5G base stations Market Size (2024 – 2030)
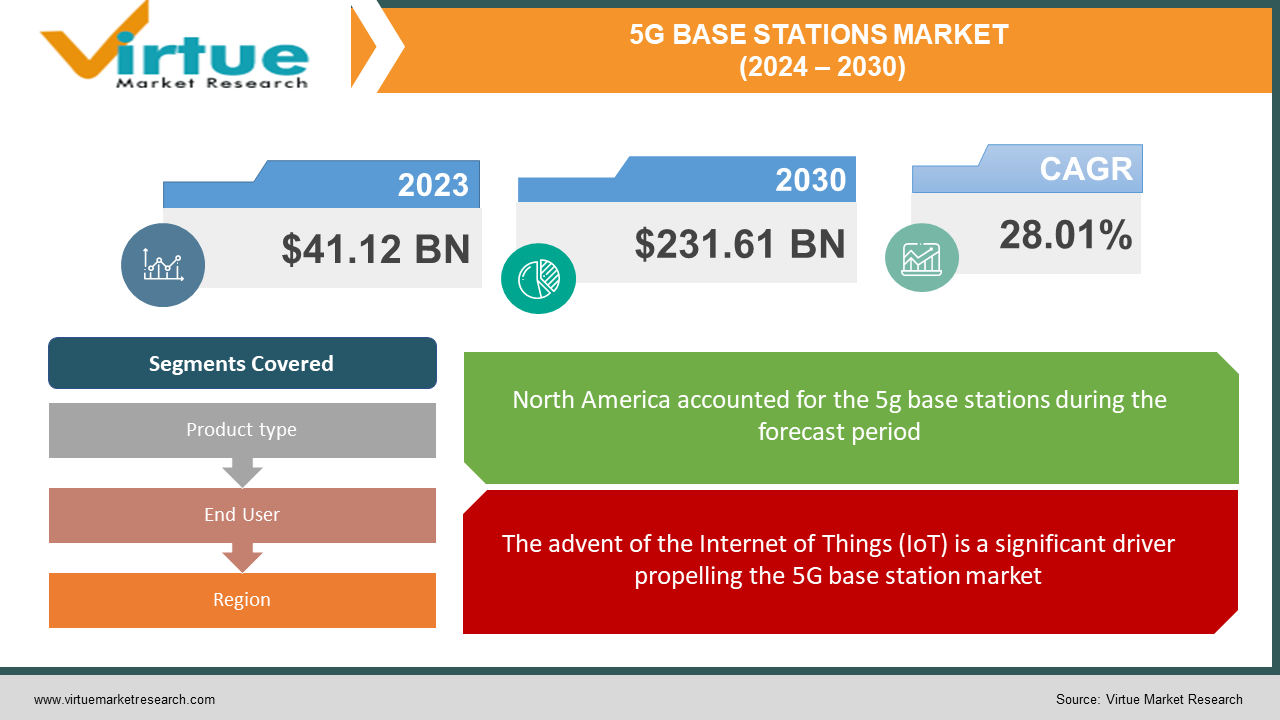
The 5G base station market was valued at USD 41.12 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 231.61 billion by the end of 2030. Over the forecast period of 2024–2030, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 28.01%.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is exploding, with billions of connected devices needing a reliable network. 5G's low latency and wide-area coverage make it perfect for this ecosystem, driving demand for base stations. Our insatiable appetite for data, from streaming binges to AR experiences, demands faster networks. 5G base stations are the key to unlocking this potential, catering to consumers and businesses alike.5G isn't just about phones; it's about transforming industries. From connected cars in smart cities to real-time monitoring in agriculture, various applications fuel the need for robust 5G infrastructure. 5G base stations are often deployed alongside existing LTE infrastructure, creating a hybrid network that ensures a smooth transition and extends the lifespan of existing investments. Finding enough spectrum for widespread 5G deployment is a global hurdle, requiring collaboration between regulators and operators. Building and maintaining a 5G network is expensive, demanding significant investment from operators and governments. The 5G base station market is a vibrant landscape, painted with opportunity and innovation.
