Brazil
9.4.1.2 Argentina
9.4.1.3 Colombia
9.4.1.4 Chile
9.4.1.5 Rest of South America
9.4.2 By Animal Type
9.4.3 By Vaccine Type
9.4.4 By Mode of Administration
9.4.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
9.5 Middle East & Africa
9.5.1 By Country
9.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
9.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
9.5.1.3 Qatar
9.5.1.4 Israel
9.5.1.5 South Africa
9.5.1.6 Nigeria
9.5.1.7 Kenya
9.5.1.8 Egypt
9.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
9.5.2 By Animal Type
9.5.3 By Vaccine Type
9.5.4 By Mode of Administration
9.5.5 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 10. Animal Vaccines Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
10.1 Zoetis
10.2 Merck Animal Health
10.3 Boehringer Ingelheim
10.4 Ceva Santé Animale
10.5 Elanco Animal Health
10.6 Virbac
10.7 Hester Biosciences
10.8 Biogénesis Bagó
10.9 Phibro Animal Health Corporation
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
The demand for proteins derived from animals and next-generation versions leveraging viral vectors, nucleic acids, and other cutting-edge platforms are the main market drivers.
Ensuring a smooth supply chain, stringent and lengthy regulatory pathways, and striking a balance between affordability, profitability, and innovations coupled with shifting disease outbreaks and market demands are the main concerns.
Zoetis, Merck Animal Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ceva Santé Animale, Elanco Animal Health, Virbac, Hester Biosciences, Biogénesis Bagó, and Phibro Animal Health Corporation are the major players.
North America currently holds the largest market share.
Asia-Pacific exhibits the fastest growth.