Key Market Insights:
5G doesn't operate on a single frequency; it's a complex orchestra utilizing a range of bands, each with its strengths and limitations. Low-band frequencies offer wider coverage but slower speeds, while high-band frequencies deliver lightning-fast data but have limited reach. Navigating this spectrum landscape to achieve optimal coverage, capacity, and cost-effectiveness is a key challenge and opportunity for market players. The 5G landscape is painted with geopolitical hues. From trade tensions to national security concerns, various countries are vying for dominance in this critical technology. This adds another layer of complexity to the market, influencing investment decisions, technology standards, and network deployments. The 5G base station market is constantly evolving, with research and development focused on even higher speeds, lower latency, and more efficient hardware. 5G isn't just about hardware; it's powered by software intelligence. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are embedded within base stations, enabling real-time network optimization, self-healing capabilities, and even predictive maintenance. This integration of AI unlocks new market opportunities for software and service providers. Additionally, the integration of technologies like edge computing and blockchain will further reshape the landscape, creating exciting new opportunities for market players. Bridging the digital divide is a key focus. Governments and private players are investing in extending 5G coverage to rural areas, creating a new market segment for cost-effective and energy-efficient base station solutions.
5G base stations Market Drivers:
The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) is a significant driver propelling the 5G base station market.
The surge of the Internet of Things (IoT) heralds a transformative era in the telecommunications landscape, and its profound impact serves as a cornerstone driving the exponential growth of the 5G base station market. At the heart of the massive device connectivity envisioned by 5G base stations lies the proliferation of IoT sensors. These sensors, embedded in diverse devices, generate a continuous stream of data, facilitating real-time monitoring, environmental sensing, and data-driven decision-making. The expansive coverage and low-latency capabilities of 5G base stations are instrumental in knitting together these ubiquitous sensor networks. The vision of smart cities, characterized by interconnected infrastructure and intelligent systems, is intricately linked to the capabilities of 5G base stations. From fitness trackers and smartwatches to health monitoring devices, these wearables rely on seamless connectivity for data transmission. 5G base stations, with their ability to handle numerous simultaneous connections, ensure a robust and responsive network for these personal IoT ecosystems.
The evolution of enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) is a compelling driver for the 5G base station market.
At the heart of eMBB's transformative impact is the promise of unprecedented download and upload speeds. 5G base stations, equipped with advanced technologies such as massive MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) and beamforming, facilitate faster data transmission. Users can experience download and upload speeds that far surpass those achievable with previous generations, ushering in a new era of instantaneous data access. Video streaming, a ubiquitous aspect of modern digital life, undergoes a revolutionary enhancement with eMBB. 5G base stations ensure seamless and high-quality video streaming experiences, eliminating buffering delays and providing users with instant access to high-definition content. From on-the-go video calls to immersive multimedia streaming, eMBB elevates the video consumption landscape. eMBB, facilitated by 5G base stations, brings forth a significant reduction in latency. The low-latency characteristics of 5G networks enhance the overall network performance, contributing to quicker response times and improved real-time interactions. This optimized latency is particularly crucial for applications that demand instantaneous responsiveness, such as online gaming and augmented reality experiences.
5G Base Station Market Restraints and Challenges:
One of the primary challenges facing the 5G base station market is the substantial investment required for infrastructure deployment.
Deploying a dense and comprehensive network of 5G base stations is an ambitious endeavor that comes with a significant price tag. The capital-intensive nature of 5G infrastructure arises from the need to establish a multitude of small cells, antennas, and other components to deliver the promised speed and low latency. The sheer scale of this deployment amplifies the financial commitment required, making it a strategic imperative for network operators to weigh the costs against the anticipated benefits. The challenge lies in finding the delicate equilibrium between the ambitious goal of extensive 5G coverage and the financial constraints inherent in such a vast infrastructure deployment. While the vision is to create a seamless 5G experience across urban, suburban, and rural areas, the financial realities compel operators to prioritize and sequence deployments based on factors such as population density, revenue potential, and regulatory considerations. The challenge is to strike a balance between immediate deployment needs and the flexibility to scale up infrastructure in response to growing 5G adoption.
Spectrum allocation poses a critical challenge for the 5G base station market.
Spectrum is the lifeblood of wireless communication, and its allocation is a linchpin in the deployment of 5G networks. Unlike its predecessors, 5G relies on a diverse range of spectrum bands, including low, mid, and high frequencies. Each band offers unique advantages, such as wide coverage in the lower bands and high data rates in the higher bands. The challenge lies in orchestrating a harmonious allocation that caters to the diverse needs of 5G applications. Spectrum scarcity emerges as a central challenge, fueled by the unprecedented demand for bandwidth-hungry 5G applications. As the race for frequency bands intensifies, regulatory bodies find themselves grappling with the task of balancing the interests of various stakeholders, including telecommunications companies, satellite services, and government agencies. The insatiable appetite for spectrum to support enhanced mobile broadband, IoT, and critical communications amplifies the scarcity dilemma. Governments and regulatory bodies must establish clear frameworks that define the rules for spectrum licensing, usage, and interference management. However, ambiguity in policies, evolving standards, and differing approaches across regions create challenges for industry players seeking a cohesive and standardized spectrum environment. Dynamic frequency allocation, spectrum sensing technologies, and collaborative interference management strategies are essential.
5G Base Station Market Opportunities:
The customization of 5G networks to cater to specific industry requirements presents a substantial opportunity. Sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, and energy have unique connectivity needs. Tailoring 5G base stations to address industry-specific use cases, such as ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in manufacturing or telemedicine in healthcare, opens avenues for innovation and targeted solutions. The integration of edge computing into 5G networks unlocks a plethora of opportunities. 5G base stations, strategically positioned at the edge, facilitate real-time data processing and low-latency interactions. This creates opportunities for applications that demand immediate data analysis, such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and IoT. Edge computing integration positions 5G base stations at the forefront of transformative technologies. The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) is a driving force for the 5G base station market. The ability to connect and manage a massive number of IoT devices simultaneously presents opportunities in various sectors. From smart cities and agricultural applications to industrial IoT and healthcare, 5G base stations play a pivotal role in supporting the diverse and expansive IoT ecosystem. Bridging the digital divide and extending 5G connectivity to rural and underserved areas presents a significant opportunity. 5G base stations, with their efficiency and range, can provide high-speed connectivity even in remote locations. This presents opportunities for the deployment of smart factories, predictive maintenance, and agile manufacturing practices.
5G BASE STATIONS MARKET REPORT COVERAGE:
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 - 2030 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 - 2030 |
|
CAGR |
28.01% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product type, End User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regional Scope |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, Quanta Computer, Airspan, Cisco Systems, CommScope, Radisys |
5G Base Station Market Segmentation: By Product Type
-
Macro Cells
-
Small Cells
-
Micro Cells
-
Femtocells and Picocells
Macrocells are the traditional workhorses, covering large areas with powerful signals. They currently hold the dominant share, exceeding 88% in 2023, due to their wide coverage and established deployment infrastructure. However, their share is expected to gradually decrease as smaller cell types gain traction. Small cells are smaller, lower-powered stations deployed in dense urban areas, indoor spaces, and hotspots. They offer targeted coverage and high capacity, and their segment is estimated to hold a share of around 12%. This segment is projected to experience the fastest growth, with a CAGR exceeding 20% due to the increasing demand for capacity and improved indoor coverage. Microcells fall between macro and small cells, covering medium-sized areas with moderate power. Their market share is currently smaller, but they're expected to see moderate growth in specific deployments like enterprise campuses and transportation hubs. Femtocells and picocells are tiny cells designed for indoor coverage in homes and small businesses. While their individual market share is minimal, they cater to a specific niche and see steady growth. Small cells are the fastest-growing segment due to emerging applications like AR/VR and connected autonomous vehicles that rely on the low latency and high capacity offered by small cells. Miniaturization and improved performance make small cells increasingly cost-effective and easier to deploy.
5G Base Station Market Segmentation: by End User
-
Commercial
-
Industrial
-
Residential
-
Government and Defense
-
Others
Commercial (45–50%) shares are the dominant segment in 2023, which encompasses businesses, enterprises, and public spaces. Driven by the demand for high-speed connectivity for mobile workforces, cloud applications, and immersive customer experiences, its growth remains steady. The industrial segment is the fastest-growing segment, with a share of around 20–25%. The industrial IoT revolution fuels this segment's expansion. Factories, logistics hubs, and energy grids crave high-bandwidth, low-latency connections for automation, remote monitoring, and real-time data analysis. The industrial sector exhibits the most dynamic growth driven by the industrial IoT surge as factories and infrastructure are rapidly adopting connected devices, necessitating robust and reliable 5G networks for seamless data transfer and real-time control. The residential segment has around 15–20% of the market. Homes are increasingly equipped with smart devices, demanding reliable and fast connections for streaming, gaming, and connected appliances. While growing, its pace lags behind commercial and industrial segments. Government & Defense (5–10%) shares: this segment utilizes 5G for secure communication, public safety services, and smart city initiatives. Growth depends on government funding and specific national priorities.
5G Base Station Market Segmentation: Regional Analysis
-
North America
-
Asia-Pacific
-
Europe
-
South America
-
Middle East and Africa
North America, with a 35% share in 2023, is the dominant region, driven by the early adoption of 5G technology, high investments by operators, and strong demand from various industries like automotive and healthcare. Asia-Pacific, with a 25% share in 2023, is expected to be the fastest-growing region in the 5G base station market, with a projected CAGR of over 30% in the coming years. This growth is driven by China's aggressive rollout as it has deployed a massive number of 5G base stations and aims to become a global leader in technology. Countries like India, South Korea, and Japan are also rapidly adopting 5G. The vast population in the region creates a significant demand for mobile data services. Many governments in the region are supporting 5G deployment through subsidies and other incentives. Europe, with a 30% share, has investments that are increasing, and growth is expected to pick up. The Middle East and Africa have a 5% share; they are in the early stages of 5G deployment, with the potential for significant growth in the future due to government initiatives and infrastructure development.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis on the Global 5G Base Station Market.
Global lockdowns and travel restrictions disrupted the flow of critical components from key manufacturing hubs, leading to delays in base station deployments. Reduced consumer spending and business investment impacted operator budgets, causing delays and even cancellations of 5G rollout plans. Some government auctions for valuable 5G spectrum licenses were postponed, further hindering deployment timeframes. The pandemic highlighted the need for robust and reliable connectivity, pushing industries towards 5G adoption for remote work, online learning, and e-commerce. Many governments injected financial aid into telecom infrastructure projects, including 5G base station deployments, to accelerate economic recovery. The pandemic forced players to optimize costs and explore innovative solutions. This led to advancements in remote deployment and management technologies. After the initial shock, the market is witnessing a rebound, with analysts predicting a CAGR of around 10% in the coming years. The impact and recovery differ across regions. Asia Pacific, led by China's aggressive rollout, is expected to emerge as the fastest-growing market.
Latest Trends/ Developments:
Closed, proprietary systems are giving way to the Open RAN (Radio Access Network) architecture. This allows different vendors to contribute components, fostering faster innovation and a wider range of base station solutions. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming base stations into intelligent entities. These thinking stations can optimize network performance, predict failures, and self-heal issues, leading to increased efficiency and an improved user experience. A network that adjusts in real-time to traffic demands, ensuring seamless connectivity even during peak usage periods, is possible. 5G base stations are shrinking, thanks to advancements in chip technology and antenna design. This miniaturization not only reduces deployment costs but also minimizes environmental impact. Additionally, energy-efficient designs and renewable energy integration are gaining traction, paving the way for a more sustainable 5G future. Data processing is shifting closer to the source, with 5G base stations incorporating edge computing capabilities. This enables faster response times, lower latency, and improved network efficiency for applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Key Players:
-
Huawei
-
Ericsson
-
Nokia
-
ZTE
-
Samsung
-
Quanta Computer
-
Airspan
-
Cisco Systems
-
CommScope
-
Radisys
Chapter 1. 5G base stations Market – Scope & Methodology
1.1 Market Segmentation
1.2 Scope, Assumptions & Limitations
1.3 Research Methodology
1.4 Primary Sources
1.5 Secondary Sources
Chapter 2. 5G base stations Market – Executive Summary
2.1 Market Size & Forecast – (2024 – 2030) ($M/$Bn)
2.2 Key Trends & Insights
2.2.1 Demand Side
2.2.2 Supply Side
2.3 Attractive Investment Propositions
2.4 COVID-19 Impact Analysis
Chapter 3. 5G base stations Market – Competition Scenario
3.1 Market Share Analysis & Company Benchmarking
3.2 Competitive Strategy & Development Scenario
3.3 Competitive Pricing Analysis
3.4 Supplier-Distributor Analysis
Chapter 4. 5G base stations Market - Entry Scenario
4.1 Regulatory Scenario
4.2 Case Studies – Key Start-ups
4.3 Customer Analysis
4.4 PESTLE Analysis
4.5 Porters Five Force Model
4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.5.2 Bargaining Powers of Customers
4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.5.4 Rivalry among Existing Players
4.5.5 Threat of Substitutes
Chapter 5. 5G base stations Market – Landscape
5.1 Value Chain Analysis – Key Stakeholders Impact Analysis
5.2 Market Drivers
5.3 Market Restraints/Challenges
5.4 Market Opportunities
Chapter 6. 5G base stations Market – By Product Type
6.1 Introduction/Key Findings
6.2 Macro Cells
6.3 Small Cells
6.4 Micro Cells
6.5 Femtocells and Picocells
6.6 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By Product Type
6.7 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By Product Type, 2024-2030
Chapter 7. 5G base stations Market – By End User
7.1 Introduction/Key Findings
7.2 Commercial
7.3 Industrial
7.4 Residential
7.5 Government and Defense
7.6 Others
7.7 Y-O-Y Growth trend Analysis By End User
7.8 Absolute $ Opportunity Analysis By End User, 2024-2030
Chapter 8. 5G base stations Market , By Geography – Market Size, Forecast, Trends & Insights
8.1 North America
8.1.1 By Country
8.1.1.1 U.S.A.
8.1.1.2 Canada
8.1.1.3 Mexico
8.1.2 By By Product Type
8.1.3 By End User
8.1.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.2 Europe
8.2.1 By Country
8.2.1.1 U.K
8.2.1.2 Germany
8.2.1.3 France
8.2.1.4 Italy
8.2.1.5 Spain
8.2.1.6 Rest of Europe
8.2.2 By By Product Type
8.2.3 By End User
8.2.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.3 Asia Pacific
8.3.1 By Country
8.3.1.1 China
8.3.1.2 Japan
8.3.1.3 South Korea
8.3.1.4 India
8.3.1.5 Australia & New Zealand
8.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
8.3.2 By By Product Type
8.3.3 By End User
8.3.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4 South America
8.4.1 By Country
8.4.1.1 Brazil
8.4.1.2 Argentina
8.4.1.3 Colombia
8.4.1.4 Chile
8.4.1.5 Rest of South America
8.4.2 By By Product Type
8.4.3 By End User
8.4.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.5 Middle East & Africa
8.5.1 By Country
8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
8.5.1.3 Qatar
8.5.1.4 Israel
8.5.1.5 South Africa
8.5.1.6 Nigeria
8.5.1.7 Kenya
8.5.1.8 Egypt
8.5.1.9 Rest of MEA
8.5.2 By Type
8.5.3 By End User
8.5.4 Countries & Segments - Market Attractiveness Analysis
Chapter 9. 5G base stations Market – Company Profiles – (Overview, Product Portfolio, Financials, Strategies & Developments)
9.1 Huawei
9.2 Ericsson
9.3 Nokia
9.4 ZTE
9.5 Samsung
9.6 Quanta Computer
9.7 Airspan
9.8 Cisco Systems
9.9 CommScope
9.10 Radisys
Download Sample
Choose License Type
2500
4250
5250
6900
Frequently Asked Questions
Rising mobile data consumption, evolution towards 5G, advancements in base station technology, edge computing capabilities, government initiatives for digital inclusion, and increasing demand for reliable and secure connectivity are the main key factors.
High deployment costs, energy consumption, spectrum availability, cybersecurity threats, an economic slowdown, and competition from alternative technologies are the main concerns.
Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, NEC, Airspan, Cisco Systems, and CommScope are the major players.
North America currently holds the largest market share, estimated at around 35%.
Asia-Pacific exhibits the fastest growth, driven by its massive population, expanding economies, and government programs aimed at bridging the digital divide and fostering technological innovation.